Chronemics, the study of how time influences communication, reveals how cultural attitudes towards punctuality and time management shape interactions. Understanding chronemics can enhance your ability to interpret nonverbal cues and improve relationship dynamics in both personal and professional settings. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering chronemics can transform your communication skills.
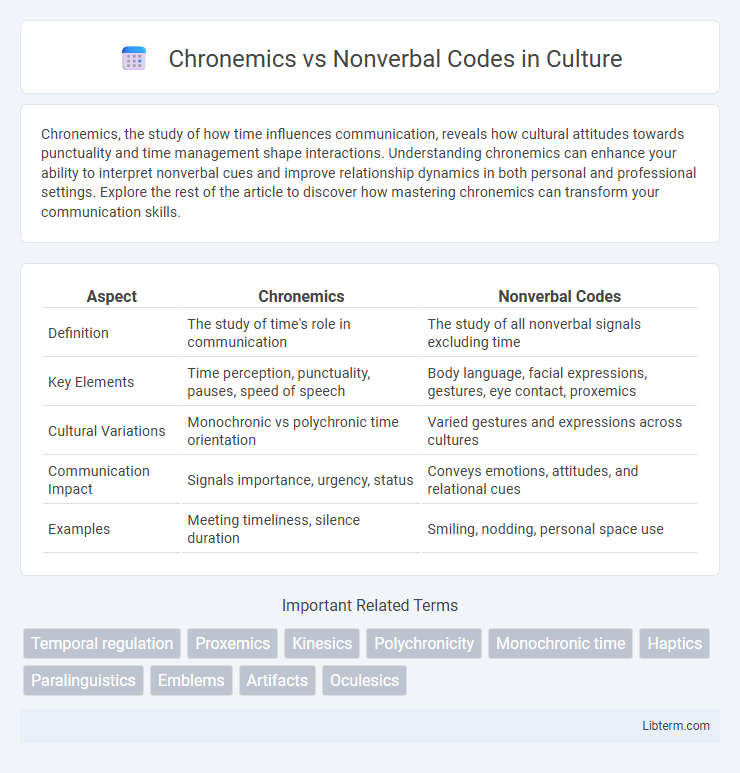
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Chronemics | Nonverbal Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The study of time's role in communication | The study of all nonverbal signals excluding time |
| Key Elements | Time perception, punctuality, pauses, speed of speech | Body language, facial expressions, gestures, eye contact, proxemics |
| Cultural Variations | Monochronic vs polychronic time orientation | Varied gestures and expressions across cultures |
| Communication Impact | Signals importance, urgency, status | Conveys emotions, attitudes, and relational cues |
| Examples | Meeting timeliness, silence duration | Smiling, nodding, personal space use |
Introduction to Chronemics and Nonverbal Codes
Chronemics, a key branch of nonverbal communication, studies how humans perceive and utilize time in interactions, influencing meanings through punctuality, pace, and timing. Nonverbal codes encompass various systems such as kinesics (body language), proxemics (personal space), haptics (touch), and chronemics, collectively shaping social communication beyond words. Understanding chronemics within nonverbal codes reveals how temporal behavior affects interpersonal dynamics, cultural norms, and message interpretation.
Defining Chronemics in Communication
Chronemics explores how time influences communication, examining the use of punctuality, tempo, and timing as nonverbal cues that shape interactions. It highlights the cultural variations in perceiving and valuing time, such as monochronic versus polychronic time orientations. Understanding chronemics enhances interpretation of communication patterns and improves interpersonal effectiveness by recognizing time's role as a dynamic nonverbal code.
Overview of Nonverbal Codes
Nonverbal codes encompass a range of communication methods including kinesics (body language), proxemics (use of space), haptics (touch), and chronemics (time). These codes convey emotions, intentions, and social cues without spoken words, playing a critical role in interpersonal communication. Understanding nonverbal codes enhances interpretation of underlying messages beyond verbal content.
Key Differences Between Chronemics and Other Nonverbal Codes
Chronemics specifically studies the role of time in communication, analyzing how punctuality, waiting times, and the pacing of interactions influence social dynamics. Other nonverbal codes encompass a broader range of behaviors such as kinesics (body language), proxemics (personal space), and haptics (touch), which convey meaning through physical gestures and spatial relationships rather than temporal factors. Unlike these other codes, chronemics is unique in emphasizing time-based cues as critical markers of cultural norms and interpersonal communication styles.
The Role of Time in Human Interaction
Chronemics examines how the perception and use of time influence communication, highlighting its critical role in structuring interactions and conveying social messages. In contrast, nonverbal codes encompass a broader range of signals, including body language, facial expressions, and proxemics, which complement temporal cues to enhance understanding. Cultural variations in chronemics shape punctuality, conversational pacing, and turn-taking, directly impacting relationship dynamics and communication effectiveness.
How Nonverbal Codes Influence Communication
Nonverbal codes, including facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact, play a crucial role in shaping communication by conveying emotions and attitudes beyond spoken words. Chronemics, a subcategory of nonverbal communication, focuses specifically on time-related behaviors such as punctuality and conversational pacing, influencing perceptions of respect and engagement. These nonverbal signals often regulate interaction flow and provide context that can enhance or contradict verbal messages, making them essential for accurate interpretation in interpersonal communication.
Cultural Variations in Chronemics
Chronemics, the study of time perception in communication, varies significantly across cultures influencing behaviors and social interactions. In monochronic cultures like the United States and Germany, punctuality and strict scheduling dominate, reflecting a linear time orientation. Polychronic cultures such as those in Latin America and the Middle East prioritize relationships over adherence to schedules, demonstrating a flexible approach to time that affects communication styles and expectations.
Interplay Between Chronemics and Nonverbal Signals
Chronemics, the study of time in communication, interacts dynamically with nonverbal codes such as gestures, posture, and facial expressions to convey meaning beyond words. The pace, timing, and duration of nonverbal signals influence interpersonal impressions, controlling turn-taking and emphasizing messages in social and professional contexts. Understanding this interplay enhances communication effectiveness by aligning temporal cues with body language to reinforce intent and emotional tone.
Real-World Examples of Chronemics vs Nonverbal Codes
In cross-cultural business meetings, chronemics manifests through punctuality differences; for example, German professionals prioritize strict adherence to schedules, while Latin American counterparts may exhibit more flexible time perceptions. Nonverbal codes such as eye contact and gestures vary similarly--Japanese participants often use minimal eye contact as a sign of respect, contrasting with the direct gaze common in Western cultures. These real-world examples highlight how chronemics and nonverbal communication shape interpersonal interactions and influence the interpretation of intent across diverse cultural contexts.
Implications for Effective Interpersonal Communication
Chronemics, the study of time use in communication, influences how punctuality and time management affect interpersonal dynamics, signaling respect or disrespect in various cultural contexts. Nonverbal codes, encompassing facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact, complement verbal messages by conveying emotions and intentions more authentically. Understanding the interplay between chronemics and other nonverbal cues is crucial for enhancing clarity, building trust, and avoiding misinterpretations in effective interpersonal communication.
Chronemics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com