Ideology shapes how individuals and societies interpret the world, guiding beliefs, values, and actions through a coherent set of ideas. Understanding the influence of ideology helps clarify political, social, and cultural behaviors that impact daily life. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how your ideology affects decision-making and societal trends.
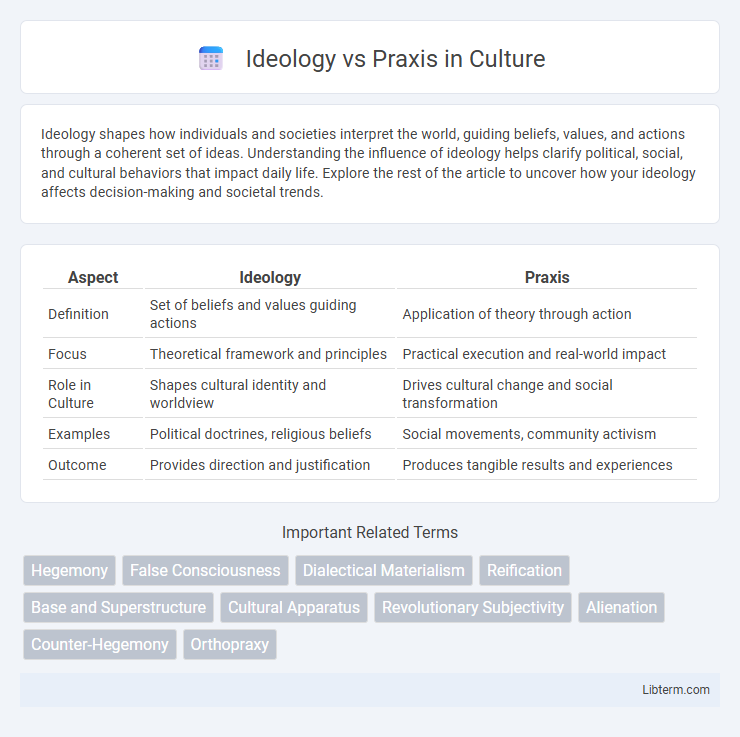
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Ideology | Praxis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set of beliefs and values guiding actions | Application of theory through action |
| Focus | Theoretical framework and principles | Practical execution and real-world impact |
| Role in Culture | Shapes cultural identity and worldview | Drives cultural change and social transformation |
| Examples | Political doctrines, religious beliefs | Social movements, community activism |
| Outcome | Provides direction and justification | Produces tangible results and experiences |
Defining Ideology: Concepts and Origins
Ideology refers to a system of ideas, beliefs, and values that shape political, social, and economic structures, often originating from historical contexts and intellectual traditions. It functions as a framework for understanding and interpreting reality, guiding collective behavior and policy-making. The origins of ideology can be traced to the Enlightenment era, where thinkers like Marx and Rousseau theorized about societal organization and human purpose.
Understanding Praxis: From Theory to Practice
Understanding praxis involves transforming ideological theories into concrete actions that drive social change. This process emphasizes the dynamic interaction between reflective thought and practical application, enabling individuals to critically evaluate and adapt their strategies in real-world contexts. Effective praxis bridges the gap between abstract concepts and tangible outcomes by fostering continuous feedback and learning.
The Relationship Between Ideology and Praxis
The relationship between ideology and praxis is foundational in shaping social and political movements, where ideology provides the theoretical framework guiding action, and praxis represents the practical implementation of these ideas. Effective praxis requires a dynamic interaction with ideology, continually testing and refining beliefs through real-world practice and feedback. This cyclical process ensures that ideology remains relevant and responsive to changing circumstances, promoting transformative social change.
Historical Case Studies: Ideology in Action
Historical case studies demonstrate how ideology shapes praxis, exemplified by the Bolshevik Revolution where Marxist principles were implemented through radical social and economic reforms. In the Chinese Cultural Revolution, Maoist ideology drove mass mobilization and political purges, highlighting the transformative but often destructive potential of ideology in practice. These cases reveal the complex interplay between theoretical ideals and their real-world consequences, underscoring the dynamic relationship between thought and action.
Theoretical Frameworks: Marxism and Beyond
Marxism provides a foundational theoretical framework that examines the relationship between ideology and praxis through dialectical materialism, emphasizing the role of class struggle in shaping social realities. Beyond Marxism, contemporary frameworks such as critical theory, post-structuralism, and intersectionality expand the analysis by interrogating power structures, identity, and cultural narratives influencing both ideological constructs and practical actions. These evolving perspectives highlight the dynamic interaction between theory and practice in transforming societal conditions and challenging hegemonic ideologies.
Challenges of Translating Ideology into Praxis
Translating ideology into praxis often encounters challenges such as misinterpretation of core principles, resource limitations, and resistance to change within organizational or social structures. Ideological frameworks may conflict with practical realities, complicating implementation and resulting in discrepancies between theoretical goals and actual outcomes. Effective praxis requires continuous adaptation and critical reflection to bridge gaps between abstract ideals and concrete actions.
Ideological Purity vs. Pragmatic Action
Ideological purity emphasizes unwavering adherence to specific principles or doctrines, often prioritizing theoretical consistency over situational flexibility. Pragmatic action values practical outcomes and adaptability, allowing compromises that achieve tangible results despite ideological deviations. Balancing ideological integrity with pragmatic decision-making is crucial for effective leadership and social change.
Contemporary Examples: Ideology vs Praxis Today
Contemporary examples of ideology versus praxis highlight the gap between political beliefs and implemented policies, such as climate change activism where governments pledge green initiatives but fall short in execution. In social justice movements, ideologies promoting equality often clash with institutional practices that maintain systemic biases. Corporate sustainability programs illustrate this tension as companies publicly endorse environmental responsibility while their operational realities frequently contradict these commitments.
Critiques and Debates: Philosophers on Praxis
Philosophers critically examine the tension between ideology and praxis, emphasizing praxis as the realization of theory through action and its potential to transform social realities. Debates highlight that rigid adherence to ideology without praxis risks dogmatism, while praxis devoid of ideological grounding may result in unreflective activism. Thinkers like Marx stress that true praxis must synthesize theory and practice, enabling critical consciousness and meaningful societal change.
Finding Balance: Harmonizing Ideology and Praxis
Achieving a balanced interplay between ideology and praxis requires integrating theoretical principles with practical actions to ensure consistent and effective outcomes. Ideology provides the foundational framework guiding values and objectives, while praxis translates these ideals into real-world applications that address tangible challenges. Harmonizing ideology and praxis enhances adaptability, promotes critical reflection, and fosters sustained social or organizational transformation.
Ideology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com