Chalcolithic culture, also known as the Copper Age, marks the transition between the Neolithic and Bronze Age, characterized by the first use of metal tools alongside stone implements. This period witnessed significant advancements in agriculture, pottery, and social organization, laying the foundation for complex societies. Discover how the innovations of Chalcolithic culture shaped human history and influenced your ancestral development in the full article.
Table of Comparison
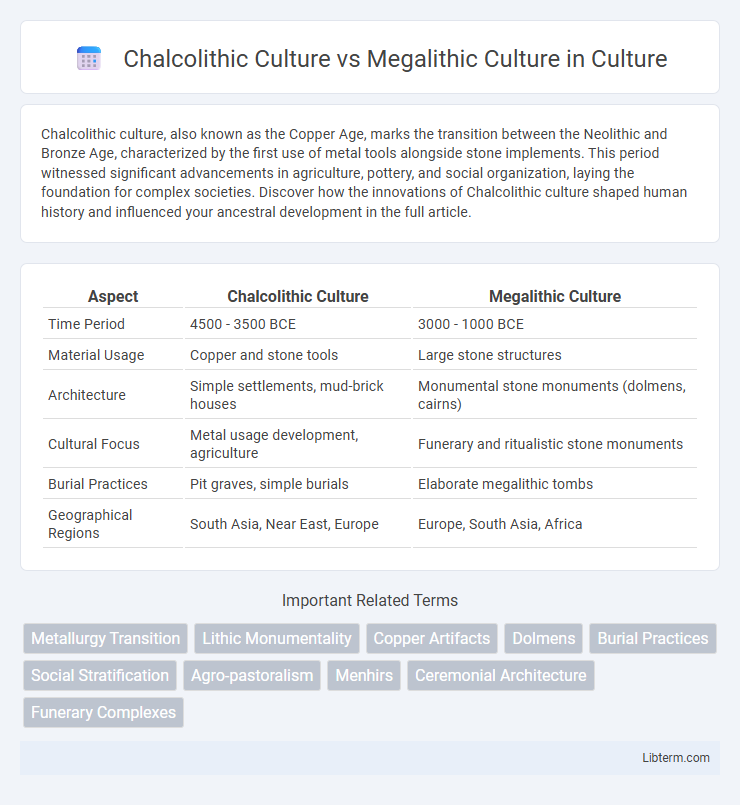
| Aspect | Chalcolithic Culture | Megalithic Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | 4500 - 3500 BCE | 3000 - 1000 BCE |
| Material Usage | Copper and stone tools | Large stone structures |
| Architecture | Simple settlements, mud-brick houses | Monumental stone monuments (dolmens, cairns) |
| Cultural Focus | Metal usage development, agriculture | Funerary and ritualistic stone monuments |
| Burial Practices | Pit graves, simple burials | Elaborate megalithic tombs |
| Geographical Regions | South Asia, Near East, Europe | Europe, South Asia, Africa |
Introduction to Chalcolithic and Megalithic Cultures
Chalcolithic culture, marking the transition from the Stone Age to the Bronze Age, is characterized by the use of copper tools alongside stone implements, reflecting early metalworking advancements. Megalithic culture is distinguished by the construction of large stone monuments and burial sites, emphasizing social organization and ritual practices in prehistoric communities. Both cultures reveal crucial stages in human technological and social evolution, with Chalcolithic focusing on metallurgy and Megalithic on monumental architecture.
Historical Timeline and Geographical Spread
The Chalcolithic Culture, dating roughly from 3500 to 1500 BCE, marks the transition between the Neolithic and Bronze Age, with key sites found in regions such as the Indian subcontinent, the Near East, and parts of Europe. The Megalithic Culture, emerging around 3000 BCE and lasting until approximately 1000 BCE, is characterized by the construction of large stone monuments and has a widespread geographical presence across Western Europe, the British Isles, and parts of South and Southeast Asia. Both cultures overlap in timeline but differ significantly in geographical distribution and material culture, reflecting diverse social and technological developments.
