Subculture shapes distinct identities within larger cultural frameworks, influencing fashion, language, and social behaviors that set groups apart. Understanding subcultures reveals how individuals express belonging and resist mainstream norms, enriching societal diversity. Dive deeper into this article to explore the impact of subcultures on your community and beyond.
Table of Comparison
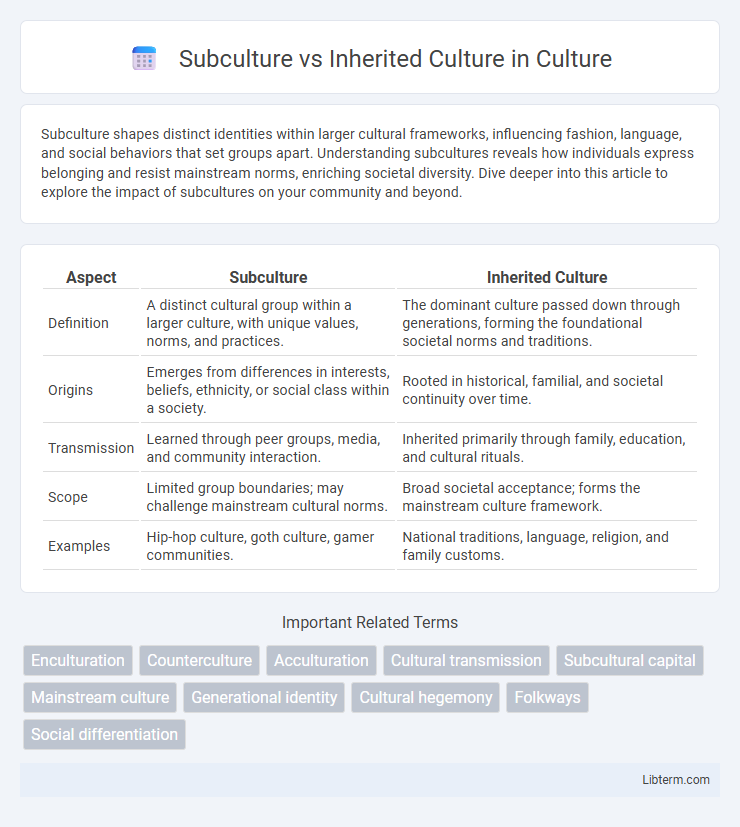
| Aspect | Subculture | Inherited Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A distinct cultural group within a larger culture, with unique values, norms, and practices. | The dominant culture passed down through generations, forming the foundational societal norms and traditions. |
| Origins | Emerges from differences in interests, beliefs, ethnicity, or social class within a society. | Rooted in historical, familial, and societal continuity over time. |
| Transmission | Learned through peer groups, media, and community interaction. | Inherited primarily through family, education, and cultural rituals. |
| Scope | Limited group boundaries; may challenge mainstream cultural norms. | Broad societal acceptance; forms the mainstream culture framework. |
| Examples | Hip-hop culture, goth culture, gamer communities. | National traditions, language, religion, and family customs. |
Understanding Subculture: Definition and Characteristics
Subculture refers to a distinct group within a larger culture that shares unique values, norms, and behaviors differentiating it from the dominant culture. Key characteristics of subcultures include shared language, symbols, and rituals that foster a strong group identity and cohesion among members. Understanding subculture involves recognizing its role in providing social support, identity, and alternative perspectives within the broader societal framework.
What Is Inherited Culture? Origins and Core Elements
Inherited culture refers to the traditions, customs, beliefs, and practices passed down from previous generations within a society, forming the foundational framework of a community's identity. Its origins are deeply rooted in historical experiences, social norms, and collective memory, shaping languages, rituals, values, and social institutions that persist over time. Core elements of inherited culture include language, religion, family structures, and moral codes, which together guide behavior and maintain social cohesion across generations.
Key Differences Between Subculture and Inherited Culture
Subculture represents a distinct cultural group within a larger society that develops unique norms, values, and practices often influenced by shared experiences or interests, whereas inherited culture consists of traditions, customs, and beliefs passed down through generations. Subcultures frequently emerge from adaptations to contemporary social environments, contrasting with inherited culture's deep-rooted historical continuity. The key difference lies in subculture's dynamic and adaptive nature compared to inherited culture's stability and transmission across time.
The Role of Identity in Subculture vs Inherited Culture
Identity in subculture centers on personal choice and active affiliation with specific beliefs, values, and practices that differ from mainstream norms, emphasizing individuality and group solidarity. Inherited culture reflects identity through traditions, customs, and norms passed down through generations, shaping a collective sense of belonging rooted in lineage and historical continuity. The role of identity in subculture contrasts with inherited culture by highlighting dynamic self-expression versus static cultural inheritance.
How Subcultures Emerge Within Inherited Cultures
Subcultures emerge within inherited cultures as distinct groups develop unique values, norms, and practices that differentiate them from the broader cultural context. These subcultures often arise through shared interests, social experiences, or responses to societal changes, allowing members to establish a collective identity within the larger inherited culture. Over time, subcultures influence and reshape aspects of the dominant cultural framework while maintaining some core inherited traditions.
Influence of Technology on Cultural Evolution
Technological advancements accelerate the evolution of subcultures by enabling rapid communication and dissemination of niche interests, contrasting with inherited culture's slower, tradition-based transmission. Digital platforms foster new cultural norms and practices that often diverge from inherited values, creating dynamic subcultures with unique identities. The continuous innovation in technology reshapes cultural landscapes by blending inherited customs with emerging digital behaviors, driving cultural hybridization.
Examples of Subcultures Across Generations
Subcultures such as punk rock emerged in the 1970s as a distinct youth movement, emphasizing rebellion and unique fashion, contrasting with the broader inherited culture's traditional norms. Skateboarding communities have grown across generations, evolving from a 1950s pastime to a global subculture with its own language, style, and values. These subcultures persist by adapting core elements while maintaining a distinct identity separate from the inherited culture passed down through families.
Cultural Transmission: From Inheritance to Innovation
Cultural transmission involves the dynamic process by which both inherited culture--traditions, norms, and practices passed down through generations--and subculture innovations coexist and evolve. Inherited culture provides a foundational framework rooted in history and collective identity, while subcultures introduce novel expressions, values, and behaviors that challenge or complement dominant cultural patterns. This continuous interplay accelerates societal adaptation by blending preservation of core cultural elements with creative transformation.
Conflicts and Synergy Between Subcultures and Inherited Cultures
Subcultures often generate conflicts with inherited cultures due to divergent values, beliefs, and practices that challenge traditional norms, leading to tension and social fragmentation. However, synergy occurs when subcultures contribute to cultural evolution by introducing innovation, diversity, and new perspectives that enrich inherited cultural frameworks. The dynamic interplay between subcultures and inherited cultures fosters social adaptation and cultural resilience in changing environments.
The Future of Cultural Diversity: Integration or Fragmentation?
Subcultures emerge from shared interests and values within larger societies, creating dynamic variations that challenge inherited cultures rooted in traditions and historical continuity. The future of cultural diversity hinges on whether integration fosters inclusive hybrid identities or if fragmentation amplifies divisions and cultural silos. Understanding the balance between subcultural innovation and inherited cultural preservation is key to navigating societal cohesion and global multiculturalism.
Subculture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com