Innovation drives progress by transforming ideas into practical solutions that address real-world challenges. It fosters creativity, enhances efficiency, and opens new opportunities across industries, fueling economic growth and improving quality of life. Explore this article to discover how innovation can inspire your success and reshape the future.
Table of Comparison
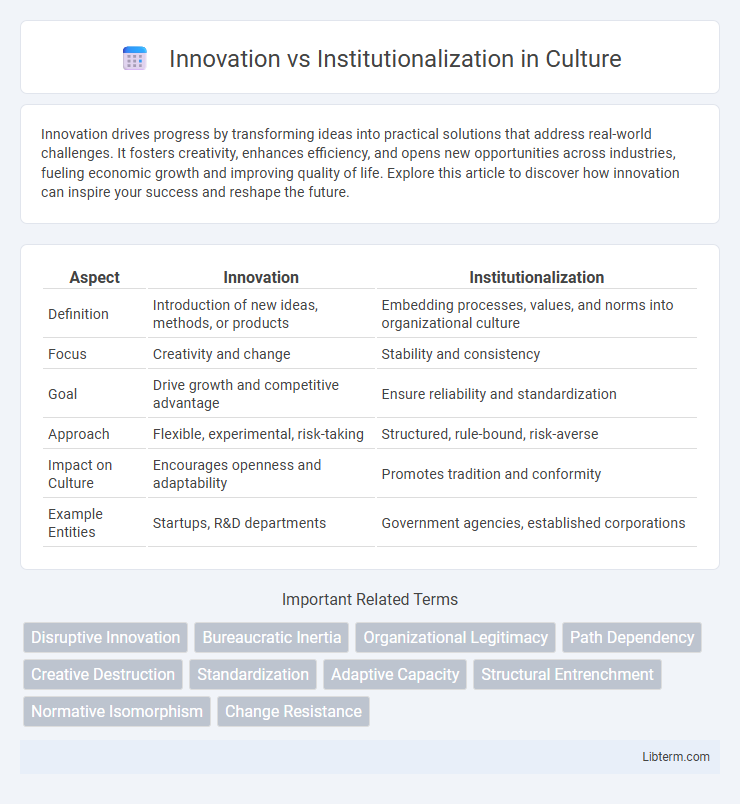
| Aspect | Innovation | Institutionalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introduction of new ideas, methods, or products | Embedding processes, values, and norms into organizational culture |
| Focus | Creativity and change | Stability and consistency |
| Goal | Drive growth and competitive advantage | Ensure reliability and standardization |
| Approach | Flexible, experimental, risk-taking | Structured, rule-bound, risk-averse |
| Impact on Culture | Encourages openness and adaptability | Promotes tradition and conformity |
| Example Entities | Startups, R&D departments | Government agencies, established corporations |
Defining Innovation and Institutionalization
Innovation refers to the process of creating and implementing novel ideas, products, or methods that drive progress and competitive advantage in various sectors. Institutionalization involves embedding these innovations into established systems, ensuring consistency, stability, and long-term sustainability within organizations or industries. Defining innovation emphasizes creativity and change, while defining institutionalization highlights structure, standardization, and integration of new practices.
The Core Differences Between Innovation and Institutionalization
Innovation drives the creation of novel ideas, technologies, or processes that disrupt existing paradigms and generate value through originality and experimentation. Institutionalization involves embedding these innovations into established structures, ensuring consistency, scalability, and long-term sustainability within organizations or society. The core difference lies in innovation's emphasis on change and novelty, whereas institutionalization focuses on stability and the formal integration of innovations into standard practices.
How Innovation Drives Organizational Growth
Innovation drives organizational growth by introducing novel products, services, and processes that increase market competitiveness and customer value. It fosters agility and responsiveness, enabling companies to adapt quickly to changing industry trends and consumer demands. Continuous innovation cultivates a culture of creativity, attracting talent and enhancing operational efficiency, which collectively fuel sustainable business expansion.
The Role of Institutionalization in Sustaining Success
Institutionalization plays a crucial role in sustaining success by embedding innovative practices into organizational culture, policies, and routines. This process transforms novel ideas into standardized procedures that ensure consistency, scalability, and long-term value creation. Effective institutionalization mitigates the risks of innovation decay, fostering continuous improvement and resilience in competitive markets.
Balancing Creativity and Structure in the Workplace
Balancing innovation and institutionalization requires integrating creative processes with established organizational structures to foster sustainable growth. Encouraging a culture where employees experiment within defined frameworks promotes both agility and consistency. Effective leadership ensures that innovation drives competitive advantage while institutional protocols maintain operational stability and compliance.
When Does Innovation Become Institutionalized?
Innovation becomes institutionalized when new ideas, processes, or technologies are consistently integrated into organizational routines, policies, and culture, resulting in sustained value and standardized practices. This transition occurs through mechanisms such as formal adoption, employee training, resource allocation, and leadership endorsement that embed innovation within the structural framework. Metrics like diffusion rate, organizational commitment, and scalability help determine the point at which innovation moves from experimentation to institutionalization.
Barriers to Innovation within Institutionalized Systems
Institutionalized systems often face significant barriers to innovation due to rigid hierarchies, entrenched routines, and resistance to change from established stakeholders. Bureaucratic processes and risk-averse cultures limit experimentation and slow the adoption of new ideas, hindering organizational agility. Overcoming these barriers requires deliberate strategies to foster a culture of openness, flexibility, and continuous learning within institutional frameworks.
Strategies for Fostering Innovation in Established Institutions
Established institutions can foster innovation by implementing dedicated innovation labs that encourage experimentation away from traditional structures, allowing for rapid prototyping and agile methodologies. Embedding cross-functional teams promotes knowledge sharing and breaks down departmental silos, enhancing creative problem solving. Incentivizing risk-taking through recognition programs and allocating resources toward emerging technologies further drives a culture of continuous innovation within institutional frameworks.
Case Studies: Innovation Triumphs and Institutional Challenges
Case studies reveal how innovative startups disrupt markets by rapidly introducing groundbreaking technologies, while established institutions often struggle with bureaucratic inertia that slows adaptation. For example, companies like Tesla achieved success by embracing risk and unconventional strategies, contrasting with traditional automakers' slower shift towards electric vehicles due to institutional barriers. These cases highlight the tension between the agility required for innovation and the structural complexities inherent in institutional processes.
Future Trends: Harmonizing Innovation with Institutional Stability
Future trends emphasize harmonizing innovation with institutional stability by integrating adaptive technologies within established frameworks, ensuring agility without sacrificing organizational coherence. Increasing use of AI-driven decision-making tools supports dynamic problem-solving while maintaining regulatory compliance and risk management protocols. Institutions that balance disruptive innovation with structured governance will lead in resilience and sustainable growth.
Innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com