Individualism emphasizes personal freedom, autonomy, and the importance of self-expression in shaping identity and achieving goals. It encourages you to prioritize your own values and beliefs while respecting others' rights to do the same. Discover how embracing individualism can enhance your life by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
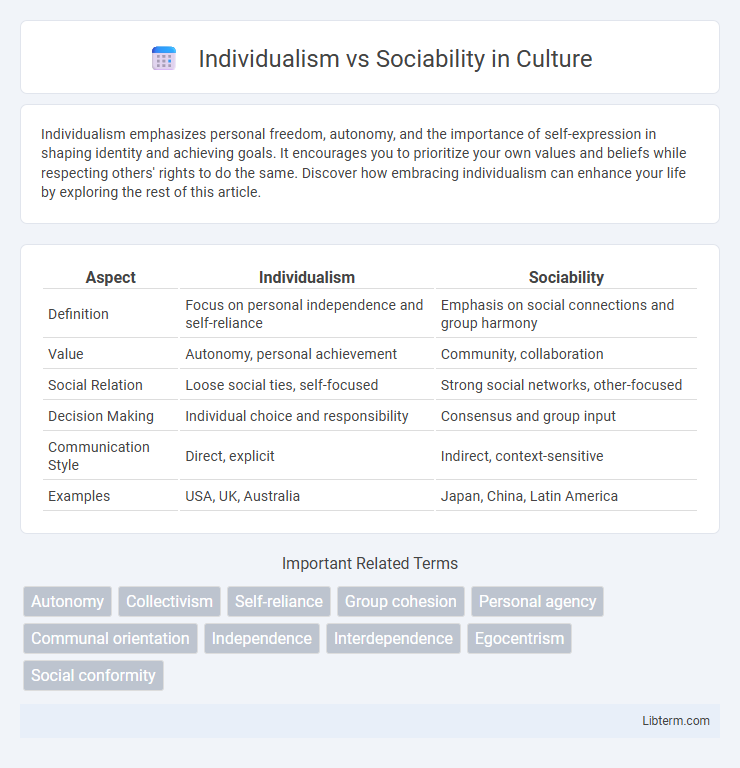
| Aspect | Individualism | Sociability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on personal independence and self-reliance | Emphasis on social connections and group harmony |
| Value | Autonomy, personal achievement | Community, collaboration |
| Social Relation | Loose social ties, self-focused | Strong social networks, other-focused |
| Decision Making | Individual choice and responsibility | Consensus and group input |
| Communication Style | Direct, explicit | Indirect, context-sensitive |
| Examples | USA, UK, Australia | Japan, China, Latin America |
Understanding Individualism: Core Concepts
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and the primacy of individual rights over collective goals, shaping social behavior and decision-making. Core concepts include personal freedom, independence, and the pursuit of individual happiness as central to identity and success. This philosophy contrasts with sociability, which values social bonds, cooperation, and group cohesion as essential for well-being.
Defining Sociability: The Essence of Social Connection
Sociability embodies the innate human capacity to engage, communicate, and form meaningful relationships within communities, driving social cohesion and collective well-being. It emphasizes adaptability in various social contexts, fostering empathy, cooperation, and mutual support essential for societal growth. Understanding sociability reveals its critical role in balancing individualism, as social bonds influence identity, behavior, and emotional health.
Historical Perspectives: How Cultures Shaped Values
Historical perspectives reveal that individualism flourished in Western cultures influenced by Enlightenment ideals emphasizing personal freedom and self-expression. In contrast, collectivist societies, particularly in East Asia, prioritized sociability and group harmony, shaped by Confucian principles valuing family and community cohesion. These cultural foundations continue to shape divergent values, impacting social behavior and interpersonal relationships worldwide.
Psychological Impacts of Individualism
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-reliance, often leading to heightened self-esteem and a strong sense of identity. However, excessive individualism can increase feelings of loneliness, social isolation, and stress due to weakened community connections. Psychological impacts include greater vulnerability to anxiety and depression as societal support networks diminish.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Sociability
Sociability fosters strong interpersonal connections, enhancing emotional support and collaboration in various social and professional settings. It promotes empathy, communication skills, and community engagement, which contribute to improved mental health and collective problem-solving. However, excessive sociability can lead to dependency, distraction, and potential conformity, potentially undermining personal autonomy and individual decision-making.
Individualism vs. Sociability in the Modern Workplace
Individualism in the modern workplace emphasizes personal achievement, autonomy, and self-reliance, often driving innovation and competitive performance. Sociability prioritizes collaboration, communication, and interpersonal relationships, fostering teamwork and a supportive work environment. Balancing individualism with sociability enhances productivity by combining independent problem-solving with collective effort and mutual support.
Family Dynamics: Balancing Self and Community
Individualism in family dynamics emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, fostering independence among members. Sociability prioritizes interdependence and collective support, strengthening emotional bonds within the household. Balancing these elements promotes healthy relationships where personal growth coexists with communal harmony.
Education Systems: Promoting Independence or Collaboration
Education systems that emphasize individualism prioritize personal achievement, critical thinking, and self-reliance, fostering students' ability to work independently and develop unique problem-solving skills. Conversely, education models centered on sociability promote collaboration, teamwork, and communication skills, preparing students for cooperative environments and collective decision-making processes. Balancing individual learning goals with group activities enhances cognitive flexibility and social competence, crucial for adapting to diverse professional and social contexts.
Technology’s Influence on Individual and Social Behavior
Technology has reshaped individualism by enabling personalized experiences and self-expression through digital platforms, fostering greater autonomy in identity formation. Simultaneously, social behavior adapts as online connectivity facilitates expansive social networks, enhances collaboration, and transforms communication patterns. The interplay between technology and behavior highlights a dynamic tension where digital tools both empower individual agency and redefine collective social interactions.
Finding Harmony: Integrating Individualism and Sociability
Balancing individualism and sociability requires embracing personal autonomy while fostering meaningful social connections that enhance mutual understanding and cooperation. Cultivating self-awareness alongside empathy promotes environments where unique perspectives enrich group dynamics without suppressing individuality. This integration supports psychological well-being and strengthens community resilience through respectful collaboration and authentic self-expression.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com