Enculturation shapes how individuals learn and adopt the behaviors, values, and norms of their culture through direct and indirect social interactions. This lifelong process influences your identity, communication style, and societal roles, embedding cultural knowledge deeply within your worldview. Explore the rest of the article to discover how enculturation impacts daily life and intercultural understanding.
Table of Comparison
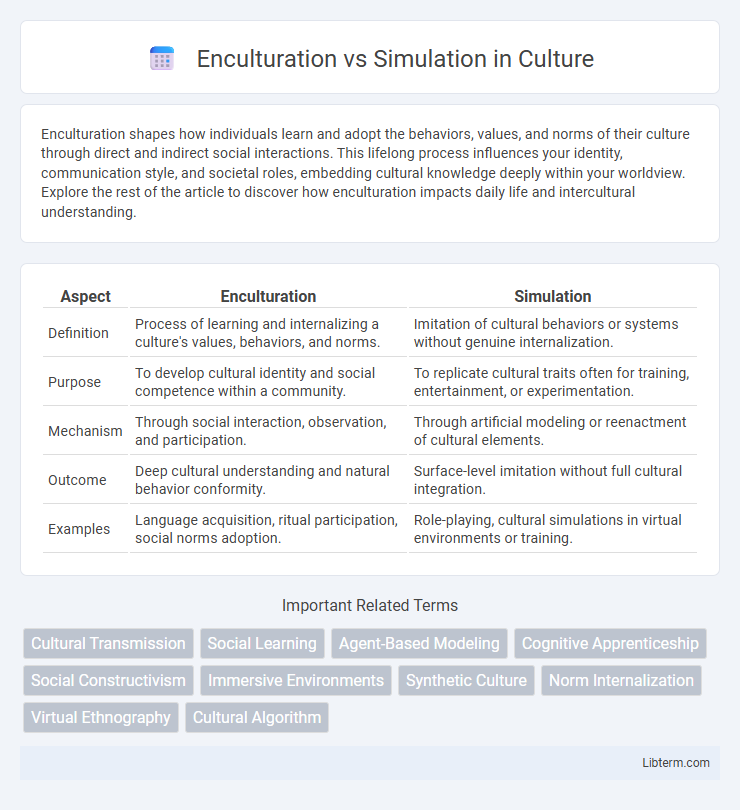
| Aspect | Enculturation | Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of learning and internalizing a culture's values, behaviors, and norms. | Imitation of cultural behaviors or systems without genuine internalization. |
| Purpose | To develop cultural identity and social competence within a community. | To replicate cultural traits often for training, entertainment, or experimentation. |
| Mechanism | Through social interaction, observation, and participation. | Through artificial modeling or reenactment of cultural elements. |
| Outcome | Deep cultural understanding and natural behavior conformity. | Surface-level imitation without full cultural integration. |
| Examples | Language acquisition, ritual participation, social norms adoption. | Role-playing, cultural simulations in virtual environments or training. |
Understanding Enculturation: Definition and Key Concepts
Enculturation refers to the process by which individuals learn and internalize the values, beliefs, customs, and social norms of their culture through direct and indirect experiences. Key concepts include socialization agents such as family, education, media, and peer groups that shape cultural knowledge and identity from early childhood onward. This foundational cultural learning contrasts with simulation, which involves artificially replicating cultural behaviors or environments without embedding authentic cultural understanding.
Defining Simulation: Foundations and Applications
Simulation involves creating virtual models that replicate real-world systems or processes, enabling detailed analysis and experimentation without physical risks. It serves as a foundational tool in fields such as engineering, healthcare, and education, facilitating strategic decision-making through predictive scenario testing. Applications range from flight simulators for pilot training to virtual patients in medical education, demonstrating its critical role in skill development and system optimization.
Historical Perspectives: Enculturation vs Simulation
Enculturation traces its origins to early anthropological studies emphasizing cultural transmission through socialization across generations, while simulation emerged from technological advancements in the 20th century, particularly in military and educational training contexts. Historical analysis reveals enculturation as a gradual, immersive learning process rooted in real-world interactions, contrasting with simulation's structured, often virtual environments designed to replicate specific scenarios for experiential learning. These divergent historical trajectories highlight enculturation's foundational role in shaping cultural identity, whereas simulation serves as a contemporary tool for skill acquisition and decision-making practice.
Cognitive Impacts: Learning Through Enculturation and Simulation
Enculturation shapes cognitive development by immersing individuals in cultural norms, language, and values, facilitating implicit learning and internalization over time. Simulation enhances cognitive skills by providing interactive, controlled environments that promote active problem-solving, experimentation, and immediate feedback, accelerating knowledge acquisition. Both methods contribute uniquely to cognitive growth, with enculturation fostering deep-rooted understanding and simulation enabling rapid, experiential learning.
Enculturation in Education and Socialization
Enculturation in education and socialization involves the gradual internalization of cultural norms, values, and behaviors through direct interaction and immersion within a cultural group, supporting identity formation and social cohesion. This process enables individuals to acquire language, customs, and social skills essential for participating effectively in their community and society. Enculturation contrasts with simulation, as it emphasizes authentic cultural experience rather than artificial or imitated learning environments.
Role of Simulation in Modern Training Environments
Simulation plays a critical role in modern training environments by providing immersive, interactive experiences that enhance skill acquisition and decision-making under realistic conditions. Advanced simulation technologies, such as virtual reality and augmented reality, enable trainees to practice complex scenarios without real-world risks, improving both competence and confidence. The effectiveness of simulation lies in its ability to replicate diverse cultural contexts, complementing enculturation processes and accelerating learning outcomes across various professional fields.
Comparing Real-World Experience and Virtual Learning
Enculturation involves acquiring cultural knowledge and social norms through direct real-world experiences, enabling deeper emotional connections and practical understanding of societal behaviors. Simulation in virtual learning environments provides immersive, controlled scenarios that foster skill development and problem-solving without real-world risks, but may lack the nuanced social cues found in authentic interactions. Comparing both, real-world enculturation offers rich, sensory engagement essential for comprehensive learning, while simulation enhances accessibility and repetitive practice in diverse contexts.
Technological Advances Influencing Simulation Practices
Technological advances such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) have revolutionized simulation practices by creating immersive, interactive environments that enhance experiential learning. High-fidelity simulators equipped with haptic feedback and AI-driven adaptive scenarios enable accurate replication of real-world conditions, improving skill acquisition and decision-making. These innovations contrast with traditional enculturation methods by accelerating knowledge transfer through technology-mediated practice rather than prolonged cultural immersion.
Cultural Transmission: Enculturation vs Simulated Experiences
Enculturation involves the natural process of cultural transmission through direct interaction, observation, and participation in a community, enabling individuals to internalize values, customs, and social norms. Simulated experiences, on the other hand, use virtual environments or role-playing to replicate cultural contexts, providing controlled, immersive opportunities for learning cultural behaviors without real-world immersion. Both methods contribute to cultural competence, but enculturation fosters authentic social integration, while simulation offers scalable, repeatable exposure to diverse cultural scenarios.
Future Trends: Integrating Enculturation and Simulation in Society
Future trends in integrating enculturation and simulation emphasize immersive technologies to enhance cultural learning and social adaptation. Virtual reality platforms enable realistic cultural experiences, promoting deeper understanding and empathy across diverse communities. The convergence of AI-driven simulations with traditional enculturation methods supports personalized education and effective societal integration in an increasingly digital world.
Enculturation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com