Totemism is a belief system where humans have a spiritual connection or kinship with a particular animal, plant, or natural object, often symbolized as a totem. This practice plays a significant role in anchoring social identity, cultural rituals, and ancestral lineage within many indigenous communities. Explore the rest of the article to understand how totemism shapes cultural heritage and personal identity.
Table of Comparison
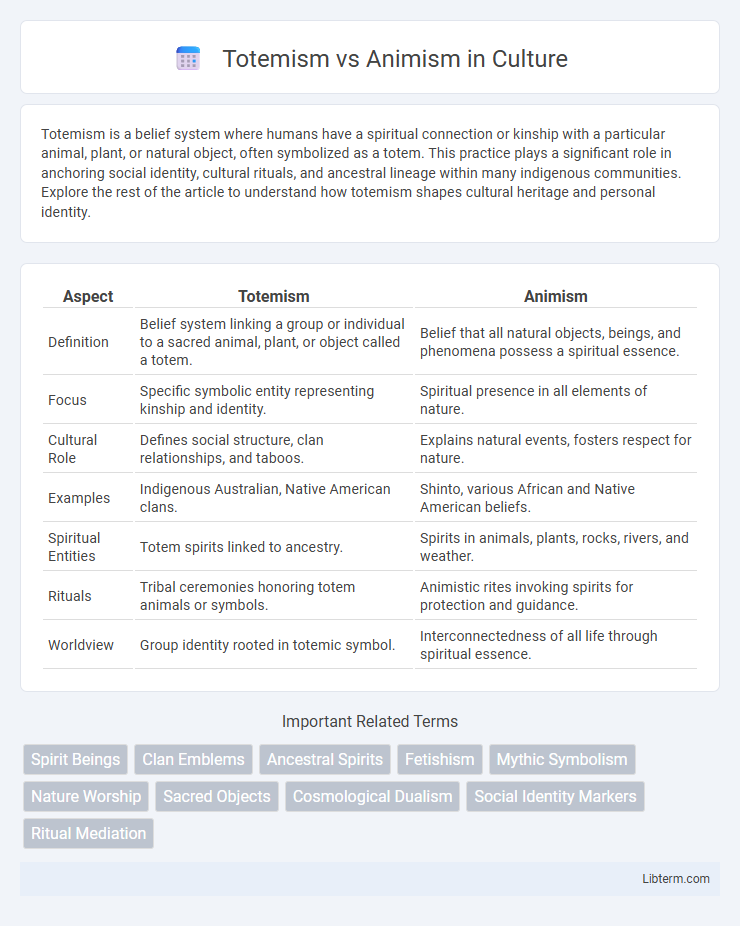
| Aspect | Totemism | Animism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief system linking a group or individual to a sacred animal, plant, or object called a totem. | Belief that all natural objects, beings, and phenomena possess a spiritual essence. |
| Focus | Specific symbolic entity representing kinship and identity. | Spiritual presence in all elements of nature. |
| Cultural Role | Defines social structure, clan relationships, and taboos. | Explains natural events, fosters respect for nature. |
| Examples | Indigenous Australian, Native American clans. | Shinto, various African and Native American beliefs. |
| Spiritual Entities | Totem spirits linked to ancestry. | Spirits in animals, plants, rocks, rivers, and weather. |
| Rituals | Tribal ceremonies honoring totem animals or symbols. | Animistic rites invoking spirits for protection and guidance. |
| Worldview | Group identity rooted in totemic symbol. | Interconnectedness of all life through spiritual essence. |
Introduction to Totemism and Animism
Totemism involves the belief in a mystical relationship between a group or individual and a specific animal, plant, or natural object serving as a totem, symbolizing identity and ancestry. Animism centers on the belief that all natural phenomena, including animals, plants, rocks, and rivers, possess a spiritual essence or soul. Both systems provide frameworks for interpreting human connections to nature, with totemism emphasizing lineage and clan identity, while animism highlights the pervasive spirituality in the natural world.
