Understanding laws is essential for navigating your rights and responsibilities within society. Legal frameworks vary widely across regions, affecting areas such as contracts, property, and personal rights. Discover how the nuances of laws impact your daily life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
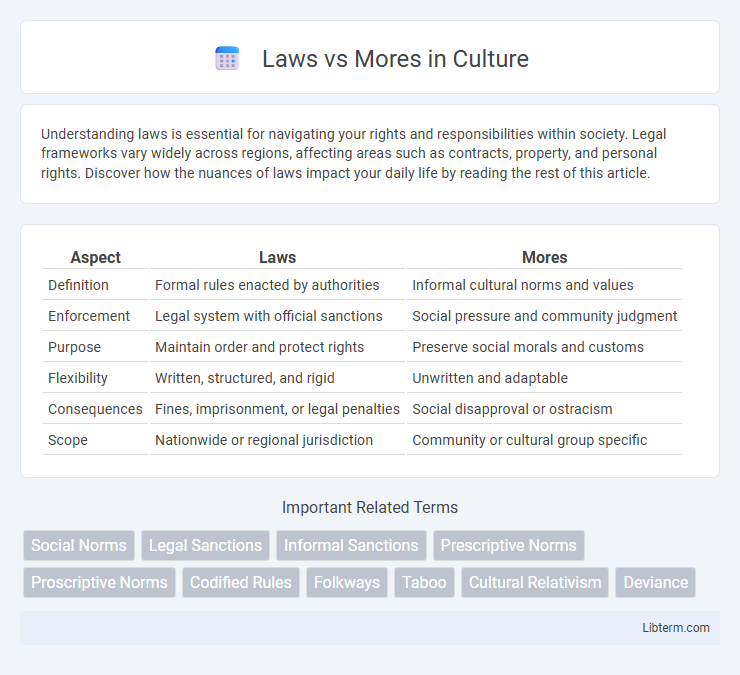
| Aspect | Laws | Mores |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal rules enacted by authorities | Informal cultural norms and values |
| Enforcement | Legal system with official sanctions | Social pressure and community judgment |
| Purpose | Maintain order and protect rights | Preserve social morals and customs |
| Flexibility | Written, structured, and rigid | Unwritten and adaptable |
| Consequences | Fines, imprisonment, or legal penalties | Social disapproval or ostracism |
| Scope | Nationwide or regional jurisdiction | Community or cultural group specific |
Defining Laws and Mores: Core Differences
Laws are formal rules established and enforced by governmental authorities to regulate behavior and maintain social order, carrying specific legal consequences for violations. Mores are deeply ingrained social norms and moral customs that guide acceptable behavior within a culture, often upheld by social approval or disapproval rather than formal sanctions. The core difference lies in laws being codified legal standards with official enforcement, whereas mores represent informal ethical expectations rooted in societal values.
Historical Origins of Laws and Mores
Laws originated from formalized codes and legal systems developed by ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Rome, reflecting societal needs for order and governance. Mores evolved from customary practices and unwritten norms deeply rooted in cultural traditions and communal values passed down through generations. While laws impose explicit rules enforceable by institutions, mores guide moral conduct and social behavior through informal societal expectations.
The Role of Laws in Society
Laws establish formal rules enforced by governmental authorities to regulate behavior and maintain social order, providing clear consequences for violations. Unlike mores, which are informal societal norms based on cultural values and ethics, laws create a standardized framework for justice and conflict resolution. They play a crucial role in safeguarding rights, promoting fairness, and enabling peaceful coexistence within diverse communities.
The Influence of Mores on Social Behavior
Mores significantly influence social behavior by establishing unwritten norms that dictate acceptable conduct within a community, often rooted in moral and cultural values. These deeply ingrained customs reinforce social cohesion and guide individuals' decisions beyond legal requirements, shaping attitudes toward right and wrong within society. Unlike formal laws, mores operate through social approval or disapproval, impacting behavior by fostering internalized ethical standards.
Legal Enforcement vs. Social Pressure
Laws are formal rules established by governments that require legal enforcement through courts and penalties to ensure compliance, while mores are social norms upheld by collective social pressure and informal sanctions within communities. Legal enforcement involves specific consequences such as fines or imprisonment imposed by state authorities, whereas social pressure relies on approval, disapproval, or ostracism by peers to regulate behavior. The enforceability of laws is codified and mandatory, contrasting with mores, which depend on cultural consensus and voluntary adherence for social harmony.
Case Studies: When Laws and Mores Conflict
Laws and mores often clash in cases like civil disobedience movements, where legal statutes prohibit actions considered morally imperative by certain groups, such as the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s United States. In such cases, laws mandate compliance while mores drive individuals to resist, exemplified by Rosa Parks' refusal to give up her bus seat, highlighting how legal frameworks can conflict with deeply held social values. Conflicts between laws and mores reveal tensions in societal norms, emphasizing the need for legal reforms to reflect evolving moral standards.
Evolution of Laws and Mores Over Time
Laws and mores have evolved distinctly, with laws formalizing societal norms into codified rules enforceable by institutions, while mores represent deeply held cultural values shaping informal social behavior. Over time, legal systems adapt to changes in societal attitudes, technological advances, and political shifts, reflecting the dynamic nature of morality within laws. Simultaneously, mores transform through generational shifts, globalization, and cultural interactions, influencing and sometimes resisting legal reforms.
Cultural Variations in Laws and Mores
Laws and mores reflect cultural variations that shape societal norms and legal systems worldwide. In collectivist cultures, mores prioritize community harmony and social obligations, influencing laws that emphasize group welfare over individual rights. Diverse legal frameworks emerge from these cultural values, underscoring the dynamic interplay between societal customs and formal regulations.
Impact of Laws and Mores on Individual Behavior
Laws establish formal rules sanctioned by governmental authority, guiding individual behavior through clear legal consequences that promote social order and predictability. Mores, rooted in cultural values and social norms, influence behavior by shaping moral expectations and social acceptance within communities, often enforced through informal social pressures rather than legal penalties. Together, laws and mores create a framework that directs individuals' actions, balancing formal regulation with ethical standards to maintain cohesion and stability in society.
Harmonizing Laws and Mores for Social Order
Harmonizing laws and mores is essential for maintaining social order, as laws codify societal norms while mores represent deeply ingrained ethical beliefs. Effective legal systems reflect prevailing mores to ensure compliance and legitimacy, reducing conflicts between formal regulations and cultural expectations. Aligning statutory laws with community values fosters trust, social cohesion, and stability within diverse societies.
Laws Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com