Substantive rationality refers to decision-making guided by the alignment of actions with ethical values, social norms, and desired outcomes, rather than mere formal logic or efficiency. It emphasizes the consideration of moral implications and the broader impact on society when evaluating choices. Explore the rest of the article to understand how substantive rationality shapes human behavior and organizational strategies.
Table of Comparison
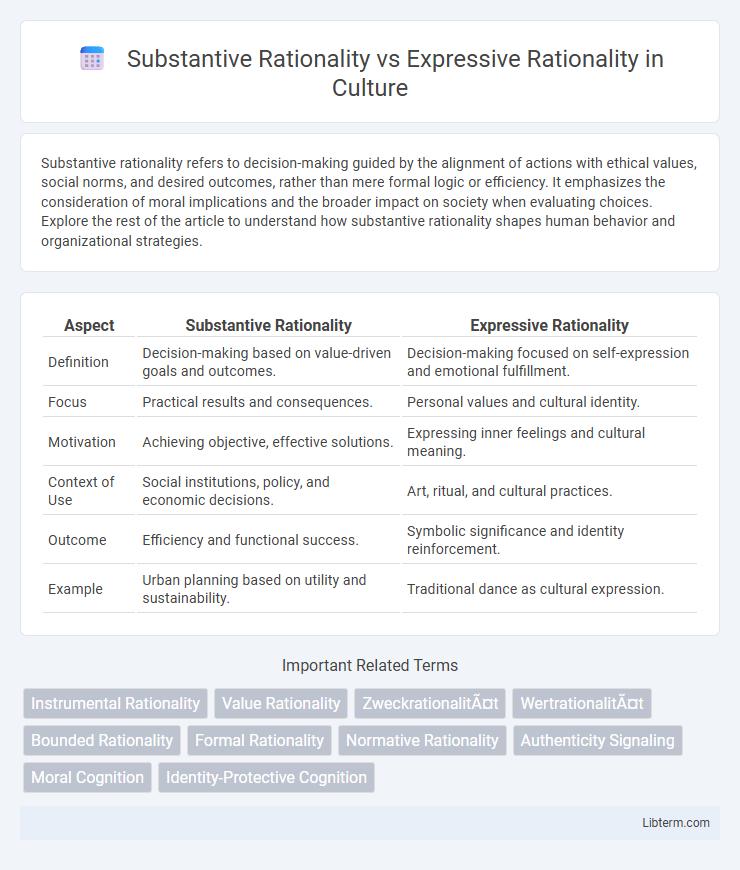
| Aspect | Substantive Rationality | Expressive Rationality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decision-making based on value-driven goals and outcomes. | Decision-making focused on self-expression and emotional fulfillment. |
| Focus | Practical results and consequences. | Personal values and cultural identity. |
| Motivation | Achieving objective, effective solutions. | Expressing inner feelings and cultural meaning. |
| Context of Use | Social institutions, policy, and economic decisions. | Art, ritual, and cultural practices. |
| Outcome | Efficiency and functional success. | Symbolic significance and identity reinforcement. |
| Example | Urban planning based on utility and sustainability. | Traditional dance as cultural expression. |
Understanding Substantive Rationality
Substantive rationality involves decision-making based on evaluating the consequences and ethical implications of actions relative to achieving overall goals, emphasizing outcomes aligned with long-term values. This form of rationality contrasts with purely procedural approaches by prioritizing meaningful ends over rigid adherence to formal rules or efficiency. Understanding substantive rationality is crucial in fields like ethics, economics, and public policy, where decisions impact broader social welfare and require balancing diverse interests.
Defining Expressive Rationality
Expressive rationality emphasizes actions motivated by individual identity, emotions, or social values rather than optimizing outcomes or efficiency. It prioritizes self-expression and authenticity, where decisions reflect personal beliefs or group norms over instrumental goals. This contrasts with substantive rationality, which seeks to maximize utility based on logical analysis and objective criteria.
Key Differences Between Substantive and Expressive Rationality
Substantive rationality involves decision-making based on the evaluation of outcomes to achieve specific goals, emphasizing efficiency and effectiveness in reaching desired ends. Expressive rationality prioritizes actions that convey values, identity, or emotional significance rather than optimal results. Key differences include the goal orientation of substantive rationality versus the symbolic or emotional focus in expressive rationality, reflecting contrasting motivations behind human behavior and choice.
Historical Perspectives on Rationality
Historical perspectives on rationality distinguish substantive rationality, which evaluates decisions based on their ultimate goals and outcomes, from expressive rationality, which emphasizes actions as expressions of values or identity. Classical thinkers like Max Weber linked substantive rationality to formal logic and objective efficiency, while expressive rationality aligns with symbolic interactionism and the subjective meaning of behavior. This dichotomy shapes the analysis of decision-making in social and economic history, highlighting tensions between instrumental calculation and cultural expression.
Substantive Rationality in Decision-Making
Substantive rationality in decision-making emphasizes evaluating choices based on the meaningful outcomes and long-term goals they achieve, rather than mere procedural correctness. It involves assessing the consequences of actions against value-laden criteria, ensuring decisions align with ethical standards and overall societal welfare. This approach contrasts with expressive rationality by prioritizing practical effectiveness and goal fulfillment over symbolic or emotional expression.
The Role of Expressive Rationality in Social Behavior
Expressive rationality plays a critical role in social behavior by driving individuals to act in ways that reflect their identities, values, and emotions rather than purely instrumental goals. This form of rationality emphasizes the importance of symbolic actions and emotional fulfillment, shaping social norms and collective behavior through shared meanings and cultural expressions. Social movements, rituals, and group memberships often illustrate expressive rationality, as participants engage in behaviors that affirm their sense of belonging and reinforce social cohesion.
Benefits and Limitations of Substantive Rationality
Substantive rationality emphasizes decision-making based on value-oriented goals and ethical considerations, offering benefits such as aligning actions with long-term societal welfare and promoting consistency in moral judgments. This approach facilitates structured, principle-driven outcomes that can enhance legitimacy and trust in institutions. However, its limitations include potential rigidity in adapting to changing circumstances and the challenge of balancing conflicting values within complex social systems.
Implications of Expressive Rationality in Modern Society
Expressive rationality prioritizes emotional fulfillment and identity expression over objective outcomes, influencing consumer behavior, political movements, and social interactions in modern society. This mode of reasoning drives individuals to make decisions that affirm their beliefs and values, often leading to polarization and challenges in consensus-building. Consequently, understanding expressive rationality is essential for addressing societal divisions and fostering effective communication in diverse communities.
Case Studies: Substantive vs Expressive Rationality
Case studies analyzing substantive versus expressive rationality reveal distinct decision-making frameworks: substantive rationality prioritizes logical evaluation of means and ends based on objective criteria, while expressive rationality emphasizes actions driven by personal values or emotional satisfaction. For example, Max Weber's analysis of bureaucratic institutions highlights substantive rationality in administrative efficiency, contrasted with political protests embodying expressive rationality as symbolic acts. Empirical research in organizational behavior further illustrates substantive rationality in profit-maximizing firms versus expressive rationality observed in non-profit organizations motivated by ideological goals.
Integrating Both Rationalities for Effective Outcomes
Integrating substantive rationality, which emphasizes goal-oriented, value-based decision-making, with expressive rationality, centered on emotional and identity-driven actions, enhances strategic effectiveness and authenticity. Organizations achieve balanced outcomes by aligning procedural efficiency with individual and cultural expression, fostering both innovation and consensus. This dual approach cultivates adaptive, resilient systems capable of addressing complex social and economic challenges.
Substantive Rationality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com