Embracing multiculture enriches your perspective by exposing you to diverse customs, languages, and traditions that foster mutual understanding and innovation. Celebrating cultural diversity in communities and workplaces enhances creativity and problem-solving by blending unique viewpoints. Explore the rest of the article to discover how multicultural experiences can transform your personal and professional life.
Table of Comparison
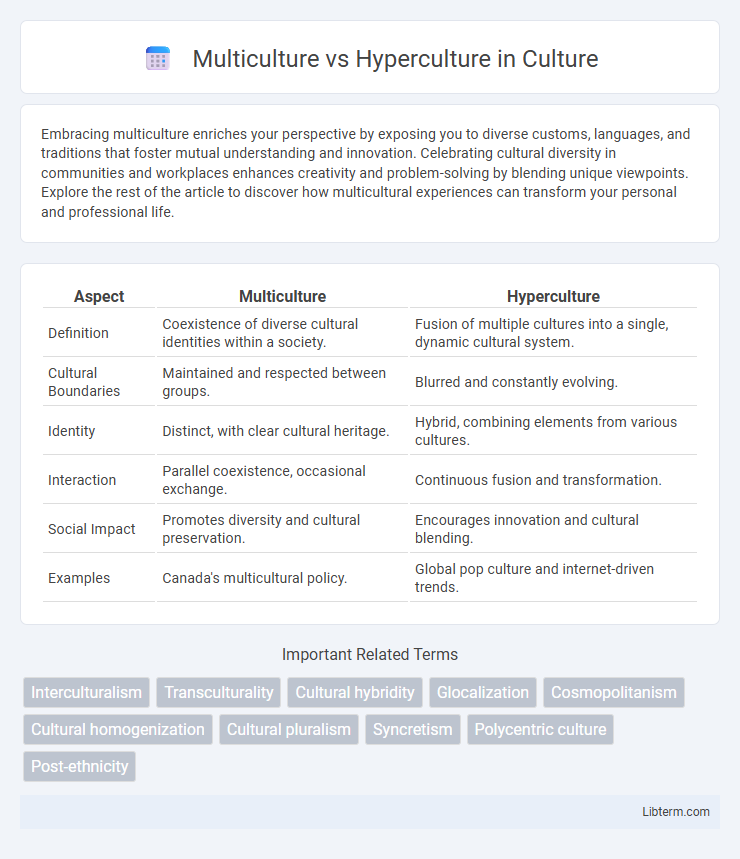
| Aspect | Multiculture | Hyperculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society. | Fusion of multiple cultures into a single, dynamic cultural system. |
| Cultural Boundaries | Maintained and respected between groups. | Blurred and constantly evolving. |
| Identity | Distinct, with clear cultural heritage. | Hybrid, combining elements from various cultures. |
| Interaction | Parallel coexistence, occasional exchange. | Continuous fusion and transformation. |
| Social Impact | Promotes diversity and cultural preservation. | Encourages innovation and cultural blending. |
| Examples | Canada's multicultural policy. | Global pop culture and internet-driven trends. |
Understanding Multiculture: Definition and Origins
Multiculture refers to the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a single society, each maintaining its distinct traditions, languages, and social practices. Originating from historical patterns of migration, colonization, and globalization, multiculture emphasizes cultural plurality without necessarily integrating or merging these differences. Understanding multiculture involves recognizing the value of cultural diversity and the ways in which social systems accommodate multiple cultural identities simultaneously.
Decoding Hyperculture: Concept and Characteristics
Decoding hyperculture involves understanding a dynamic cultural phenomenon characterized by rapid information exchange, technological integration, and the blending of global influences that transcend traditional multicultural boundaries. This concept reflects interconnectedness through digital platforms, resulting in fluid identities and innovative social practices that adapt swiftly to global trends. Hyperculture emphasizes continuous cultural evolution driven by real-time communication, fostering a collective experience rather than isolated cultural coexistence.