Defining Totemism: Concepts and Beliefs
Totemism centers on the symbolic relationship between humans and a specific animal, plant, or natural object known as the totem, which serves as an emblem of identity, lineage, and spiritual connection within a community. This belief system often encompasses rituals, taboos, and kinship ties that reinforce the sacred bond between the totem and its people. Unlike animism, which attributes spiritual essence to all entities, totemism emphasizes collective identity through a shared emblematic figure.
Understanding Animism: Core Principles
Animism centers on the belief that all natural objects, phenomena, and living beings possess a distinct spiritual essence or consciousness, fundamentally shaping human interaction with the environment. Core principles include the understanding that spirits inhabit trees, rivers, animals, and even inanimate objects, influencing health, fortune, and natural events. This spiritual interconnectedness fosters practices of respect, communication, and reciprocity between humans and the non-human world, differentiating animism from the more symbolic kinship associations found in totemism.
Historical Origins of Totemism and Animism
Totemism originated in ancient indigenous cultures, particularly among Australian Aboriginal and Native American tribes, where clans identified with specific animals or natural objects symbolizing spiritual connections and social identity. Animism dates back to prehistoric times, rooted in the belief that all living beings, natural phenomena, and inanimate objects possess a spiritual essence or soul. Both systems reflect early human attempts to explain the natural world and establish a relationship between humans, nature, and the divine.
Key Differences between Totemism and Animism
Totemism centers on symbolic relationships between groups or individuals and specific natural entities, like animals or plants, representing ancestral lineage or clan identity, while animism attributes spiritual essence to all entities in nature, including animals, plants, and inanimate objects. Totemism is often structured around social organization and collective identity, whereas animism emphasizes the presence of distinct spirits or souls within all elements of the natural world. Key differences include totemism's focus on hereditary symbols linked to social groups versus animism's broader spiritual recognition of all natural phenomena.
Similarities and Overlapping Aspects
Totemism and animism both emphasize a deep spiritual connection between humans and nature, recognizing living entities or natural elements as imbued with sacred significance or souls. Both belief systems often involve symbolic representations, such as totems or spirit animals, that serve as guides or protectors, reflecting an interconnectedness between humans and the environment. The overlapping aspects highlight a worldview where life forms and natural features possess intrinsic spiritual essence, fostering respect and reciprocal relationships within the ecosystem.
Totemism in Indigenous Cultures
Totemism in Indigenous cultures represents a profound spiritual connection between clans or groups and specific natural entities, such as animals, plants, or geographical features, symbolizing ancestral lineage and identity. This belief system establishes a framework for social organization, ecological stewardship, and ritual practices, embedding cultural values and history within the natural world. Unlike Animism, which attributes spiritual essence to all living and inanimate objects, Totemism centers on a particular emblematic figure that embodies the group's origin and moral guidelines.
Animistic Practices Around the World
Animistic practices around the world involve the belief that natural objects, animals, and plants possess a spiritual essence, influencing numerous indigenous cultures in Africa, Asia, and the Americas. Rituals often include offerings, dances, and ceremonies designed to communicate with or appease these spirits to ensure harmony and balance within the environment. These practices are deeply connected to community identity, environmental stewardship, and traditional healing methods.
Influence on Modern Spirituality and Society
Totemism and animism have profoundly influenced modern spirituality by shaping beliefs in the interconnectedness of humans, nature, and the spiritual world. Totemism's emphasis on symbolic animal or plant clans fosters a sense of identity and community, inspiring contemporary eco-spiritual movements and indigenous rights advocacy. Animism's recognition of sentient spirits in natural objects informs environmental ethics and holistic healing practices, reinforcing respect for biodiversity and sustainable living.
Conclusion: Comparing Worldviews of Totemism and Animism
Totemism and animism both emphasize the spiritual connection between humans and the natural world, yet totemism centers on symbolic relationships with specific clans or groups through animals or plants, while animism attributes a living spirit to all entities, including objects and places. Totemism structures social identity and kinship, often serving as a cultural emblem, whereas animism presents a broader, more pervasive spiritual worldview where every element of nature possesses consciousness. Understanding these distinctions highlights how indigenous belief systems interpret human-nature relationships, shaping diverse cultural practices and ecological ethics.
Totemism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com