Project-Based Learning (PBL) immerses students in hands-on projects that foster critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills, making education more engaging and effective. This approach bridges theory and practice by encouraging learners to apply knowledge in meaningful, context-driven activities that enhance retention and understanding. Explore this article to discover how PBL can transform Your educational experience and unlock new opportunities for growth.
Table of Comparison
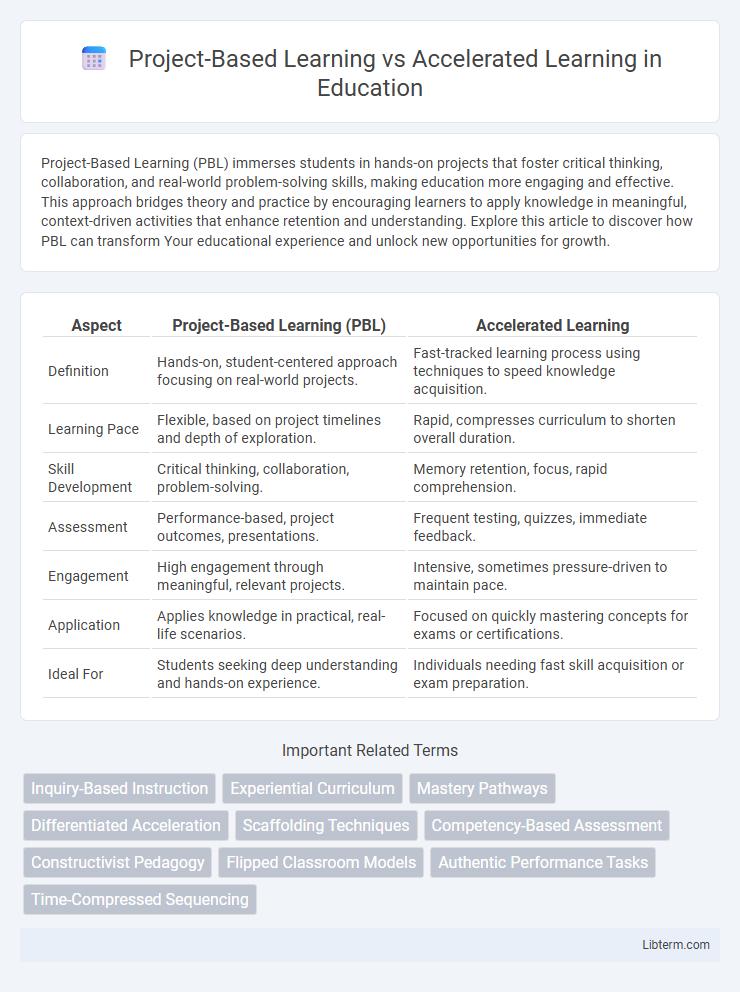
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Accelerated Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hands-on, student-centered approach focusing on real-world projects. | Fast-tracked learning process using techniques to speed knowledge acquisition. |
| Learning Pace | Flexible, based on project timelines and depth of exploration. | Rapid, compresses curriculum to shorten overall duration. |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, collaboration, problem-solving. | Memory retention, focus, rapid comprehension. |
| Assessment | Performance-based, project outcomes, presentations. | Frequent testing, quizzes, immediate feedback. |
| Engagement | High engagement through meaningful, relevant projects. | Intensive, sometimes pressure-driven to maintain pace. |
| Application | Applies knowledge in practical, real-life scenarios. | Focused on quickly mastering concepts for exams or certifications. |
| Ideal For | Students seeking deep understanding and hands-on experience. | Individuals needing fast skill acquisition or exam preparation. |
Understanding Project-Based Learning: Definition and Core Principles
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional methodology centered on engaging students in real-world projects to foster deep understanding and critical thinking skills. Core principles of PBL include sustained inquiry, student-driven collaboration, authentic problem-solving, and reflective assessment that connects academic content with practical application. This approach encourages active learning by allowing students to explore complex questions and produce meaningful outcomes over an extended period.
