Eurocentrism prioritizes European culture, history, and values as the universal standard, often marginalizing non-European perspectives and contributions. This worldview shapes education, media, and global narratives, influencing how societies understand identity and power. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Eurocentrism impacts global understanding and your perception of history.
Table of Comparison
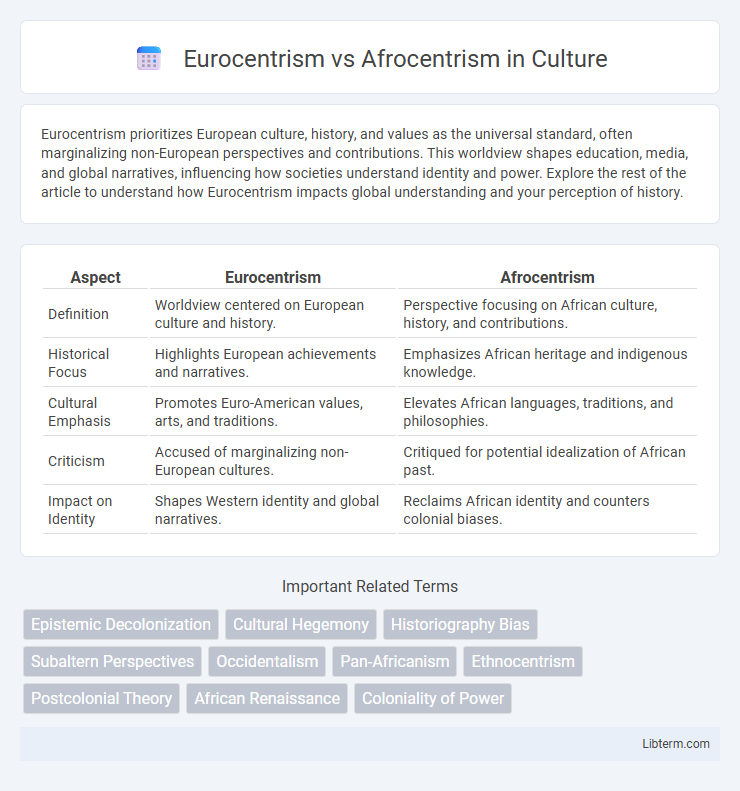
| Aspect | Eurocentrism | Afrocentrism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Worldview centered on European culture and history. | Perspective focusing on African culture, history, and contributions. |
| Historical Focus | Highlights European achievements and narratives. | Emphasizes African heritage and indigenous knowledge. |
| Cultural Emphasis | Promotes Euro-American values, arts, and traditions. | Elevates African languages, traditions, and philosophies. |
| Criticism | Accused of marginalizing non-European cultures. | Critiqued for potential idealization of African past. |
| Impact on Identity | Shapes Western identity and global narratives. | Reclaims African identity and counters colonial biases. |
Defining Eurocentrism and Afrocentrism
Eurocentrism centers historical narratives and cultural values on European experiences, often marginalizing non-European perspectives in disciplines like history and sociology. Afrocentrism challenges this by re-centering African experiences and contributions in global history, emphasizing the significance of African culture, heritage, and influence. The dialectic between Eurocentrism and Afrocentrism highlights contrasting frameworks for interpreting world history and cultural identity.
Historical Roots of Eurocentrism
Eurocentrism originated during the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods, emphasizing European culture as the pinnacle of civilization while marginalizing non-European histories. This worldview was reinforced by colonialism and the transatlantic slave trade, which positioned Europe as a global hegemon shaping historical narratives. Scholars critique Eurocentrism for distorting global history by prioritizing European experiences and ignoring indigenous African contributions and perspectives.
The Emergence of Afrocentrism
Afrocentrism emerged in the late 20th century as a response to Eurocentric historical narratives that marginalized African contributions and perspectives. Scholars like Molefi Kete Asante emphasized the importance of centering African culture, history, and identity to counteract colonial and racist ideologies. This intellectual movement reclaims African heritage by revising historical discourse and promoting a more balanced global cultural understanding.
Key Differences Between Eurocentrism and Afrocentrism
Eurocentrism centers Western European history, culture, and values as the universal standard, often marginalizing non-European perspectives and contributions. Afrocentrism emphasizes African history, culture, and identity, challenging Eurocentric narratives by asserting the importance of African civilizations and their global influence. The key difference lies in Eurocentrism's prioritization of European dominance versus Afrocentrism's goal to reframe history from an African-centered viewpoint.
Impact on Historical Narratives
Eurocentrism shapes historical narratives by centering European experiences and contributions, often marginalizing or oversimplifying African histories and cultures. Afrocentrism challenges this by reasserting African agency, emphasizing indigenous knowledge systems, achievements, and perspectives that have been historically neglected. This shift influences educational curricula, cultural identity, and global understandings of history, promoting a more balanced and inclusive interpretation of the past.
Influence on Education and Curriculum
Eurocentrism in education often prioritizes Western history, literature, and cultural achievements, shaping curricula that marginalize non-European perspectives and contributions. Afrocentrism challenges this by centering African civilizations, histories, and philosophies, promoting a more inclusive and accurate representation of global knowledge. Incorporating Afrocentric perspectives diversifies learning materials, enhances cultural awareness, and addresses systemic biases in traditional Eurocentric curricula.
Representation in Media and Literature
Eurocentrism dominates media and literature by centering European perspectives and often marginalizing non-European cultures, impacting global narratives and cultural perceptions. Afrocentrism challenges this imbalance by promoting African history, voices, and cultural contributions, seeking to reshape representation in literature, film, and art to reflect African identities authentically. Increased Afrocentric representation influences diverse storytelling, fostering cultural pride and offering counter-narratives to Eurocentric historical dominance.
Eurocentrism and Global Power Dynamics
Eurocentrism centers European history and values as universal, shaping global power dynamics by influencing political, economic, and cultural institutions worldwide. This worldview often marginalizes non-European perspectives, reinforcing Western dominance in international relations and global governance. The persistence of Eurocentric narratives impacts education, media, and policy, perpetuating unequal power structures in the modern global order.
Afrocentrism’s Role in Cultural Identity
Afrocentrism plays a crucial role in reclaiming African heritage and countering the dominant narrative shaped by Eurocentrism, which often marginalizes African contributions to history and culture. By centering African perspectives, Afrocentrism fosters a sense of pride, unity, and identity among people of African descent, emphasizing indigenous knowledge, traditions, and achievements. This approach not only challenges historical biases but also promotes cultural empowerment and social cohesion within the African diaspora.
Toward a Pluralistic Worldview
Eurocentrism prioritizes Western perspectives and histories, often marginalizing non-European cultures, while Afrocentrism seeks to re-center African experiences and contributions within global narratives. Toward a pluralistic worldview, embracing multiple cultural epistemologies fosters mutual respect and deeper understanding across diverse societies. This approach challenges hegemonic narratives and promotes a more inclusive, balanced representation of global histories and identities.
Eurocentrism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com