Language preservation safeguards cultural heritage by maintaining the unique identity embedded within every dialect and tongue. Engaging in language preservation efforts helps your community retain historical traditions and fosters intergenerational communication. Discover how you can contribute to this vital mission by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
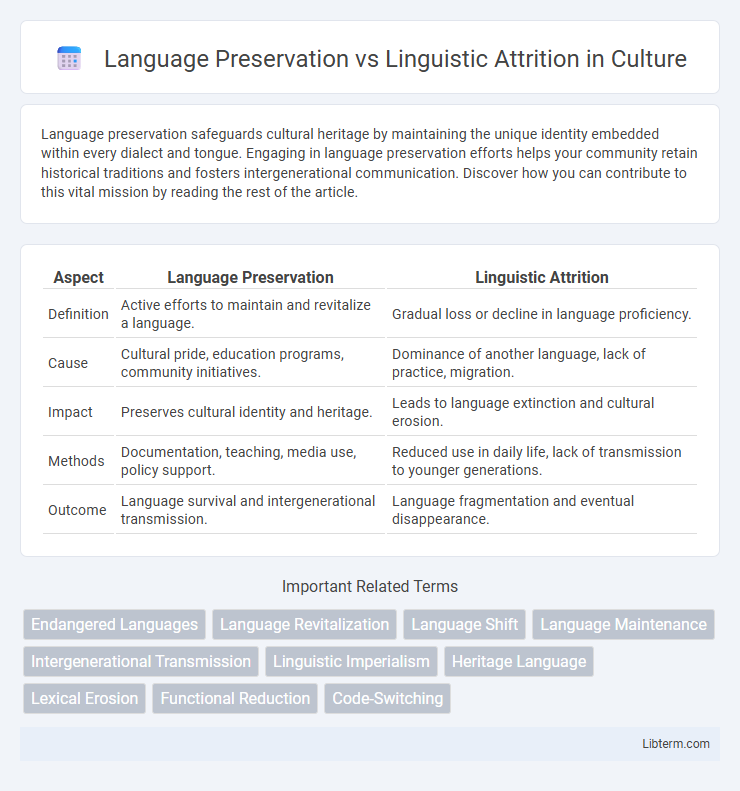
| Aspect | Language Preservation | Linguistic Attrition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active efforts to maintain and revitalize a language. | Gradual loss or decline in language proficiency. |
| Cause | Cultural pride, education programs, community initiatives. | Dominance of another language, lack of practice, migration. |
| Impact | Preserves cultural identity and heritage. | Leads to language extinction and cultural erosion. |
| Methods | Documentation, teaching, media use, policy support. | Reduced use in daily life, lack of transmission to younger generations. |
| Outcome | Language survival and intergenerational transmission. | Language fragmentation and eventual disappearance. |
Introduction to Language Preservation and Linguistic Attrition
Language preservation involves safeguarding endangered languages to maintain cultural heritage and linguistic diversity across communities. Linguistic attrition refers to the gradual loss of language proficiency, often occurring when speakers shift to dominant languages and discontinue using their native tongue. Understanding both concepts is crucial for developing strategies that support language revitalization and prevent language extinction globally.
Defining Language Preservation: Goals and Strategies
Language preservation aims to maintain and revitalize endangered languages by documenting vocabulary, grammar, and oral histories to ensure intergenerational transmission. Key strategies include community-based education programs, development of written materials, and digital archiving to support fluent speaker engagement and attract new learners. Preserving linguistic diversity helps safeguard cultural heritage and cognitive diversity within global populations.
Understanding Linguistic Attrition: Causes and Consequences
Linguistic attrition occurs when speakers gradually lose proficiency in a language due to factors like lack of use, limited exposure, or dominance of another language in social or educational settings. This process can lead to diminished cognitive abilities related to the language, erosion of cultural identity, and loss of unique linguistic features such as vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. Understanding the causes and consequences of linguistic attrition is essential for developing effective language preservation strategies that maintain linguistic diversity and cultural heritage.
Historical Trends in Language Loss and Maintenance
Historical trends reveal a pattern of language loss accelerated by colonialism, urbanization, and globalization, causing many indigenous languages to face extinction. Language preservation efforts, such as documentation, revitalization programs, and educational policies, have been critical in maintaining linguistic diversity. Despite these challenges, certain communities sustain their languages through intergenerational transmission and cultural resilience.
The Role of Communities in Safeguarding Languages
Communities play a crucial role in safeguarding languages by fostering intergenerational transmission and creating environments where native languages thrive naturally. Active participation in cultural practices and local education programs strengthens linguistic identity and helps counteract linguistic attrition. Empowering community members to use and promote their heritage languages ensures long-term preservation and resilience against language loss.
Technology’s Impact on Language Preservation and Attrition
Technology significantly influences language preservation and linguistic attrition by providing digital platforms for documenting and revitalizing endangered languages while simultaneously accelerating the decline of less dominant languages through the widespread use of global languages like English and Mandarin. Digital tools such as language learning apps, online dictionaries, and social media enable communities to maintain and share their linguistic heritage, increasing accessibility and engagement among younger generations. However, technological dominance also encourages language shift and diminishes daily use of minority languages, contributing to their gradual attrition in favor of more globally dominant languages.
Education and Policy Interventions for Language Survival
Education systems incorporating bilingual and heritage language programs play a crucial role in combating linguistic attrition by fostering proficiency and daily use among younger generations. Policy interventions such as official recognition, funding for language revitalization projects, and community-based language initiatives enhance language survival by creating supportive environments for endangered languages. Empirical studies demonstrate that integrated educational policies combined with legislative support significantly increase intergenerational language transmission rates.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures in Language Revitalization
Case studies in language preservation reveal varied outcomes in efforts to revive endangered languages, such as the successful revitalization of the Maori language in New Zealand through immersive education and governmental support. In contrast, linguistic attrition remains prevalent in smaller communities, like the decline of the Eyak language in Alaska, due to lack of resources and intergenerational transmission. These examples underscore the crucial role of community engagement, institutional backing, and comprehensive documentation in determining the success or failure of language revitalization initiatives.
Ethical Considerations in Language Preservation Efforts
Language preservation efforts raise critical ethical considerations surrounding community autonomy and consent, ensuring indigenous voices guide revitalization processes rather than external imposition. Linguistic attrition highlights risks of cultural erasure when dominant languages overshadow minority tongues, necessitating respect for linguistic diversity and heritage. Ethical frameworks must prioritize empowerment, equitable resource allocation, and protection of intellectual property rights related to endangered languages.
Future Perspectives: Balancing Preservation and Natural Language Change
Future perspectives on language preservation emphasize integrating advanced digital technologies and community-driven initiatives to document and revitalize endangered languages while accommodating natural linguistic evolution. Strategies focus on creating dynamic language resources, such as AI-powered dictionaries and immersive virtual reality experiences, to engage younger generations in active language use. This balance acknowledges that while preserving linguistic heritage is vital, embracing organic language change ensures cultural relevance and adaptability in a globalized world.
Language Preservation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com