Lasting culture shapes the core values, traditions, and identities within societies, influencing behaviors and long-term social norms. Fad culture revolves around short-lived trends that rapidly gain and lose popularity, often driven by social media and consumerism. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these contrasting cultural phenomena impact your daily life and societal evolution.
Table of Comparison
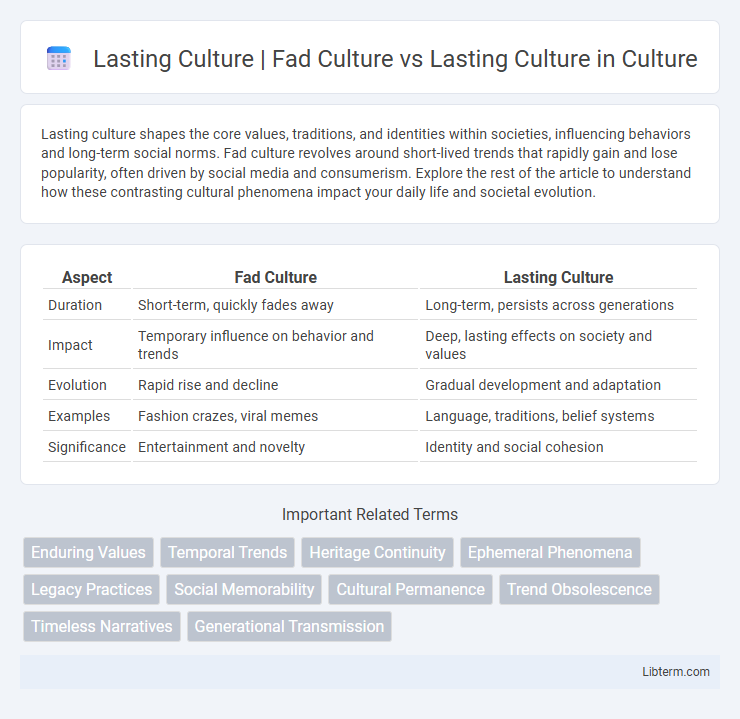
| Aspect | Fad Culture | Lasting Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Short-term, quickly fades away | Long-term, persists across generations |
| Impact | Temporary influence on behavior and trends | Deep, lasting effects on society and values |
| Evolution | Rapid rise and decline | Gradual development and adaptation |
| Examples | Fashion crazes, viral memes | Language, traditions, belief systems |
| Significance | Entertainment and novelty | Identity and social cohesion |
Understanding Lasting Culture
Lasting culture embodies enduring values, traditions, and practices that persist across generations, shaping identities and societal norms over time. It contrasts with fad culture, which is characterized by temporary trends driven by popular appeal and rapid cultural shifts. Understanding lasting culture involves recognizing its deep-rooted role in fostering social cohesion, transmitting collective wisdom, and sustaining meaningful connections within communities.
Defining Fad Culture
Fad culture refers to a social phenomenon characterized by rapid adoption and intense popularity of trends that fade quickly, often driven by viral social media, celebrity endorsements, and consumer hype. These trends typically lack deep cultural significance or lasting impact, with their appeal rooted in novelty and short-term excitement. Fad culture contrasts with lasting culture, which develops over time and embeds meaningful values, traditions, and sustained societal influence.
Key Differences: Fad vs Lasting Culture
Fad culture is characterized by short-lived trends driven by novelty and rapid social media spread, often lacking deep meaning or long-term impact. Lasting culture evolves over extended periods, rooted in shared values, traditions, and sustained social practices that shape community identity and continuity. The key difference lies in durability and cultural significance, with fad culture fading quickly while lasting culture persists and influences future generations.
Origins and Evolution of Cultural Trends
Lasting culture emerges from deep-rooted traditions and values that evolve gradually over centuries, reflecting collective experiences and historical continuity. Fad culture, by contrast, originates from rapid, often media-driven phenomena that gain sudden popularity but lack enduring significance. The evolution of cultural trends reveals a dynamic interplay where fads may influence or fade into lasting culture, but only those with meaningful societal impact achieve permanence.
Factors That Sustain Lasting Culture
Factors that sustain lasting culture include deeply rooted values, consistent community engagement, and adaptability to social changes. Lasting culture thrives on shared traditions, collective memory, and the transmission of meaningful practices across generations. Unlike fad culture, which is driven by fleeting trends and external influences, lasting culture is anchored in a strong sense of identity and purpose.
Why Fads Fade Quickly
Fad culture fades quickly because it relies on novelty and social hype rather than enduring values or meaningful connections, leading to rapid bursts of popularity followed by swift decline. The transient nature of fads is driven by consumer desire for constant novelty and the viral spread of trends through social media, which accelerates both their rise and fall. Lasting culture endures by embedding deep cultural significance, shared values, and traditions that resonate across generations.
Social and Economic Impacts of Each
Fad culture drives rapid social trends that often fade quickly, leading to transient consumer behavior and short-term economic boosts primarily in industries like fashion and tech gadgets. Lasting culture fosters stable social norms and sustained economic growth by reinforcing traditions, long-term brand loyalty, and consistent market demand. The cyclical nature of fad culture can strain resources and create waste, whereas lasting culture promotes sustainable development and deeper economic resilience.
Case Studies: Examples of Each Culture
Case studies reveal that fad culture thrives on rapid consumption and fleeting trends, exemplified by phenomena like Pokemon Go and the Ice Bucket Challenge, which saw explosive but short-lived popularity. In contrast, lasting culture is characterized by enduring impact and sustained relevance, as seen in the global influence of Shakespearean literature and the timeless appeal of classic rock music. These examples demonstrate how lasting cultural contributions shape society over decades, whereas fad culture generates swift, momentary engagement.
Learning from Lasting Cultural Movements
Lasting cultural movements such as the Renaissance and the Civil Rights Movement provide invaluable lessons in creating enduring social impact through deep-rooted values and widespread societal engagement. Unlike fad culture, which thrives on rapid, short-term popularity fueled by trends or viral phenomena, lasting culture establishes sustained influence by shaping collective identity, norms, and behaviors over generations. Understanding the mechanisms behind these durable movements enables creators and influencers to foster meaningful change by promoting authenticity, community participation, and adaptability.
Balancing Innovation and Tradition in Culture
Balancing innovation and tradition in culture requires integrating novel ideas that drive progress while preserving core values and practices that provide identity and continuity. Lasting culture sustains community cohesion by evolving through meaningful adaptations, contrasting with fad culture's rapid, superficial changes that lack deep roots. Emphasizing long-term relevance, lasting culture nurtures innovation within a framework of heritage, ensuring cultural resilience and authenticity.
Lasting Culture | Fad Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com