Individualism emphasizes the importance of personal autonomy and self-expression in shaping one's identity and choices. It encourages you to prioritize your unique values and goals over collective norms, fostering creativity and independent thinking. Discover how embracing individualism can transform your approach to life in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
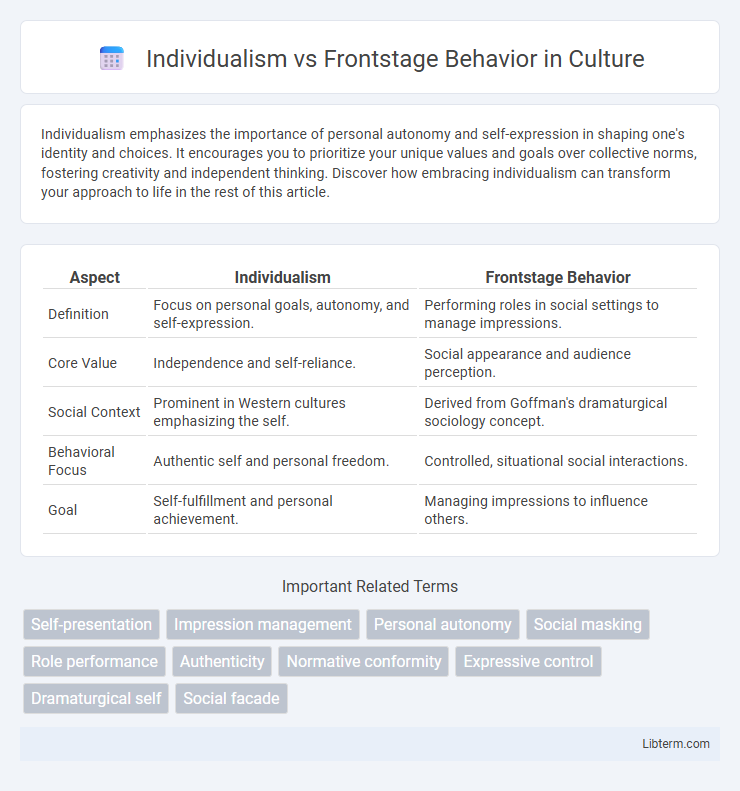
| Aspect | Individualism | Frontstage Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on personal goals, autonomy, and self-expression. | Performing roles in social settings to manage impressions. |
| Core Value | Independence and self-reliance. | Social appearance and audience perception. |
| Social Context | Prominent in Western cultures emphasizing the self. | Derived from Goffman's dramaturgical sociology concept. |
| Behavioral Focus | Authentic self and personal freedom. | Controlled, situational social interactions. |
| Goal | Self-fulfillment and personal achievement. | Managing impressions to influence others. |
Understanding Individualism: Core Concepts
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-expression, and the prioritization of individual goals over group objectives. This cultural orientation values independence, personal responsibility, and the development of unique identities, which shapes behavior and social interactions. Understanding individualism involves recognizing its impact on decision-making, communication styles, and the way individuals present themselves in social contexts, especially when contrasted with frontstage behavior that highlights performance and social expectations.
Defining Frontstage Behavior in Social Contexts
Frontstage behavior refers to the actions and presentations individuals perform in social settings to convey a desired image or adhere to societal expectations. This concept, rooted in Erving Goffman's dramaturgical theory, highlights how people manage impressions by controlling their expressions and interactions in public contexts. Frontstage behavior contrasts with individualistic tendencies by emphasizing social roles and collective norms over personal authenticity.
Historical Roots of Individualism
The historical roots of individualism trace back to the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods, where emphasis on human reason, personal autonomy, and self-expression challenged collectivist social norms. Philosophers like John Locke promoted natural rights and personal liberty, fostering a cultural shift towards valuing individual identity over group conformity. This ideological foundation influenced frontstage behavior, where individuals consciously perform roles to align with societal expectations while maintaining a private sense of self.
The Social Psychology Behind Frontstage Behavior
Frontstage behavior represents the socially constructed persona individuals adopt to align with societal expectations and norms, often masking true individualism for acceptance or status. This performative aspect, rooted in Erving Goffman's dramaturgical theory, emphasizes the conscious effort to manage impressions within social interactions. Understanding frontstage behavior reveals the psychological tension between authentic self-expression and the desire for social approval.
Individualism in Modern Society
Individualism in modern society emphasizes personal autonomy, self-expression, and the pursuit of individual goals over collective norms. This cultural value fosters innovation, creativity, and diversity by encouraging people to prioritize unique identities and private beliefs. However, it can also lead to challenges in social cohesion as individuals balance personal desires with public expectations in frontstage behavior.
Navigating Public and Private Selves
Navigating public and private selves requires balancing individualism with frontstage behavior, where individuals tailor actions to social expectations in public settings. Frontstage behavior often involves performing roles aligned with societal norms, while individualism emphasizes authentic expression and personal values privately. This dynamic tension shapes identity management, influencing how people present themselves differently in various social contexts.
Cultural Variations: East vs West Perspectives
Individualism in Western cultures emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, shaping frontstage behavior to highlight uniqueness and personal achievements. In contrast, Eastern cultures prioritize collectivism and social harmony, where frontstage behavior often reflects group conformity and respect for social roles. These cultural variations profoundly influence how individuals present themselves in public, balancing personal identity with societal expectations.
Impacts of Individualism on Social Interactions
Individualism promotes personal autonomy and self-expression, reshaping social interactions by encouraging authentic and unique presentations of self in frontstage behavior. This cultural emphasis leads individuals to prioritize personal goals over collective norms, influencing how they manage impressions in social settings. As a result, frontstage behavior becomes a strategic performance where individual identity is highlighted to achieve social validation and personal agency.
Challenges of Authenticity in Frontstage Settings
Frontstage behavior often challenges individualism by pressuring individuals to conform to social norms and expectations, leading to a performative self that may diverge from their authentic identity. The tension between maintaining a socially acceptable facade and expressing genuine thoughts or emotions creates a dissonance that undermines personal authenticity. Navigating this dynamic requires constant self-monitoring and adaptation, which can result in emotional exhaustion and diminished self-coherence.
Finding Balance: Embracing Individuality in Social Spaces
Balancing individualism and frontstage behavior requires recognizing the importance of authentic self-expression while adapting to social norms. Embracing individuality in social spaces enhances personal identity and fosters deeper connections without compromising social harmony. Effective navigation of these dynamics encourages genuine interactions that respect both personal uniqueness and collective expectations.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com