Observable culture encompasses the visible and tangible elements of an organization, such as dress code, workspace layout, rituals, and behaviors exhibited by its members. These aspects serve as outward expressions of deeper values and beliefs, shaping how employees interact and influence overall workplace dynamics. Explore the rest of this article to understand how recognizing observable culture can enhance your ability to adapt and thrive within any organization.
Table of Comparison
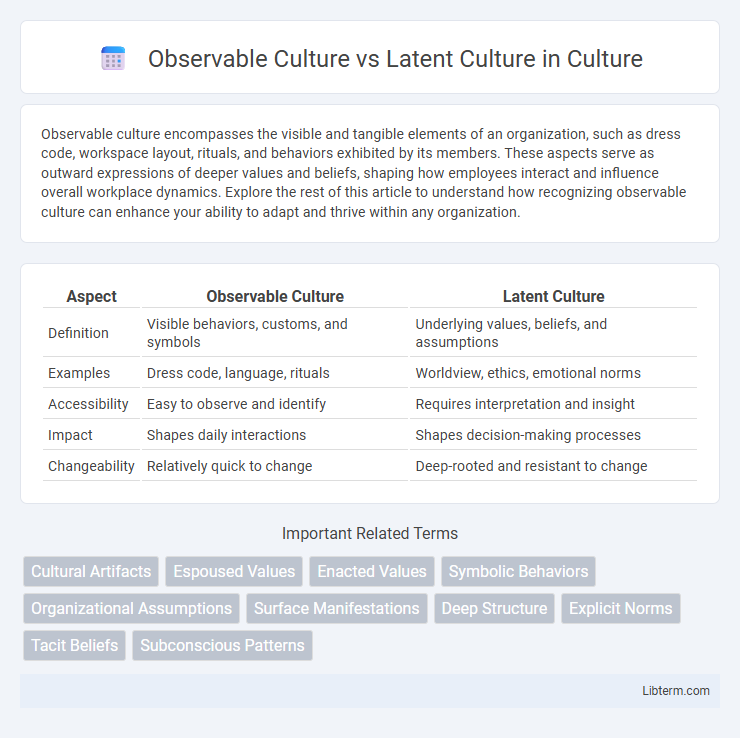
| Aspect | Observable Culture | Latent Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visible behaviors, customs, and symbols | Underlying values, beliefs, and assumptions |
| Examples | Dress code, language, rituals | Worldview, ethics, emotional norms |
| Accessibility | Easy to observe and identify | Requires interpretation and insight |
| Impact | Shapes daily interactions | Shapes decision-making processes |
| Changeability | Relatively quick to change | Deep-rooted and resistant to change |
Defining Observable and Latent Culture
Observable culture consists of visible elements such as language, clothing, rituals, and behaviors that people easily notice and describe. Latent culture encompasses the underlying values, beliefs, attitudes, and thought patterns that shape these visible behaviors but remain hidden from direct observation. Understanding the distinction between observable and latent culture is essential for accurately interpreting cultural interactions and avoiding superficial judgments.
Key Characteristics of Observable Culture
Observable Culture encompasses visible elements such as dress codes, language, rituals, and behaviors that are easily noticed and measured within an organization or society. It reflects explicit norms and practices that guide daily interactions and communication patterns. These tangible aspects serve as indicators for understanding deeper, underlying values and beliefs, which belong to Latent Culture.
Key Traits of Latent Culture
Latent culture encompasses the underlying values, beliefs, and assumptions that drive observable behaviors within a group but remain hidden beneath the surface. Key traits include deep-seated norms, subconscious motivations, and unspoken rules that shape decision-making and interpersonal dynamics. Understanding latent culture is essential for addressing root causes of organizational challenges and fostering authentic change.
The Role of Symbols and Artifacts
Symbols and artifacts serve as tangible expressions of observable culture, representing explicit cultural values and social norms. Latent culture encompasses the deeper meanings, beliefs, and assumptions embedded in these symbols, often unconsciously influencing behavior and attitudes. Understanding the role of symbols and artifacts helps decode the underlying cultural framework that guides group identity and social interactions.
Underlying Values and Beliefs
Observable culture consists of visible elements like rituals, language, and behaviors, providing a surface-level understanding of a society. Latent culture, defined by underlying values and beliefs, shapes these observable actions and governs social norms and decision-making processes. Examining underlying values such as individualism versus collectivism reveals the deep-rooted motivations influencing observable cultural expressions.
Influence on Organizational Behavior
Observable culture consists of visible artifacts such as dress codes, rituals, and formal policies that directly influence organizational behavior by shaping employees' daily actions and communication patterns. Latent culture includes underlying values, beliefs, and assumptions that subtly guide decision-making, problem-solving, and interpersonal relationships within the organization. The interplay between observable and latent culture creates a dynamic environment affecting motivation, collaboration, and overall organizational effectiveness.
Methods for Identifying Observable Culture
Observable culture is identified through explicit methods such as direct observation of behaviors, rituals, language, and artifacts within an organization. Techniques like ethnographic studies, surveys, interviews, and document analysis help uncover visible elements such as dress codes, workspace layout, and communication patterns. These methods provide tangible data that reveal the surface-level manifestations of organizational culture.
Challenges in Uncovering Latent Culture
Uncovering latent culture presents significant challenges due to its intangible nature, as it consists of underlying values, beliefs, and assumptions that are not immediately visible in observable behaviors or artifacts. Researchers and organizations often face difficulties in identifying latent culture because it requires deep interpretive methods such as ethnographic studies, interviews, and long-term observation, which can be time-consuming and subjective. Misinterpretation or overlooking these subtle cultural elements can lead to ineffective communication, misguided policies, and conflict within multicultural environments.
Implications for Change Management
Observable culture, including visible behaviors, rituals, and symbols, shapes employees' immediate experiences and sets expectations for change initiatives, making it crucial to align these elements during change management. Latent culture, consisting of underlying values, beliefs, and assumptions, profoundly influences how change is internally perceived and accepted, requiring deep engagement to address resistance. Effective change management strategies integrate both observable and latent culture aspects to foster sustainable adoption and embed new practices within the organization.
Bridging the Gap Between Observable and Latent Culture
Bridging the gap between observable culture, which includes visible behaviors, rituals, and symbols, and latent culture, encompassing underlying values, beliefs, and thought patterns, requires intentional strategies such as immersive cross-cultural training and open communication channels. Organizations can foster cultural intelligence by encouraging reflection on implicit assumptions and promoting dialogue that uncovers hidden norms influencing workplace dynamics. Understanding this duality enhances collaboration and drives effective intercultural engagement across diverse teams.
Observable Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com