Traditional lectures remain a cornerstone of education, delivering structured content directly from instructor to student to foster foundational knowledge. This method emphasizes clear communication, active listening, and note-taking skills vital for academic success. Discover how traditional lectures can enhance your learning experience by exploring the benefits and strategies detailed in the rest of the article.
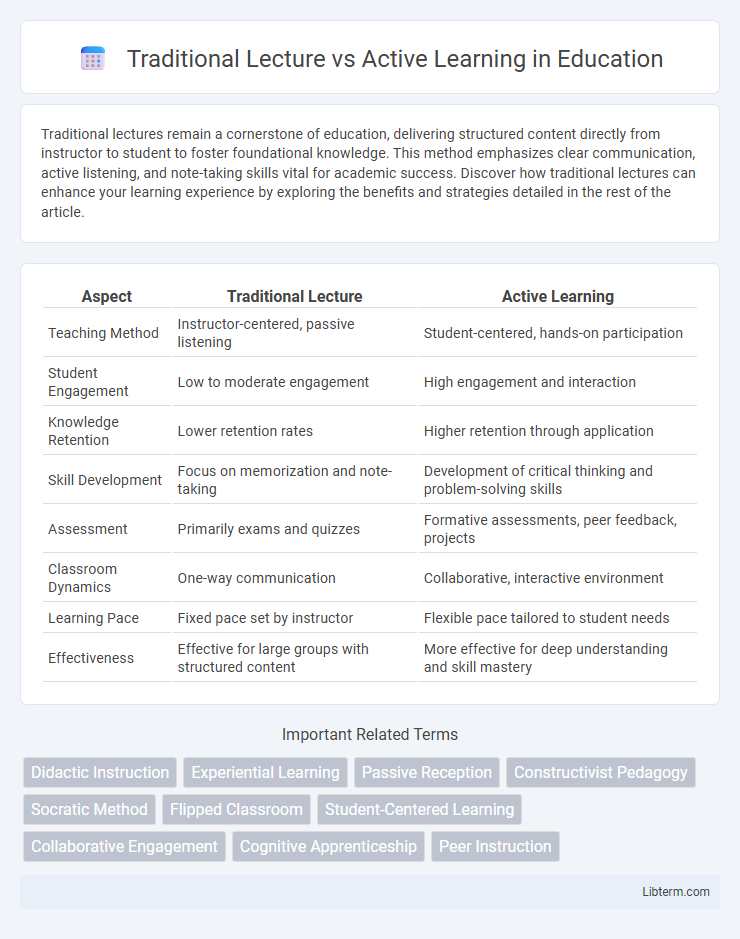
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Lecture | Active Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Method | Instructor-centered, passive listening | Student-centered, hands-on participation |
| Student Engagement | Low to moderate engagement | High engagement and interaction |
| Knowledge Retention | Lower retention rates | Higher retention through application |
| Skill Development | Focus on memorization and note-taking | Development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills |
| Assessment | Primarily exams and quizzes | Formative assessments, peer feedback, projects |
| Classroom Dynamics | One-way communication | Collaborative, interactive environment |
| Learning Pace | Fixed pace set by instructor | Flexible pace tailored to student needs |
| Effectiveness | Effective for large groups with structured content | More effective for deep understanding and skill mastery |
Introduction to Teaching Methods
Traditional Lecture involves passive knowledge transmission where the instructor delivers content while students listen, often limiting engagement and critical thinking. Active Learning emphasizes student participation through discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative activities, enhancing comprehension and retention in teaching methods. Research in education consistently shows that Active Learning improves student outcomes compared to Traditional Lecture formats.
Defining Traditional Lecture-Based Learning
Traditional lecture-based learning centers on the instructor delivering content directly to students through oral presentations, often with minimal student interaction or engagement. This method emphasizes passive reception of knowledge, where students primarily listen and take notes without frequent opportunities for hands-on practice or collaborative activities. Its structured format allows for efficient coverage of curriculum but may limit critical thinking and active participation.
What Is Active Learning?
Active learning emphasizes student participation through activities like group discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on exercises, fostering critical thinking and retention. Unlike traditional lectures that prioritize passive listening, active learning engages students in constructing knowledge and applying concepts in real-time. Research shows that active learning can improve student performance and increase understanding by encouraging interaction and immediate feedback.
Key Differences Between Lecture and Active Learning
Traditional lecture relies on passive information delivery where instructors speak, and students listen, often leading to limited engagement and retention. Active learning emphasizes student participation through discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative activities, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. Research shows active learning significantly improves academic performance and long-term knowledge retention compared to traditional lectures.
Advantages of Traditional Lecture Formats
Traditional lecture formats efficiently deliver large volumes of structured information to diverse classrooms, ensuring consistent coverage of curriculum content. This method leverages the instructor's expertise to guide learners through complex concepts with clear explanations and real-time clarification. Lectures also facilitate time management in educational settings, maximizing learning efficiency for foundational knowledge acquisition.
Benefits of Active Learning Approaches
Active learning approaches enhance student engagement and retention by encouraging critical thinking and collaboration through interactive activities. Research shows that active learning increases knowledge application and problem-solving skills compared to traditional lecture methods. This dynamic learning environment fosters deeper understanding and long-term academic performance improvement.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Traditional lecture methods often face challenges such as passive student engagement and limited opportunities for critical thinking, resulting in lower retention rates. Active learning, while promoting higher participation and deeper understanding, can encounter obstacles like time constraints, increased preparation demands for instructors, and potential discomfort among students unaccustomed to interactive formats. Both methods require strategic implementation to balance content delivery efficiency with meaningful student involvement for optimal educational outcomes.
Student Engagement and Participation Comparisons
Active learning significantly increases student engagement compared to traditional lectures by incorporating interactive activities such as group discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on experiments. Research shows that active learning environments boost participation rates and enhance retention by promoting critical thinking and collaboration. Traditional lectures often result in passive learning, leading to lower attention spans and minimal student involvement.
Impact on Learning Outcomes and Retention
Active learning significantly enhances learning outcomes and retention by engaging students in problem-solving, discussion, and hands-on activities, which promotes deeper understanding and long-term memory consolidation. Traditional lectures often lead to passive information absorption, resulting in lower retention rates and limited critical thinking skills. Studies indicate that students participating in active learning achieve higher exam scores and demonstrate improved knowledge application compared to those in lecture-based settings.
Choosing the Best Approach for Your Classroom
Evaluating the effectiveness of traditional lectures compared to active learning hinges on student engagement, retention, and comprehension metrics. Active learning strategies, such as collaborative projects and problem-solving tasks, consistently demonstrate higher retention rates and improved critical thinking skills across diverse educational settings. Tailoring the approach to classroom dynamics, including class size, subject complexity, and learner preferences, ensures optimized educational outcomes and maximized student participation.
Traditional Lecture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com