Cyberculture shapes the way we interact, communicate, and create communities in the digital age, influencing social norms and behaviors online. Understanding the dynamics of cyberculture helps you navigate virtual spaces more effectively and be aware of its impact on society and individual identity. Explore the rest of the article to discover the key elements defining this digital phenomenon.
Table of Comparison
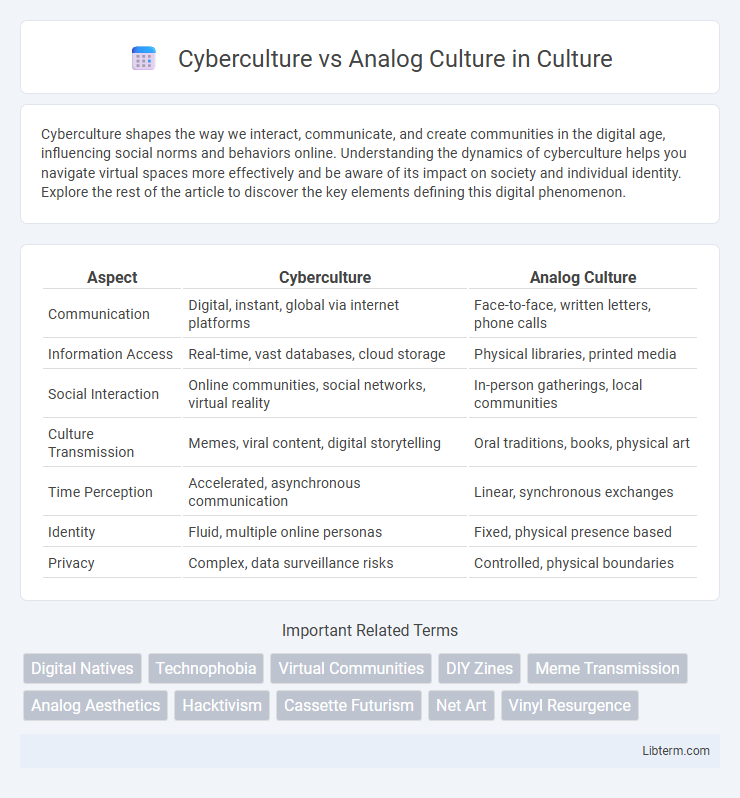
| Aspect | Cyberculture | Analog Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Digital, instant, global via internet platforms | Face-to-face, written letters, phone calls |
| Information Access | Real-time, vast databases, cloud storage | Physical libraries, printed media |
| Social Interaction | Online communities, social networks, virtual reality | In-person gatherings, local communities |
| Culture Transmission | Memes, viral content, digital storytelling | Oral traditions, books, physical art |
| Time Perception | Accelerated, asynchronous communication | Linear, synchronous exchanges |
| Identity | Fluid, multiple online personas | Fixed, physical presence based |
| Privacy | Complex, data surveillance risks | Controlled, physical boundaries |
Defining Cyberculture and Analog Culture
Cyberculture encompasses the social behaviors, practices, and norms emerging from digital technology use, emphasizing virtual communication, online communities, and digital identities. Analog culture refers to traditional, non-digital social interactions and media, relying on physical presence, face-to-face communication, and tangible artifacts. The distinction lies in cyberculture's integration with internet technologies versus analog culture's grounding in real-world, sensory experiences.
Historical Evolution of Cultural Mediums
The historical evolution of cultural mediums traces a shift from analog culture, characterized by physical media such as books, vinyl records, and face-to-face interactions, to cyberculture enabled by digital technologies like the internet, social media, and virtual reality. Analog culture relied on tangible artifacts and linear communication, while cyberculture emphasizes instant, networked, and interactive exchanges that transcend geographic boundaries. This transition reflects broader technological advancements impacting how societies create, share, and consume cultural content.
Communication Styles: Digital vs Physical
Cyberculture emphasizes rapid, text-based communication through digital platforms like social media, emails, and instant messaging, enabling instant global connectivity and asynchronous interactions. Analog culture relies on face-to-face conversations, physical gestures, and vocal tones, fostering deeper personal connections and non-verbal cues vital for emotional understanding. The contrast highlights digital communication's efficiency and reach versus analog communication's richness and immediacy in conveying meaning.
Social Interactions in Online and Offline Realms
Cyberculture transforms social interactions by enabling instant communication, global connectivity, and virtual communities that transcend physical boundaries, fostering diverse relationships and knowledge exchange. Analog culture emphasizes face-to-face interactions, nonverbal cues, and tangible experiences, which contribute to deeper emotional connections and shared physical presence. The shift between online and offline realms impacts social behavior patterns, influencing identity expression, empathy development, and community engagement in unique ways.
Influence of Technology on Daily Life
Cyberculture reshapes daily life by integrating digital technologies into communication, work, and social interactions, enhancing connectivity and information access. Analog culture emphasizes tactile experiences, face-to-face interactions, and slower information exchange, fostering personal connections and mindfulness. The influence of technology drives a transition from physical to virtual environments, impacting lifestyle, habits, and social dynamics globally.
Preservation and Loss of Tradition
Cyberculture transforms the preservation of tradition by digitizing artifacts, enabling global access and interactive reinterpretations while risking the dilution of original cultural contexts. Analog culture emphasizes physical, direct engagement with traditions, preserving authenticity through tactile experiences but faces challenges in accessibility and vulnerability to degradation over time. The tension between digital preservation and the potential loss of embodied cultural nuances highlights the need for hybrid approaches that safeguard both innovation and heritage integrity.
Creativity and Artistic Expression in Both Cultures
Cyberculture fosters creativity and artistic expression through digital tools, virtual spaces, and interactive media, enabling artists to experiment with multimedia and global collaboration. Analog culture emphasizes tactile techniques, traditional craftsmanship, and physical media, nurturing skills grounded in manual processes and materiality. Both cultures enrich artistic diversity by offering distinct methods for innovation and cultural storytelling.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Cyberculture intensifies privacy and security concerns through pervasive data collection, surveillance, and digital tracking, raising risks of identity theft and unauthorized access. Analog culture relies on physical privacy safeguards, presenting fewer digital vulnerabilities but limited in scalability and real-time data control. The shift from analog to cyberculture demands robust encryption, user education, and regulatory frameworks to mitigate evolving cyber threats.
Impact on Education and Learning Methods
Cyberculture has revolutionized education by facilitating digital learning platforms, interactive multimedia resources, and instant access to global information, enhancing student engagement and personalized learning experiences. Analog culture, rooted in traditional classroom settings and physical textbooks, emphasizes face-to-face interaction and hands-on activities, which foster deep social connections and tactile learning. The integration of cyberculture in education promotes adaptive learning methodologies, increased collaboration, and expanded accessibility, transforming conventional pedagogical approaches and knowledge acquisition.
Future Trends: Blending Cyber and Analog Worlds
Future trends indicate a seamless integration of cyberculture and analog culture, where digital interfaces enhance physical experiences through augmented reality and smart environments. Hybrid spaces will merge tactile analog elements with virtual connectivity, fostering new social interactions and cultural expressions. Emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G connectivity will drive this convergence, enabling real-time data exchange between cyber and analog realms.
Cyberculture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com