Existential anxiety arises from deep questions about life's meaning, purpose, and your place in the universe, often triggering feelings of uncertainty and dread. This phenomenon impacts mental health by confronting individuals with the inevitability of death, freedom, and isolation. Dive into the rest of the article to understand how to navigate and find peace amidst existential anxiety.
Table of Comparison
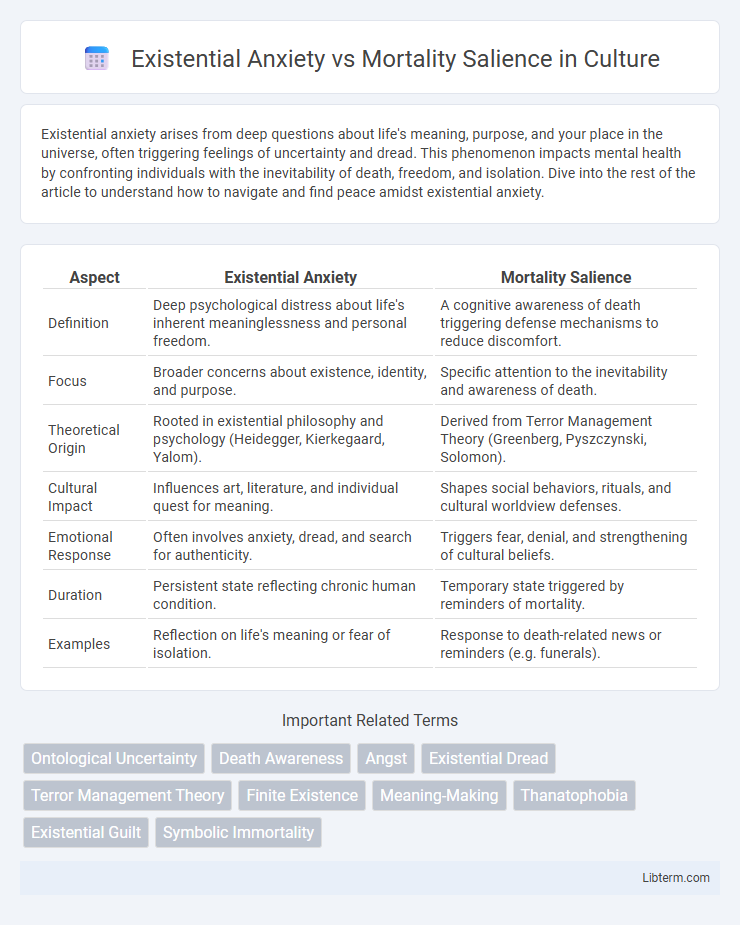
| Aspect | Existential Anxiety | Mortality Salience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deep psychological distress about life's inherent meaninglessness and personal freedom. | A cognitive awareness of death triggering defense mechanisms to reduce discomfort. |
| Focus | Broader concerns about existence, identity, and purpose. | Specific attention to the inevitability and awareness of death. |
| Theoretical Origin | Rooted in existential philosophy and psychology (Heidegger, Kierkegaard, Yalom). | Derived from Terror Management Theory (Greenberg, Pyszczynski, Solomon). |
| Cultural Impact | Influences art, literature, and individual quest for meaning. | Shapes social behaviors, rituals, and cultural worldview defenses. |
| Emotional Response | Often involves anxiety, dread, and search for authenticity. | Triggers fear, denial, and strengthening of cultural beliefs. |
| Duration | Persistent state reflecting chronic human condition. | Temporary state triggered by reminders of mortality. |
| Examples | Reflection on life's meaning or fear of isolation. | Response to death-related news or reminders (e.g. funerals). |
Understanding Existential Anxiety
Existential anxiety arises from the awareness of life's inherent uncertainties and the search for meaning amid inevitable death, distinguishing it from mortality salience, which specifically deals with the conscious recognition of one's mortality. Understanding existential anxiety involves exploring how individuals confront fears related to freedom, isolation, meaninglessness, and mortality itself, influencing behaviors and mental health. Research indicates that managing existential anxiety effectively can enhance psychological resilience and promote a more purposeful life despite the unavoidable presence of death.
