Asceticism emphasizes disciplined self-denial and minimalism to achieve spiritual growth and inner peace. Practitioners often renounce worldly pleasures and material possessions to cultivate mental clarity and deeper insight. Discover how embracing asceticism could transform your perspective and lifestyle by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
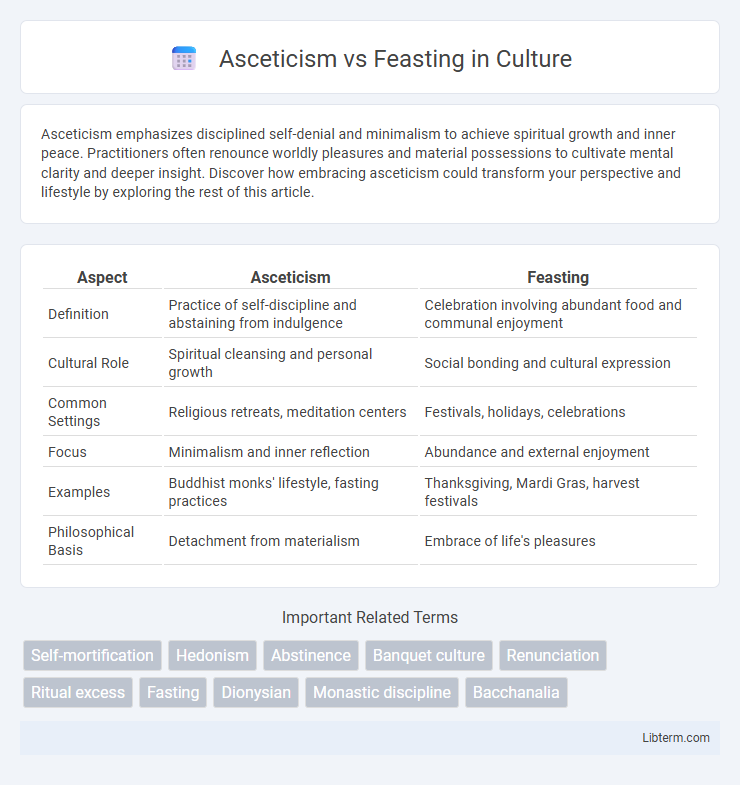
| Aspect | Asceticism | Feasting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practice of self-discipline and abstaining from indulgence | Celebration involving abundant food and communal enjoyment |
| Cultural Role | Spiritual cleansing and personal growth | Social bonding and cultural expression |
| Common Settings | Religious retreats, meditation centers | Festivals, holidays, celebrations |
| Focus | Minimalism and inner reflection | Abundance and external enjoyment |
| Examples | Buddhist monks' lifestyle, fasting practices | Thanksgiving, Mardi Gras, harvest festivals |
| Philosophical Basis | Detachment from materialism | Embrace of life's pleasures |
Understanding Asceticism: A Path of Self-Discipline
Asceticism emphasizes rigorous self-discipline and the deliberate renunciation of physical pleasures to achieve spiritual growth and inner clarity. This practice involves fasting, minimalistic living, and meditation to cultivate control over desires and foster mental resilience. Ascetic lifestyles have been integral to many religious and philosophical traditions, promoting detachment as a means to enlightenment and moral purity.
The Philosophy Behind Feasting and Celebration
Feasting and celebration embody a philosophy that emphasizes abundance, communal joy, and the sensory experience of life, reflecting a worldview that values shared happiness and gratitude. Rooted in cultural and religious traditions, feasting serves as a symbolic act of prosperity, social harmony, and the cyclic renewal of community bonds. This practice contrasts asceticism by embracing indulgence as a path to spiritual or social fulfillment rather than rejection of material pleasures.
Historical Perspectives: Asceticism and Feasting Across Cultures
Asceticism and feasting have shaped cultural and religious practices across history, with asceticism emphasizing self-discipline and spiritual purity in traditions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, and Christianity. Feasting, symbolizing celebration and social cohesion, is integral to festivals like the Roman Saturnalia, Islamic Eid, and Indian Diwali. These opposing approaches reflect varying cultural values regarding moderation, communal identity, and human experience throughout historical contexts.
Psychological Impacts: Restraint vs Indulgence
Asceticism promotes psychological resilience through self-discipline and restraint, often leading to reduced stress and heightened mental clarity by minimizing distractions and external stimuli. In contrast, feasting triggers pleasure centers in the brain, providing temporary emotional gratification and social bonding but can foster dependency and emotional imbalance if overindulged. Balancing restraint and indulgence is critical for sustainable mental health, as excessive austerity may cause anxiety, while unchecked excess often results in guilt and decreased well-being.
Ascetic Practices in Major World Religions
Ascetic practices in major world religions emphasize self-discipline, renunciation, and spiritual purification, often involving fasting, celibacy, and minimal material possessions. Hinduism promotes asceticism through practices like tapas and sannyasa, while Buddhism highlights monastic life with strict codes of conduct and meditation aimed at detachment from worldly desires. Christianity and Islam also incorporate ascetic elements, such as Lent and Ramadan fasting, which foster self-control and spiritual reflection.
Feasting Traditions: Symbolism and Social Bonds
Feasting traditions serve as powerful symbols of abundance, prosperity, and communal unity, reinforcing social bonds within cultures through shared meals and rituals. These celebrations often mark important events such as harvests, weddings, or religious festivals, where the act of eating collectively fosters trust and strengthens interpersonal relationships. The symbolic exchange of food during feasts reflects cultural values and social hierarchies, highlighting feasting as a vital practice in maintaining community coherence and identity.
Moderation, Balance, and the Middle Way
Asceticism and feasting represent two extremes in lifestyle choices, with asceticism emphasizing self-denial and feasting embracing indulgence. The principle of moderation advocates for a balanced approach, where neither extreme dictates behavior, promoting sustainable well-being and mental clarity. The Middle Way, rooted in Buddhist philosophy, encapsulates this harmonious balance, guiding individuals to seek equilibrium between deprivation and excess for optimal spiritual and physical health.
Modern Interpretations: Minimalism and Hedonism
Modern interpretations of asceticism emphasize minimalism as a lifestyle that encourages simplicity, intentional consumption, and the pursuit of meaning through self-discipline. Conversely, hedonism in contemporary culture celebrates sensory pleasure, indulgence, and experiential wealth as pathways to happiness and fulfillment. These contrasting philosophies reflect ongoing cultural debates about balance, well-being, and values in a consumer-driven society.
Health Implications: Restriction Versus Abundance
Asceticism promotes health benefits through caloric restriction, which can enhance longevity, reduce inflammation, and improve metabolic function. In contrast, feasting, characterized by nutritional abundance, risks obesity, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular diseases when practiced excessively. Balancing these approaches is essential for optimal health outcomes, emphasizing moderation over extremes.
Finding Personal Harmony: Integrating Asceticism and Feasting
Balancing asceticism and feasting enables individuals to cultivate personal harmony by harmonizing discipline with enjoyment, leading to enhanced physical and mental well-being. Incorporating mindful fasting practices alongside periodic feasts promotes metabolic health while satisfying social and cultural connections. This integrative approach fosters sustainable lifestyle choices that support emotional resilience and holistic vitality.
Asceticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com