Folkways are the everyday norms and customs that guide social behavior within a community, shaping how people interact and maintain order effortlessly. These unwritten rules influence your daily routines, ensuring smooth social interactions without the need for formal enforcement. Explore the rest of the article to understand how folkways impact your social environment and cultural identity.
Table of Comparison
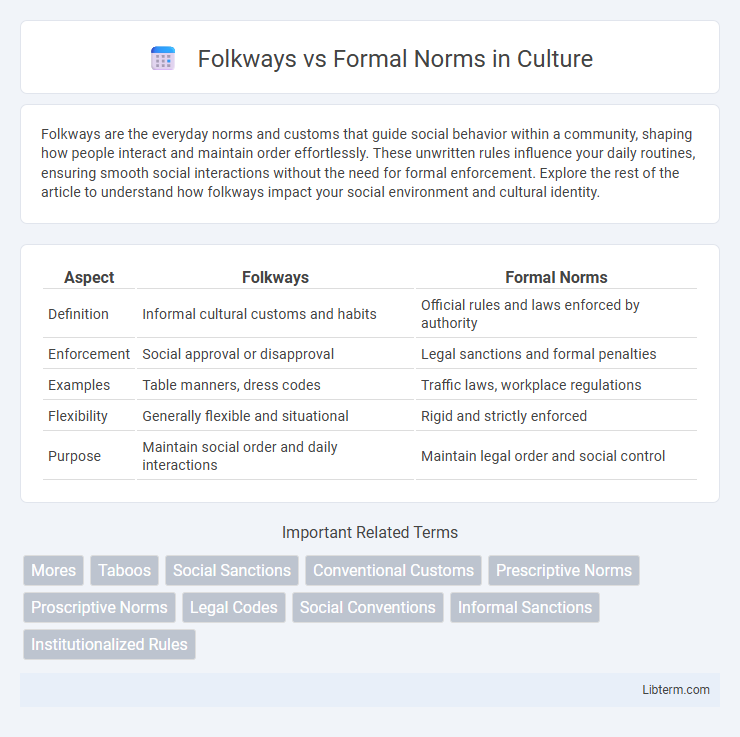
| Aspect | Folkways | Formal Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal cultural customs and habits | Official rules and laws enforced by authority |
| Enforcement | Social approval or disapproval | Legal sanctions and formal penalties |
| Examples | Table manners, dress codes | Traffic laws, workplace regulations |
| Flexibility | Generally flexible and situational | Rigid and strictly enforced |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and daily interactions | Maintain legal order and social control |
Understanding Folkways and Formal Norms
Folkways are everyday social conventions that guide casual interactions and reflect cultural customs, such as dressing appropriately or saying "please" and "thank you," without severe consequences if violated. Formal norms are codified rules and laws established by institutions that regulate serious behaviors, including legal requirements and workplace policies, with clear sanctions for non-compliance. Understanding the distinction between folkways and formal norms is essential for comprehending how societies maintain order through informal social expectations and formal regulatory mechanisms.
Defining Folkways: Everyday Social Practices
Folkways are informal social norms that govern everyday behaviors and customs, such as greetings, dress codes, and table manners, reflecting the cultural habits of a community. Unlike formal norms, folkways lack legal sanctions but influence social interactions by promoting predictability and cohesion within society. These practices evolve naturally over time, embedding themselves in daily routines and shaping the collective social fabric.
What Are Formal Norms?
Formal norms are official, written rules and laws established by institutions to regulate behavior within society, such as traffic laws, workplace regulations, and legal codes. They carry specific sanctions or penalties when violated, ensuring order and predictability in social interactions. Unlike folkways, which are informal customs and everyday practices, formal norms require explicit compliance and are enforced through authoritative entities.
Key Differences Between Folkways and Formal Norms
Folkways are informal, everyday customs that guide casual interactions, while formal norms encompass written laws and regulations enforced by authorities. The key difference lies in enforcement: violations of folkways typically result in mild social disapproval, whereas breaking formal norms leads to legal penalties or sanctions. Folkways evolve naturally within cultures, whereas formal norms are deliberately established to maintain order and structure in society.
Examples of Folkways in Daily Life
Folkways in daily life include customs like greeting people with a handshake, dressing appropriately for different social settings, and using polite language such as saying "please" and "thank you." These informal norms guide everyday interactions without strict enforcement, unlike formal norms such as laws and regulations. Observing folkways helps maintain social order and fosters mutual respect within communities.
Examples of Formal Norms in Society
Formal norms in society include laws such as traffic regulations, which mandate driving on a specific side of the road to ensure safety. Institutional rules like workplace dress codes require employees to adhere to certain attire standards. Additionally, academic policies enforce strict plagiarism guidelines to maintain integrity in educational settings.
Social Functions of Folkways
Folkways serve as informal social norms guiding everyday behavior and promote social cohesion by establishing expectations for routine interactions such as greetings, dress codes, and table manners. These unwritten rules facilitate predictability and order without legal enforcement, reinforcing group identity and cultural continuity. In contrast, formal norms carry explicit sanctions and govern more serious behaviors through institutions like laws and regulations.
The Role of Formal Norms in Social Order
Formal norms establish clear rules and expectations that guide behavior in structured settings such as schools, workplaces, and legal systems. These codified standards enforce compliance through official sanctions, ensuring predictability and stability within society. By providing a framework for consistent conduct, formal norms play a critical role in maintaining social order and reducing conflict.
Consequences of Violating Folkways vs Formal Norms
Violating folkways typically results in mild social sanctions such as disapproval, ridicule, or gossip, reflecting informal social control mechanisms within a community. In contrast, breaching formal norms often triggers more severe consequences, including legal penalties, fines, or imprisonment, due to their codification in laws or institutional rules. The distinction emphasizes that folkways govern everyday social interactions, while formal norms regulate critical societal functions with enforceable authority.
How Folkways and Formal Norms Shape Culture
Folkways, which are informal customs and everyday behaviors, shape culture by establishing routines and social expectations that guide interpersonal interactions within communities. Formal norms, codified through laws and regulations, provide structured frameworks that enforce societal order and define acceptable conduct on a broader scale. Together, folkways and formal norms create a dynamic cultural system where informal practices influence social cohesion while formal rules ensure consistent governance and compliance.
Folkways Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com