Defining Mortality Salience
Mortality salience refers to the heightened awareness of one's own death and the inevitable nature of mortality, triggering cognitive and emotional responses aimed at managing existential threats. This concept, central to Terror Management Theory, posits that reminders of death influence behavior by motivating individuals to seek meaning, self-esteem, and cultural worldviews that provide psychological security. Unlike broader existential anxiety, mortality salience specifically targets the conscious recognition of death, shaping attitudes and actions to mitigate the fear of nonexistence.
Core Differences Between Existential Anxiety and Mortality Salience
Existential anxiety refers to the deep, pervasive fear and unease stemming from the awareness of life's fundamental uncertainties and the search for meaning, whereas mortality salience specifically highlights the conscious awareness of one's inevitable death. Existential anxiety encompasses broader concerns about purpose, isolation, freedom, and meaninglessness, while mortality salience focuses narrowly on death-related thoughts triggering defensive psychological responses. Core differences lie in the scope of these experiences: existential anxiety is an ongoing, diffuse condition tied to human existence, whereas mortality salience is a situational state activated by reminders of death.
Psychological Theories Behind Existential Anxiety
Existential anxiety arises from the confrontation with the inherent meaninglessness and uncertainty of life, as emphasized in existential psychology by theorists like Viktor Frankl and Rollo May. Mortality salience, a core concept in Terror Management Theory, specifically refers to the heightened awareness of one's death, triggering defense mechanisms to uphold self-esteem and cultural worldviews. Psychological theories highlight how existential anxiety motivates individuals to find purpose and resilience through meaning-making processes and symbolic immortality.
The Role of Terror Management Theory
Terror Management Theory (TMT) explains how Existential Anxiety arises from Mortality Salience, the awareness of one's inevitable death. TMT posits that individuals cope by reinforcing cultural worldviews and self-esteem to mitigate death-related fears. This psychological mechanism serves to buffer against the paralyzing effects of existential dread triggered by mortality awareness.
Manifestations of Mortality Salience in Daily Life
Mortality salience manifests in daily life through heightened awareness of death triggers, such as encountering obituaries, health scares, or witnessing accidents. This often leads to behavioral changes like increased pursuit of meaning, stronger adherence to cultural beliefs, or intensified relationships as coping mechanisms. The psychological impact includes fluctuations in anxiety levels, prompting individuals to seek symbolic immortality or legacy-building activities.
Existential Anxiety: Causes and Triggers
Existential anxiety arises from the awareness of one's finite existence and the uncertainty of life's meaning, often triggered by thoughts of death, freedom, isolation, and meaninglessness. These triggers provoke deep psychological discomfort as individuals confront fundamental questions about their purpose and the inevitability of mortality. Stressful life events, trauma, or philosophical reflection can intensify existential anxiety, leading to heightened self-awareness and existential crises.
How Mortality Salience Influences Behavior
Mortality salience triggers an intensified awareness of death, profoundly influencing human behavior by motivating individuals to seek meaning and reinforce cultural worldviews. This heightened death awareness often leads to increased adherence to societal norms, bolstered self-esteem, and the pursuit of symbolic immortality through legacy-building activities. Research shows mortality salience can also provoke defensive reactions such as exclusion of out-groups and risk aversion to manage existential threats effectively.
Coping Strategies for Existential Anxiety and Mortality Salience
Existential anxiety and mortality salience trigger profound awareness of life's impermanence, prompting individuals to seek coping mechanisms that restore psychological equilibrium. Common strategies include finding meaning through purposeful goals, engaging in mindfulness practices to reduce distress, and cultivating social connections that reinforce a sense of belonging and legacy. Therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and existential psychotherapy effectively assist individuals in reframing fears associated with mortality, promoting resilience in the face of existential concerns.
Implications for Mental Health and Wellbeing
Existential anxiety and mortality salience both trigger awareness of life's finitude but differ in their psychological impact; existential anxiety involves a chronic, pervasive dread about meaning and existence, while mortality salience is a situational reminder of death. Research links heightened existential anxiety to increased risk of depression and anxiety disorders, whereas mortality salience can either provoke defensive coping mechanisms or foster meaningful behavior and resilience. Understanding these distinctions informs therapeutic approaches, emphasizing tailored interventions to mitigate existential distress and enhance mental health and overall wellbeing.
Existential Anxiety Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com