Historical Evolution of Multiculture and Hyperculture
Multiculture emerged historically as societies evolved through colonization, migration, and trade, leading to diverse cultural coexistence within shared geographical spaces, often marked by distinct ethnic, linguistic, and religious identities. Hyperculture, by contrast, developed in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, driven by globalization and digital technologies that fuse cultural elements into interconnected, fluid identities transcending traditional boundaries. This evolution signifies a shift from static multicultural frameworks towards dynamic hypercultural networks influenced by transnational communication and hybrid cultural practices.
Key Differences Between Multiculture and Hyperculture
Multiculture refers to the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a society, each maintaining distinct identities and traditions, whereas hyperculture emphasizes the blending and merging of these cultures into a singular, dynamic cultural entity. Multiculture highlights cultural preservation and parallel existence, while hyperculture focuses on integration and the creation of new, hybrid cultural expressions. The key difference lies in multiculturalism's acceptance of diversity as separate and equal, contrasted with hyperculture's emphasis on cultural synthesis and transformation.
The Role of Technology in Hyperculture
Technology serves as the foundation of hyperculture by enabling seamless global communication, instantaneous information exchange, and the creation of interconnected digital communities that transcend traditional cultural boundaries. Unlike multiculturalism, which emphasizes coexistence of distinct cultures, hyperculture leverages platforms like social media, virtual reality, and AI-driven content to blend cultural elements into a dynamic, evolving digital ecosystem. This technological integration accelerates cultural fusion, driving innovation and reshaping identities in an increasingly networked world.
Societal Impacts of Multiculture vs Hyperculture
Multiculture fosters societal diversity by promoting coexistence of distinct cultural identities, enhancing social cohesion and mutual respect. Hyperculture blends multiple cultural elements into a unified, global cultural framework, accelerating cultural homogenization and influencing social norms worldwide. The societal impact of multiculture centers on preserving cultural heritage, while hyperculture drives globalization and cross-cultural integration, reshaping collective identities.
Identity and Belonging in Mixed Cultural Landscapes
Multiculture fosters a coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a shared space, emphasizing individual belonging and the preservation of unique traditions. Hyperculture transcends traditional cultural boundaries by blending multiple cultural elements into a hybrid identity that shapes collective belonging and dynamic social interactions. In mixed cultural landscapes, identity is negotiated continuously, balancing the affirmation of distinct heritages with the creation of inclusive, interconnected communities.
Challenges and Opportunities in Multicultural Societies
Multicultural societies face challenges such as cultural misunderstandings, identity conflicts, and social fragmentation, impacting social cohesion and communication. Opportunities arise through enriched creativity, innovation from diverse perspectives, and enhanced global competitiveness by leveraging varied cultural insights. Effective policies promoting inclusion, intercultural dialogue, and equitable resource distribution are essential for transforming challenges into sustainable societal growth and harmony.
The Future of Cultural Integration: Multiculture or Hyperculture?
The future of cultural integration hinges on the evolution from traditional multiculture, where diverse cultures coexist with distinct identities, toward hyperculture, which blends elements from multiple cultures into a unified dynamic framework. Hyperculture emphasizes fluidity, constant innovation, and hybrid cultural expressions, fostering global connectivity and shared values beyond geographical and ethnic boundaries. Adopting hyperculture can enhance social cohesion and creativity in increasingly interconnected societies, redefining cultural identity in the digital age.
Navigating Globalization: Striking a Balance
Navigating globalization requires balancing the diversity of multicultural environments with the homogenizing tendencies of hyperculture, where global brands and digital connectivity create shared experiences worldwide. Multiculture emphasizes preserving distinct cultural identities and traditions, fostering local creativity and diverse perspectives, while hyperculture promotes a unified global culture driven by mass media, technology, and consumerism. Striking this balance enables societies to benefit from global integration without eroding cultural uniqueness, supporting both innovation and cultural sustainability.
Multiculture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com