What is Accelerated Learning? Key Features and Methods
Accelerated Learning is an educational approach designed to speed up the acquisition of knowledge and skills by combining cognitive, emotional, and physical learning processes. Key features include multisensory engagement, collaborative activities, and the use of mnemonic devices to enhance memory retention. Methods often involve immersive simulations, spaced repetition, and active problem-solving to optimize learning efficiency and deepen understanding.
Comparative Overview: PBL vs Accelerated Learning Approaches
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes hands-on, real-world problem solving through extended projects that develop critical thinking and collaboration skills, fostering deep understanding and retention of subject matter. Accelerated Learning focuses on speeding up the acquisition of knowledge and skills using techniques like multi-sensory engagement, spaced repetition, and cognitive strategies to enhance memory and comprehension in a shorter time frame. While PBL promotes experiential, in-depth exploration of topics, Accelerated Learning aims to maximize efficiency and rapid mastery, making each approach suitable for different educational goals and learner needs.
Curriculum Design: Structuring for Project-Based vs. Accelerated Models
Curriculum design in Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers around organizing content into immersive, real-world projects that promote critical thinking and collaboration over extended periods. In contrast, Accelerated Learning designs curricula to cover key concepts rapidly through intensive, focused instruction and frequent assessments aimed at maximizing retention within shorter timelines. Both models require alignment of learning objectives and materials, but PBL emphasizes depth and integration, whereas Accelerated Learning prioritizes speed and efficiency in content delivery.
Learner Engagement: Motivating Students in Both Methods
Project-Based Learning boosts learner engagement by immersing students in real-world challenges that require active problem-solving and collaboration, fostering intrinsic motivation. Accelerated Learning enhances engagement through fast-paced, multi-sensory techniques and frequent feedback loops, keeping students mentally stimulated and focused. Both methods prioritize personalized learning experiences that increase motivation by aligning with learners' interests and cognitive rhythms.
Skill Development: Critical Thinking vs. Rapid Mastery
Project-Based Learning enhances critical thinking by engaging students in real-world problem solving, fostering deep analytical skills and creativity. Accelerated Learning emphasizes rapid mastery, enabling learners to quickly acquire and apply new skills through intensive, focused study techniques. Both methods contribute distinct advantages to skill development, with PBL cultivating long-term cognitive abilities and Accelerated Learning promoting swift competency acquisition.
Assessment Strategies: Evaluating Outcomes in Each Method
Project-Based Learning assessment strategies emphasize authentic evaluation through real-world tasks, using rubrics that measure critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Accelerated Learning relies on frequent formative assessments and diagnostic tests to quickly identify knowledge gaps and adjust instruction for rapid mastery. Both methods prioritize outcome-based evaluations, but Project-Based Learning centers on process and product quality, whereas Accelerated Learning focuses on speed and retention efficacy.
Applications in Diverse Educational Settings
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking and collaboration by engaging students in real-world problem-solving, making it ideal for diverse classrooms seeking contextualized knowledge. Accelerated Learning techniques speed up comprehension and retention through multisensory approaches and cognitive strategies, benefiting time-constrained programs or remedial education. Both methods adapt well across K-12, higher education, and adult learning environments, offering flexibility to meet varied learner profiles and institutional goals.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Approach
Project-Based Learning enhances critical thinking and collaboration skills by engaging students in real-world problem-solving, but it may require extensive resources and time management challenges. Accelerated Learning boosts knowledge retention and speeds skill acquisition through immersive, intensive techniques, yet it can overwhelm learners and may not suit all learning styles. Both methods offer tailored educational experiences, demanding careful consideration of student needs and instructional goals.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Project-Based Learning (PBL) and Accelerated Learning depends on factors such as learner goals, time constraints, and subject complexity. PBL is ideal for developing critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills, especially in long-term educational settings. Accelerated Learning suits learners needing rapid skill acquisition or exam preparation, emphasizing intensive, focused instruction and active engagement.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com