Key Characteristics of Chalcolithic Culture
The Chalcolithic Culture, also known as the Copper Age, is marked by the use of copper tools alongside stone implements, reflecting an early transition from the Neolithic period. This culture is characterized by settled agricultural practices, pottery with distinct geometric patterns, and the emergence of metalworking skills. Unlike the Megalithic Culture known for large stone monuments, Chalcolithic societies primarily focused on small-scale metal use and village life.
Key Characteristics of Megalithic Culture
Megalithic culture is characterized by the construction of large stone monuments such as dolmens, menhirs, and stone circles used for ceremonial and burial purposes. These structures demonstrate advanced knowledge of stone quarrying, transportation, and alignment with astronomical events. The culture also exhibits complex social organization reflected in communal labor and ritual practices distinct from the Chalcolithic period's smaller-scale copper tool usage and settlement patterns.
Major Archaeological Sites and Evidence
The Chalcolithic Culture is characterized by sites such as Mehrgarh in Pakistan and Ahar-Banas in India, where evidence of copper tools, pottery, and early agricultural practices has been uncovered. In contrast, the Megalithic Culture is distinguished by large stone structures at locations like Stonehenge in England, the Carnac stones in France, and various dolmens found across South India, indicating advanced megalithic construction and burial rituals. Archaeological evidence from these sites reveals distinct technological and ritualistic developments, with Chalcolithic sites emphasizing metallurgy and farming, while Megalithic sites focus on monumental stone architecture and funerary practices.
Technology and Tools: A Comparative Analysis
Chalcolithic Culture is characterized by the use of copper tools alongside stone implements, marking the transition from the Stone Age to the Metal Age with advancements in metallurgy and smelting techniques. Megalithic Culture, on the other hand, is distinguished by the construction of large stone monuments like dolmens and menhirs using advanced stone-cutting and transportation methods, reflecting significant architectural innovation. The Chalcolithic period shows early metal tool usage improving agricultural and craft efficiency, while the Megalithic era emphasizes monumental stone structures demonstrating social organization and technological skill in stone manipulation.
Burial Practices and Religious Beliefs
Chalcolithic culture is characterized by burial practices involving individual graves with pottery and copper tools, reflecting early ritualistic beliefs centered on ancestor worship. Megalithic culture is distinguished by large stone monuments, such as dolmens and menhirs, used for collective burials and elaborate ceremonies emphasizing community and afterlife beliefs. The shift from individual to communal burial sites in megalithic culture indicates evolving religious complexity and social structure.
Artifacts, Pottery, and Artistic Expressions
Chalcolithic Culture is characterized by polished stone tools and early metal artifacts often made of copper, while Megalithic Culture is renowned for its large stone constructions like dolmens and menhirs serving as tombs or ritual sites. Pottery in Chalcolithic sites typically features handmade, painted ware with geometric patterns, whereas Megalithic pottery is more robust, often undecorated or with simple incised designs reflecting utilitarian use. Artistic expressions in Chalcolithic culture include intricate beadwork and figurines, contrasting with the monumental stone art and engraved symbols seen in Megalithic contexts, highlighting differing cultural emphases on personal adornment versus collective memory and ritual.
Social Organization and Community Life
Chalcolithic Culture exhibited early forms of social stratification with emerging leadership roles and specialized occupations, reflecting a community life centered around agriculture and metallurgy. In contrast, Megalithic Culture displayed more complex social organization with collective efforts evident in the construction of large stone monuments, indicating a strong emphasis on ritual and ancestor worship within tightly knit communities. The communal labor and social cohesion required for megalithic architecture point to advanced cooperation and hierarchical structures distinct from the more individual household-based communities of the Chalcolithic period.
Legacy and Influence on Subsequent Cultures
The Chalcolithic Culture laid the foundation for early metallurgy and agricultural practices, directly influencing the development of urban societies and craft specialization in subsequent Bronze Age civilizations. In contrast, the Megalithic Culture is renowned for its monumental stone structures, which served as religious and social centers, shaping the ritualistic and burial traditions of later communities across Europe and Asia. Both cultures contributed significantly to the architectural, technological, and societal frameworks that defined early complex human settlements.
Chalcolithic Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com