Socialization shapes your ability to interact effectively with others by teaching essential social norms and communication skills. It influences personal development, emotional intelligence, and the formation of meaningful relationships throughout life. Explore the rest of this article to understand how socialization impacts various aspects of your daily interactions and growth.
Table of Comparison
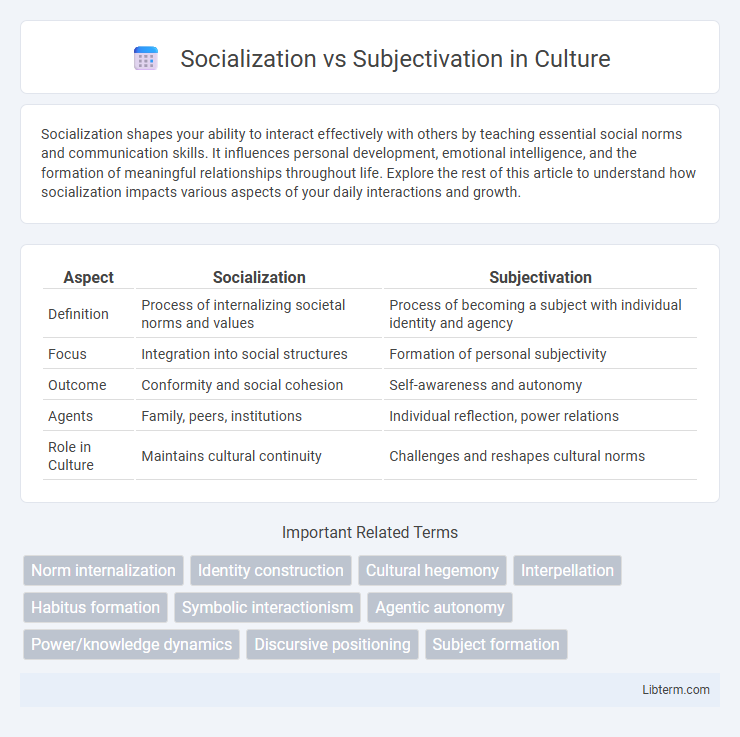
| Aspect | Socialization | Subjectivation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of internalizing societal norms and values | Process of becoming a subject with individual identity and agency |
| Focus | Integration into social structures | Formation of personal subjectivity |
| Outcome | Conformity and social cohesion | Self-awareness and autonomy |
| Agents | Family, peers, institutions | Individual reflection, power relations |
| Role in Culture | Maintains cultural continuity | Challenges and reshapes cultural norms |
Introduction to Socialization and Subjectivation
Socialization is the process through which individuals internalize societal norms, values, and behaviors, enabling them to function effectively within their community. Subjectivation refers to the formation of individual identity and self-awareness as people actively interpret and negotiate social influences. Understanding both concepts is essential to grasp how personal identity and social integration co-develop within cultural and institutional contexts.
Defining Socialization: Concepts and Processes
Socialization refers to the dynamic process through which individuals internalize cultural norms, values, behaviors, and social roles essential for functioning within society. This process involves continuous interactions with family, peers, institutions, and media, shaping identity and social competence from childhood through adulthood. Key concepts include primary socialization, where foundational skills and norms are acquired, and secondary socialization, which adapts individuals to specific social environments and roles.
What is Subjectivation? Core Perspectives
Subjectivation refers to the process by which individuals become subjects through the internalization of social norms, power structures, and cultural meanings, shaping their identity and agency. Core perspectives on subjectivation emphasize Michel Foucault's concept of power relations and self-formation, highlighting how individuals actively produce their subjectivity within discursive frameworks. This contrasts with socialization, which primarily focuses on the passive absorption of societal roles and norms.
Historical Evolution of Socialization and Subjectivation
Socialization has historically evolved as the process through which individuals internalize societal norms, values, and roles, shaping their identity within a cultural framework. Subjectivation emerged later as a critical concept in philosophy and social theory, emphasizing the active formation of the self through power relations and personal agency within historical contexts. Key thinkers like Michel Foucault highlighted subjectivation's role in resistance and self-governance, marking a shift from passive social integration to dynamic self-constitution.
Key Theories and Thinkers
Socialization involves the process through which individuals internalize societal norms, heavily influenced by theorists like Emile Durkheim and George Herbert Mead, who emphasize the role of social institutions and symbolic interactionism. Subjectivation, rooted in Michel Foucault's work, highlights the formation of individual identity through power relations and self-formation within societal structures. Key distinctions arise as socialization stresses conformity and integration into society, while subjectivation focuses on the active, often critical, construction of the self.
Socialization Mechanisms: Family, School, and Media
Socialization mechanisms such as family, school, and media shape individual identity by transmitting cultural norms, values, and behaviors essential for social integration. Family acts as the primary agent, instilling foundational social skills and emotional frameworks, while schools formalize knowledge acquisition and promote civic responsibilities through structured curricula and peer interactions. Media influences socialization by providing diverse narratives and role models that impact perception, cultural understanding, and social roles, highlighting the dynamic interplay between individual experiences and societal expectations.
Subjectivation in Contemporary Society
Subjectivation in contemporary society emphasizes the process by which individuals actively construct their identities and subjectivities through personal experiences, social interactions, and power relations, contrasting traditional socialization that focuses on conforming to existing social norms. The digital age, globalization, and diverse cultural flows intensify subjectivation by enabling multiple identity formations and resistance to hegemonic structures. This dynamic highlights the importance of autonomy, reflexivity, and self-determination in shaping modern subjectivities within complex social frameworks.
Socialization vs Subjectivation: Major Differences
Socialization involves the process through which individuals internalize societal norms, values, and behaviors to function within a community, emphasizing conformity and social integration. Subjectivation, conversely, centers on the formation of individual subjectivity and self-awareness, highlighting personal agency and the development of unique identity beyond mere social roles. The major differences lie in socialization's focus on external adaptation to collective expectations versus subjectivation's emphasis on internal transformation and autonomous self-constitution.
Impacts on Identity Formation
Socialization shapes identity formation by instilling societal norms, values, and roles that individuals internalize to function within a community. Subjectivation influences identity through personal experiences and self-reflection, promoting autonomous identity construction beyond external expectations. The dynamic interplay between socialization and subjectivation determines the balance between conformity to social structures and the development of unique individual identity.
Future Trends and Implications
Future trends in socialization emphasize digital interactions and virtual communities, reshaping how individuals develop identities and social norms. Subjectivation increasingly involves personal agency in crafting self-concepts amid technological mediation and data-driven environments. These shifts imply a transformation in social dynamics where power, autonomy, and identity formation are negotiated through evolving digital infrastructures.
Socialization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com