Cooperative learning enhances student engagement by promoting collaboration and shared responsibility in the classroom. This approach fosters critical thinking, communication skills, and deeper understanding of the material through peer interaction. Discover how cooperative learning can transform your educational experience by reading the full article.
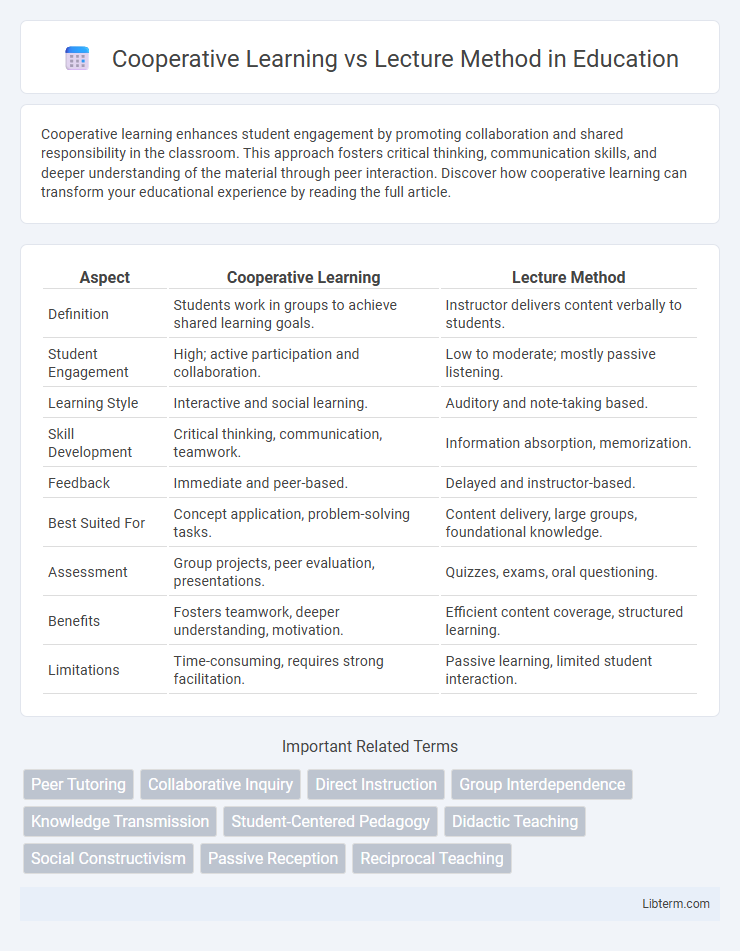
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cooperative Learning | Lecture Method |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students work in groups to achieve shared learning goals. | Instructor delivers content verbally to students. |
| Student Engagement | High; active participation and collaboration. | Low to moderate; mostly passive listening. |
| Learning Style | Interactive and social learning. | Auditory and note-taking based. |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, communication, teamwork. | Information absorption, memorization. |
| Feedback | Immediate and peer-based. | Delayed and instructor-based. |
| Best Suited For | Concept application, problem-solving tasks. | Content delivery, large groups, foundational knowledge. |
| Assessment | Group projects, peer evaluation, presentations. | Quizzes, exams, oral questioning. |
| Benefits | Fosters teamwork, deeper understanding, motivation. | Efficient content coverage, structured learning. |
| Limitations | Time-consuming, requires strong facilitation. | Passive learning, limited student interaction. |
Introduction to Cooperative Learning and Lecture Method
Cooperative Learning is an instructional strategy where students work in small groups to achieve shared learning goals, promoting active engagement, critical thinking, and social interaction. The Lecture Method involves a teacher-centered approach where information is delivered orally to students, emphasizing content transmission and note-taking. Both methods serve distinct educational purposes, with Cooperative Learning enhancing collaboration and deeper understanding while the Lecture Method efficiently conveys foundational knowledge to large groups.
Core Principles of Cooperative Learning
Cooperative Learning centers on core principles such as positive interdependence, individual accountability, and promotive interaction, fostering active student engagement and mutual support. This method contrasts with the Lecture Method, which primarily involves passive information delivery from teacher to students, limiting collaboration and interactive learning. Emphasizing group tasks that require shared responsibility enhances critical thinking, communication skills, and deeper understanding of subject matter.
Overview of the Lecture Method
The Lecture Method involves a structured, teacher-centered approach where information is delivered directly to students, emphasizing clarity and organization of content. This method allows efficient coverage of extensive material within limited class time, facilitating the transmission of expert knowledge and foundational concepts. While it supports large groups and ensures standardized instruction, it often limits student interaction and active engagement compared to cooperative learning techniques.
Student Engagement: Cooperative vs Lecture
Cooperative learning significantly enhances student engagement by promoting active participation, collaboration, and peer-to-peer interaction, which leads to deeper understanding and retention of material. The lecture method often results in passive learning, where students primarily absorb information without actively engaging, reducing motivation and attentiveness. Research shows that classrooms using cooperative learning strategies experience higher levels of student motivation, participation, and overall academic achievement compared to traditional lecture-based instruction.
Academic Achievement Outcomes
Cooperative learning significantly enhances academic achievement by promoting active engagement, critical thinking, and collaborative problem-solving among students, leading to deeper understanding and retention of material. In contrast, the lecture method often results in passive learning, limiting student interaction and reducing opportunities for immediate feedback, which can negatively impact knowledge acquisition and application. Empirical studies consistently demonstrate higher test scores and improved cognitive development in learners exposed to cooperative learning compared to traditional lectures.
Communication Skills Development
Cooperative learning enhances communication skills by promoting active dialogue, teamwork, and peer feedback, fostering critical listening and clear expression. The lecture method primarily delivers information passively, limiting opportunities for interactive communication practice. Studies show that cooperative learning environments significantly improve students' verbal interactions and collaborative problem-solving abilities compared to traditional lectures.
Teacher’s Role in Each Method
In cooperative learning, the teacher acts as a facilitator who guides student interaction, encourages collaboration, and monitors group progress to ensure active participation and shared responsibility. In contrast, the lecture method positions the teacher as the primary source of knowledge, delivering structured content while students primarily listen and take notes. The teacher's role in cooperative learning emphasizes fostering critical thinking and communication, whereas in lectures, the focus is on clear, organized information transmission.
Classroom Management Differences
Cooperative learning emphasizes student collaboration, requiring teachers to facilitate group dynamics and monitor peer interactions to maintain classroom order. In contrast, the lecture method centers on direct instruction, allowing for more controlled and teacher-directed management with less need for managing student interaction. Effective classroom management in cooperative learning involves strategies to balance active participation and minimize disruptions, while lecture settings rely on maintaining attention and minimizing off-task behavior during teacher-led presentations.
Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison
Cooperative learning enhances student engagement, promotes critical thinking, and improves communication skills by encouraging collaboration and peer interaction, but it may lead to unequal participation and longer time requirements for task completion. The lecture method efficiently delivers large amounts of information to many students simultaneously, providing structure and clarity; however, it often results in passive learning, limited student interaction, and reduced retention rates. Balancing these teaching strategies involves considering course objectives, student needs, and available resources to optimize learning outcomes.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Classroom
Cooperative learning enhances student engagement and critical thinking by promoting collaboration, making it ideal for classrooms aiming to develop social skills and deeper understanding. The lecture method efficiently delivers large amounts of information, best suited for content-heavy subjects requiring structured knowledge transmission. Selecting the right method depends on curriculum goals, class size, and learner needs, with a blended approach often providing balanced benefits.
Cooperative Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com