Diaspora literature explores themes of displacement, identity, and cultural hybridity experienced by communities living outside their ancestral homelands. It reveals the complexities of belonging and memory through diverse narratives that challenge traditional notions of nation and ethnicity. Discover how diaspora literature enriches your understanding of cultural connections by delving deeper into this article.
Table of Comparison
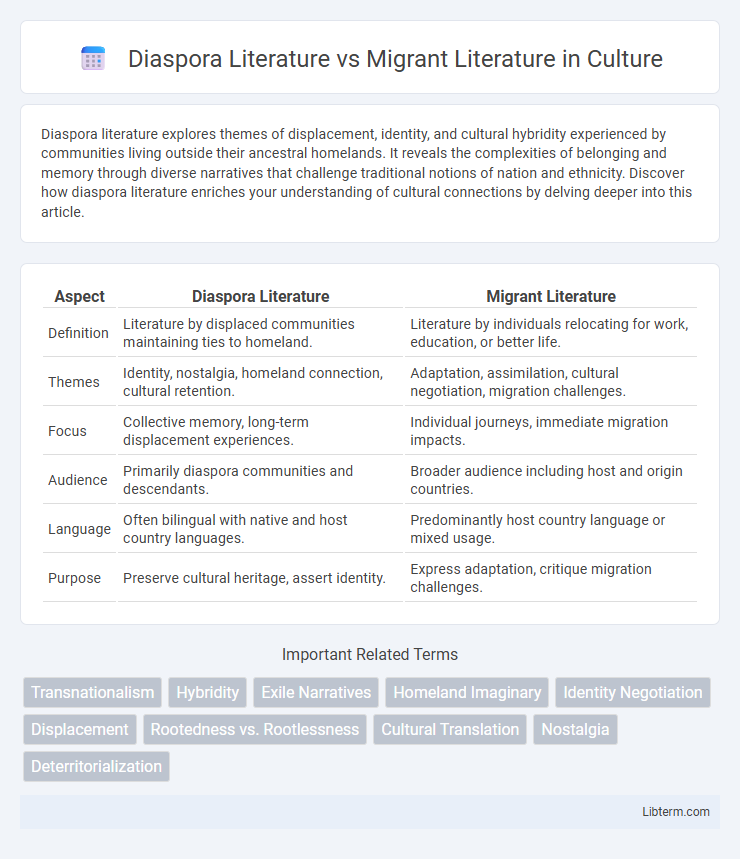
| Aspect | Diaspora Literature | Migrant Literature |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literature by displaced communities maintaining ties to homeland. | Literature by individuals relocating for work, education, or better life. |
| Themes | Identity, nostalgia, homeland connection, cultural retention. | Adaptation, assimilation, cultural negotiation, migration challenges. |
| Focus | Collective memory, long-term displacement experiences. | Individual journeys, immediate migration impacts. |
| Audience | Primarily diaspora communities and descendants. | Broader audience including host and origin countries. |
| Language | Often bilingual with native and host country languages. | Predominantly host country language or mixed usage. |
| Purpose | Preserve cultural heritage, assert identity. | Express adaptation, critique migration challenges. |
Defining Diaspora Literature
Diaspora literature explores the cultural, historical, and emotional experiences of dispersed communities maintaining connections to their homeland while navigating identity in foreign environments. It emphasizes themes of rootlessness, memory, displacement, and hybrid identities that arise from the forced or voluntary migration of ethnic groups over generations. This contrasts with migrant literature, which typically centers on individual or recent migration experiences, focusing on adaptation and personal transformation in new social contexts.
Understanding Migrant Literature
Migrant Literature centers on the lived experiences and cultural negotiations of individuals who relocate across borders for work, education, or refuge, emphasizing themes of identity, displacement, and adaptation. It often explores personal narratives and socio-economic challenges within the host country's context, distinguishing it from Diaspora Literature, which broadly addresses collective memory, homeland connections, and transnational identity. Understanding Migrant Literature requires analyzing its focus on mobility, assimilation processes, and the reconstruction of self within new socio-political environments.
