Polygraphy is a technique used to detect physiological changes in the body that may indicate deception, commonly known as lie detection. This scientific method measures indicators such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and skin conductivity to assess truthfulness during interviews or investigations. Discover how polygraphy can impact legal and security fields by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
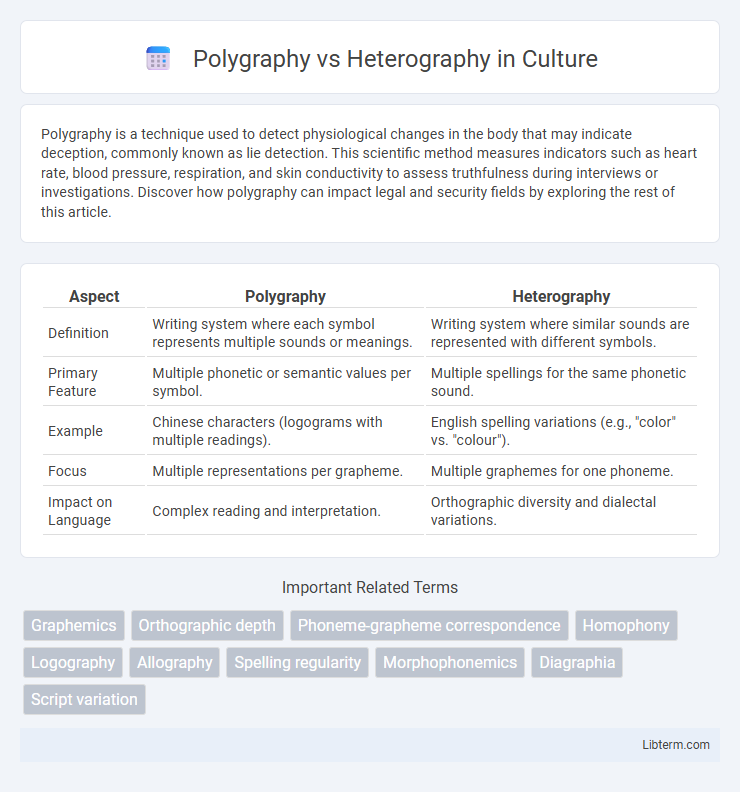
| Aspect | Polygraphy | Heterography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Writing system where each symbol represents multiple sounds or meanings. | Writing system where similar sounds are represented with different symbols. |
| Primary Feature | Multiple phonetic or semantic values per symbol. | Multiple spellings for the same phonetic sound. |
| Example | Chinese characters (logograms with multiple readings). | English spelling variations (e.g., "color" vs. "colour"). |
| Focus | Multiple representations per grapheme. | Multiple graphemes for one phoneme. |
| Impact on Language | Complex reading and interpretation. | Orthographic diversity and dialectal variations. |
Introduction to Polygraphy and Heterography
Polygraphy refers to the practice of writing words that accurately represent their sounds, ensuring phonetic transparency and clear pronunciation cues. Heterography involves spelling words in ways that do not correspond directly to their phonetic sounds, often leading to irregular or unpredictable spelling patterns. Understanding polygraphy and heterography is essential for linguistic studies, phonetics, and orthographic design, influencing language learning and literacy development.
Defining Polygraphy: Meaning and Scope
Polygraphy refers to the ability to write or express oneself in multiple languages, encompassing both the skill and practice of multilingual writing. It involves not only translation but also original creation in diverse linguistic systems, highlighting a deep proficiency across different alphabets, grammar structures, and cultural contexts. This concept broadens the scope of written communication, enabling enriched literary and informational exchanges beyond monolingual boundaries.
Understanding Heterography: Concepts and Application
Heterography refers to the use of different spellings for words that sound the same, emphasizing phonetic variance in written language to resolve ambiguities. This concept plays a crucial role in understanding linguistic variations, dialectal differences, and orthographic evolution across languages. Applications of heterography include improving speech recognition systems, linguistic research, and language learning tools by accurately reflecting spoken variations in written form.
Historical Development of Polygraphy and Heterography
Polygraphy, the early form of written communication where words are spelled exactly as they sound, emerged with the development of phonetic alphabets in ancient civilizations like Egypt and Mesopotamia around 3000 BCE. Heterography, characterized by diverse spellings of the same sounds, became prominent in languages with complex phonological systems, such as Old English and Ancient Greek, reflecting variations in regional dialects and writing traditions between 500 BCE and 1500 CE. The historical divergence between polygraphy and heterography illustrates the evolution of orthographic conventions influenced by linguistic, cultural, and technological changes over millennia.
Key Differences Between Polygraphy and Heterography
Polygraphy refers to the accurate and consistent spelling of words according to standard orthographic rules, while heterography involves varied or non-standard spellings of the same word or sound. The key difference lies in polygraphy's emphasis on uniformity and correctness in written language, contrasted with heterography's allowance for multiple spellings reflecting dialects or phonetic interpretations. Understanding these distinctions is essential in linguistics and language education to address orthographic variation and spelling norms.
Similarities and Overlapping Aspects
Polygraphy and heterography both involve the use of written language but differ in their approach to spelling and orthographic conventions. Polygraphy emphasizes the production of multiple diverse written texts, highlighting creativity and variability, while heterography focuses on non-standardized or irregular spelling patterns that deviate from conventional norms. Both concepts overlap in exploring the flexibility and variability of written expression, demonstrating how language can be represented in diverse forms beyond strict orthographic rules.
Polygraphy and Heterography in Linguistics
Polygraphy in linguistics refers to the phenomenon where a single sound corresponds to multiple spellings, posing challenges for phoneme-grapheme mapping and literacy acquisition. Heterography involves different words or forms that share pronunciation but differ in spelling and meaning, such as homophones, complicating semantic interpretation and language processing. Understanding the distinctions between polygraphy and heterography aids in refining orthographic systems and enhancing natural language processing algorithms.
Implications in Language Learning and Teaching
Polygraphy, the practice of spelling words exactly as pronounced, contrasts with heterography, where spelling diverges from pronunciation, significantly impacting language acquisition and instruction. Learners exposed to heterographic languages like English face increased cognitive load due to inconsistent spelling-sound correspondences, potentially hindering phonemic awareness and reading fluency. Effective teaching strategies must address these orthographic complexities by integrating phonics-based approaches and contextual vocabulary exercises to enhance orthographic mapping and literacy outcomes.
Modern Usage and Relevance
Polygraphy refers to the practice of writing words exactly as they sound, often used in phonetic transcription and language learning tools to improve pronunciation accuracy. Heterography, by contrast, involves spelling words differently from their pronunciation, commonly seen in English orthography, which preserves historical and etymological spellings despite modern phonetic shifts. Modern usage favors polygraphy in digital language processing and speech recognition applications, while heterography remains relevant in literary contexts and standardized spelling systems that maintain linguistic heritage.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Polygraphy and Heterography
Polygraphy emphasizes consistent, phonetic spelling aligning with speech sounds, enhancing readability and aiding language learners. Heterography reflects historical, etymological, or morphological aspects, preserving linguistic heritage but often complicating spelling rules. Selecting between polygraphy and heterography depends on prioritizing either phonetic clarity or traditional orthographic depth based on educational and linguistic goals.
Polygraphy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com