Effective moderation maintains the balance of online communities by ensuring respectful and relevant interactions while preventing harmful content. Employing clear guidelines and consistent enforcement fosters a safe environment that encourages positive engagement and trust among members. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical strategies for enhancing your moderation approach.
Table of Comparison
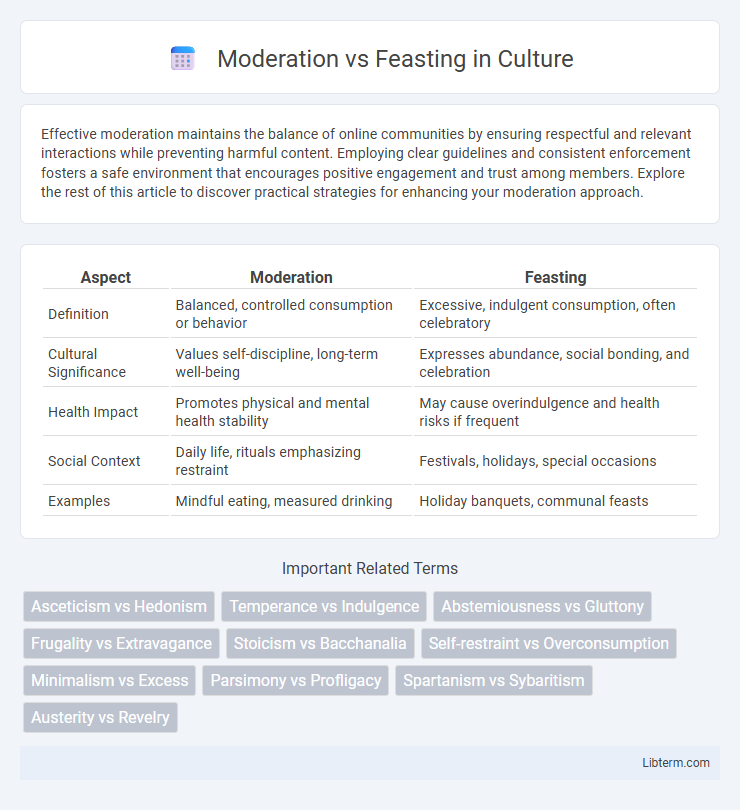
| Aspect | Moderation | Feasting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Balanced, controlled consumption or behavior | Excessive, indulgent consumption, often celebratory |
| Cultural Significance | Values self-discipline, long-term well-being | Expresses abundance, social bonding, and celebration |
| Health Impact | Promotes physical and mental health stability | May cause overindulgence and health risks if frequent |
| Social Context | Daily life, rituals emphasizing restraint | Festivals, holidays, special occasions |
| Examples | Mindful eating, measured drinking | Holiday banquets, communal feasts |
Understanding Moderation and Feasting
Understanding moderation involves recognizing the balance between indulgence and restraint, allowing individuals to enjoy food without overconsumption or guilt. Feasting refers to occasions of abundant eating, often characterized by rich, diverse dishes that celebrate culture and social connection. Both concepts highlight different approaches to nutrition and lifestyle, emphasizing the importance of context and intention in dietary choices.
Historical Perspectives on Eating Habits
Historical perspectives on eating habits reveal that moderation was often linked to moral and religious virtues, seen in ancient Greek and Roman philosophies promoting balance for health and character. In contrast, feasting served as a social and political tool in many cultures, symbolizing wealth, power, and communal celebration, evident in medieval banquets and royal courts. These practices reflect the dynamic tension between restraint and excess, shaping societal norms around food consumption throughout history.
The Psychology Behind Moderation
The psychology behind moderation highlights how balanced consumption enhances long-term satisfaction and mental well-being by preventing guilt and overindulgence. Self-regulation activates prefrontal cortex functions, promoting impulse control and mindful decision-making during eating behaviors. Neural pathways associated with reward and habit formation adapt better under moderation, supporting sustainable lifestyle changes over the fleeting gratification of feasting.
The Appeal of Feasting Culture
Feasting culture appeals through its celebration of abundance, social bonding, and sensory indulgence, creating memorable experiences that contrast with the restraint of moderation. Lavish feasts often symbolize prosperity and generosity, enhancing communal ties and cultural identity. The vibrant display of diverse foods and communal sharing amplifies feelings of joy and belonging, making feasting a powerful cultural ritual.
Health Benefits of Moderation
Moderation in eating supports balanced nutrient intake, reduces the risk of obesity, and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, promoting long-term heart health. Consistent portion control minimizes digestive stress and lowers the chances of developing metabolic disorders such as diabetes and hypertension. Emphasizing moderation fosters sustained energy levels, improved mental clarity, and overall enhanced well-being compared to the negative effects associated with feasting episodes.
Risks and Rewards of Feasting
Feasting offers social bonding and enhanced pleasure through indulgence but carries risks such as overconsumption, digestive issues, and long-term health problems like obesity and heart disease. The immediate reward of heightened enjoyment and cultural celebration must be balanced against potential negative physical effects and impaired judgment. Moderation helps mitigate these risks by promoting controlled intake, preserving well-being while still allowing occasional enjoyment of feasts.
Social Influences on Eating Patterns
Social influences significantly shape eating patterns, where moderation often emerges in environments promoting health-conscious norms, while feasting is prevalent in communal or celebratory settings encouraging indulgence. Peer pressure and cultural traditions can drive individuals toward either restrained or excessive food intake depending on social expectations and shared rituals. Understanding these dynamics highlights how social context directly impacts dietary choices and long-term nutritional habits.
Finding Balance: Integrating Both Approaches
Balancing moderation and feasting involves strategically combining consistent healthy eating habits with occasional indulgent meals to promote overall well-being. Emphasizing nutrient-dense foods in daily meals supports sustained energy and health, while planned feasts allow enjoyment without derailing dietary goals. This integrated approach fosters a sustainable lifestyle by aligning physiological needs with psychological satisfaction.
Moderation vs Feasting in Different Cultures
Moderation in eating is often emphasized in cultures like Japan and Mediterranean regions, where balanced portions and nutrient-rich foods support longevity and health. Feasting traditions, prevalent in Middle Eastern and Indian cultures, celebrate abundance and communal bonding through lavish meals rich in spices and diverse dishes. These contrasting approaches reflect cultural values prioritizing health, social connection, or celebration, illustrating the diverse roles of food in human societies.
Practical Tips for a Sustainable Eating Lifestyle
Adopting moderation over feasting promotes sustainable eating by encouraging portion control and balanced nutrient intake, reducing overeating and food waste. Practical tips include mindful eating practices, such as listening to hunger cues and choosing whole, minimally processed foods that provide lasting energy. Consistently applying these strategies supports long-term health and environmental sustainability by fostering responsible consumption patterns.
Moderation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com