Presentism is the philosophical approach that interprets past events through the lens of current knowledge and values, often leading to biased judgments. It poses challenges in historical analysis by projecting modern perspectives onto historical contexts that operated under different norms. Explore the rest of the article to understand how presentism affects our view of history and methods to mitigate its influence.
Table of Comparison
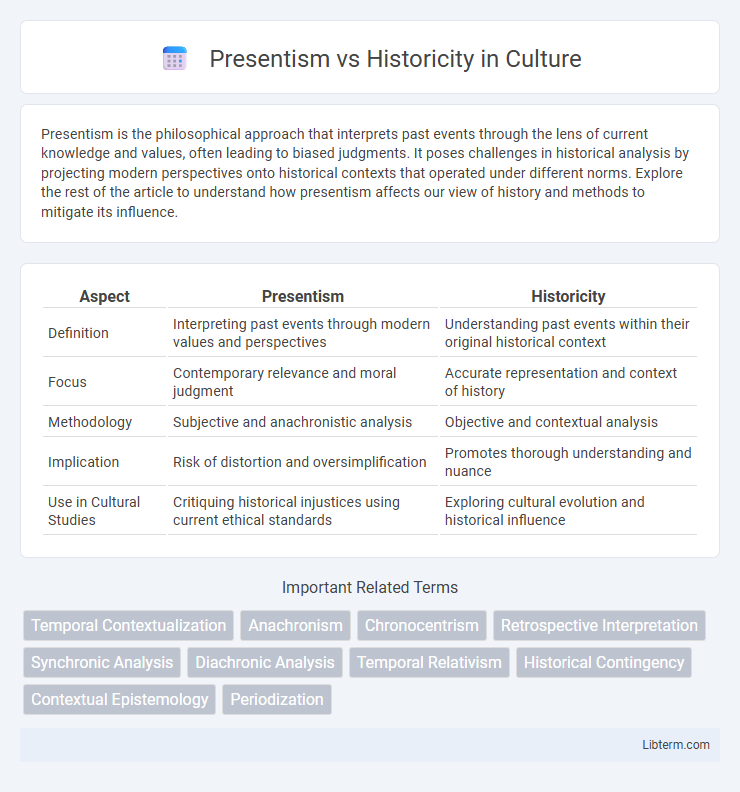
| Aspect | Presentism | Historicity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpreting past events through modern values and perspectives | Understanding past events within their original historical context |
| Focus | Contemporary relevance and moral judgment | Accurate representation and context of history |
| Methodology | Subjective and anachronistic analysis | Objective and contextual analysis |
| Implication | Risk of distortion and oversimplification | Promotes thorough understanding and nuance |
| Use in Cultural Studies | Critiquing historical injustices using current ethical standards | Exploring cultural evolution and historical influence |
Defining Presentism and Historicity
Presentism refers to the interpretation of historical events through the lens of contemporary values and knowledge, often leading to anachronistic judgments. Historicity emphasizes understanding past events within their own historical context, recognizing the influence of time, culture, and circumstances on human actions. Defining these concepts involves contrasting the biased imposition of current perspectives (Presentism) with the objective analysis of history based on period-specific realities (Historicity).
Historical Context of Presentism
Presentism involves interpreting past events through the lens of contemporary values and beliefs, often leading to anachronistic judgments that disregard the original historical context. The historical context of Presentism highlights the risk of projecting modern moral standards onto historical figures and societies, potentially distorting the understanding of their actions and motivations within their own time period. Scholars emphasize the importance of Historicity, which respects the temporal and cultural conditions in which past events occurred, ensuring a more accurate and nuanced analysis of history.
Understanding Historicity in Scholarship
Understanding historicity in scholarship involves recognizing the embedded historical context and temporal particularities that shape events and texts. This approach emphasizes analyzing sources within their original socio-political, cultural, and intellectual environments to avoid anachronistic interpretations common in presentism. Scholars prioritize a nuanced, evidence-based reconstruction of past realities to deepen comprehension of historical processes and meanings.
Presentism’s Influence on Historical Interpretation
Presentism significantly shapes historical interpretation by applying contemporary values and perspectives to analyze past events, often leading to anachronistic judgments and a distorted understanding of historical contexts. This approach risks oversimplifying complex socio-cultural dynamics and disregards the nuances inherent in historical periods. Scholars emphasize the importance of balancing present-day insights with a rigorous examination of historical evidence to maintain accuracy and respect for the integrity of past societies.
The Role of Context in Historical Analysis
Presentism often distorts historical analysis by imposing current values and perspectives on past events, thus obscuring the original context and intentions. Historicity emphasizes understanding events within their specific temporal and cultural frameworks, preserving the integrity of historical actors' experiences and decisions. Contextual analysis ensures a more accurate interpretation by situating events in their authentic social, political, and economic environments.
Criticisms of Presentism
Criticisms of presentism emphasize its tendency to distort historical understanding by projecting contemporary values and perspectives onto past events, leading to anachronistic interpretations. Scholars argue that presentism undermines the complexity of historical contexts and disregards the cultural and temporal specificity of past societies. This approach also risks oversimplifying historical narratives, reducing them to modern moral judgments rather than objective analyses.
Defending the Value of Historicity
Historicity preserves the complexity and context of past events, allowing a deeper understanding of cultural, social, and political developments. Defending the value of historicity emphasizes the importance of acknowledging temporal nuances and resisting the reduction of history to present-day interpretations. Maintaining historicity supports accurate scholarship and prevents the distortion of past realities to fit contemporary agendas.
Case Studies: Presentism vs Historicity in Practice
Case studies reveal the challenges of balancing presentism and historicity when interpreting historical events, with modern values often influencing judgments about past actions. In legal contexts, historical cases require applying contemporary laws without anachronistically imposing current moral standards, demonstrating the tension between ethical presentism and factual historicity. Museums and educational institutions frequently navigate this debate by curating exhibits that contextualize artifacts within their original time while addressing present-day social relevance.
Balancing Modern Values with Historical Understanding
Balancing modern values with historical understanding requires recognizing presentism as the imposition of contemporary moral standards onto past events, which can distort the complexities of history. Historicity emphasizes context by evaluating historical actions and beliefs within their specific cultural and temporal frameworks, fostering a nuanced interpretation. Scholars advocate integrating presentist insights cautiously to maintain historical accuracy while using modern perspectives to inform ethical reflections and social progress.
Future Directions in Historical Methodology
Future directions in historical methodology emphasize integrating digital technologies, such as AI-driven data analysis and virtual reconstructions, to overcome presentist biases and enhance temporal contextualization. Embracing interdisciplinary approaches strengthens the historicity principle by situating events within their unique socio-cultural frameworks rather than projecting contemporary perspectives. This evolution fosters more nuanced, dynamic interpretations of the past that respect temporal complexity while leveraging innovative tools for deeper insight.
Presentism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com