Historical Contexts and Origins
Diaspora Literature emerged from the forced displacement and scattering of communities due to colonialism, slavery, and political upheaval, reflecting transnational identities and collective memory across generations. Migrant Literature originates primarily from voluntary or economic migration in the 20th and 21st centuries, focusing on individual experiences of relocation, adaptation, and cultural negotiation in new host countries. Both literatures address themes of identity and belonging but Diaspora Literature is more deeply rooted in historical trauma and ancestral connections.
Identity and Belonging in Diaspora Literature
Diaspora literature explores themes of fragmented identity and the perpetual negotiation of belonging within transnational spaces, emphasizing the emotional and cultural dislocation experienced by dispersed communities. It delves into the complex interplay between memory, heritage, and the search for a cohesive self amid multiple cultural influences. Unlike migrant literature, which often focuses on the physical journey and adaptation to new environments, diaspora literature foregrounds the internal struggle for identity preservation and collective belonging across generations.
Themes of Migration and Displacement
Diaspora Literature explores themes of long-term cultural identity, exile, and the collective memory of dispersed communities, emphasizing the tension between homeland attachment and assimilation in new environments. Migrant Literature centers on the individual experience of migration, highlighting personal struggles with displacement, adaptation, and the search for belonging amid socio-economic challenges. Both genres critically examine the complexities of migration, but Diaspora Literature foregrounds intergenerational identity and historical displacement, while Migrant Literature often portrays immediate, lived realities of movement and resettlement.
Cultural Hybridity and Negotiation
Diaspora literature explores cultural hybridity through the lens of displacement, memory, and the ongoing negotiation of identity across generations and geographies. Migrant literature emphasizes the lived experiences of migration and adaptation, highlighting the negotiation between homeland traditions and host country realities, often portraying cultural hybridity as a dynamic process. Both literatures engage with themes of belonging, identity fragmentation, and the challenge of sustaining multiple cultural affiliations amid societal pressures.
Narrative Perspectives: Insider vs. Outsider
Diaspora literature often presents narrative perspectives from insiders who maintain a deep cultural connection to their homeland, allowing authentic explorations of identity, memory, and displacement. Migrant literature typically provides outsider viewpoints, emphasizing encounters with new environments and the challenges of assimilation, often highlighting hybridity and cultural negotiation. These differing narrative stances shape the thematic focus and emotional resonance within each literary tradition.
Language, Memory, and Reclamation
Diaspora literature often explores fragmented language forms and hybrid identities, emphasizing collective memory and cultural reclamation through multilingual narratives that connect displaced communities. Migrant literature focuses on individual linguistic adaptations and personal memory reconstruction, highlighting the negotiation of identity within host cultures and the active reclamation of self through language. Both literatures engage with memory as a site of resistance, using language reclamation to challenge dominant narratives and affirm cultural heritage.
Representation in Contemporary Literature
Diaspora literature emphasizes the collective memory and cultural identity of dispersed communities, often exploring themes of historical displacement and transgenerational trauma in contemporary narratives. Migrant literature primarily focuses on individual experiences of movement and adaptation, highlighting challenges of assimilation, identity negotiation, and the socio-political realities faced by migrants. Representation in contemporary literature reveals how diaspora texts foreground community resilience and hybridity, while migrant texts offer intimate portrayals of migration's personal and immediate impacts.
Diaspora vs. Migrant Literature: Key Differences
Diaspora literature explores the collective identity and cultural memory of communities dispersed from their original homeland, emphasizing themes of rootlessness and transnational belonging. Migrant literature centers on individual experiences of movement and adaptation, highlighting personal struggles with identity, displacement, and assimilation in new environments. While diaspora narratives often address generational continuity and historical trauma, migrant texts focus on contemporary migration dynamics and the complexities of acculturation.
Diaspora Literature Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com