Project-Based Learning emphasizes hands-on experiences where students actively engage in solving real-world problems, fostering critical thinking and collaboration skills. This approach enhances retention and practical understanding by connecting academic concepts to tangible outcomes. Explore this article to discover how Your learning can be transformed through immersive, project-driven education.
Table of Comparison
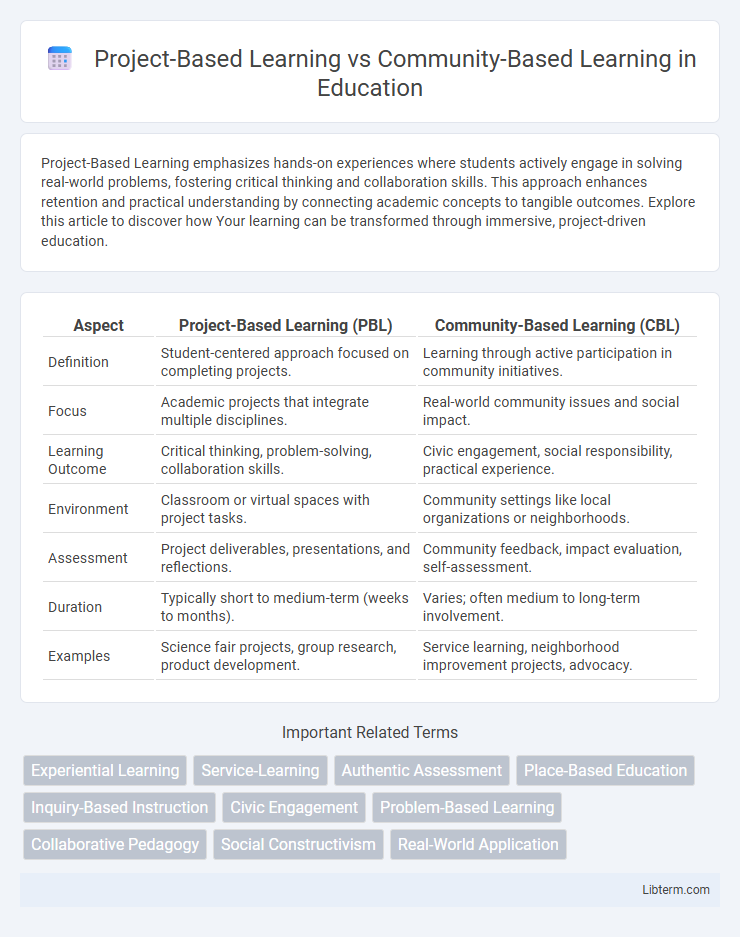
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Community-Based Learning (CBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach focused on completing projects. | Learning through active participation in community initiatives. |
| Focus | Academic projects that integrate multiple disciplines. | Real-world community issues and social impact. |
| Learning Outcome | Critical thinking, problem-solving, collaboration skills. | Civic engagement, social responsibility, practical experience. |
| Environment | Classroom or virtual spaces with project tasks. | Community settings like local organizations or neighborhoods. |
| Assessment | Project deliverables, presentations, and reflections. | Community feedback, impact evaluation, self-assessment. |
| Duration | Typically short to medium-term (weeks to months). | Varies; often medium to long-term involvement. |
| Examples | Science fair projects, group research, product development. | Service learning, neighborhood improvement projects, advocacy. |
Introduction to Project-Based and Community-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on students engaging in complex, real-world projects that foster critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Community-Based Learning (CBL) integrates academic curriculum with community service, emphasizing experiential learning and civic responsibility through direct involvement in local contexts. Both approaches enhance student engagement and practical knowledge by connecting education to meaningful, authentic experiences.
Defining Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional approach where students actively explore real-world problems and challenges over an extended period, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. This method emphasizes student-driven inquiry and the creation of tangible outcomes or products that demonstrate understanding and mastery of subjects. PBL contrasts with traditional learning by integrating interdisciplinary content and promoting deeper engagement through meaningful, hands-on projects.
Understanding Community-Based Learning
Community-Based Learning immerses students in real-world environments, promoting active engagement with local issues and stakeholders to enhance practical knowledge and social responsibility. This approach fosters deeper connections with the community by addressing authentic challenges, thereby developing critical thinking, collaboration, and civic awareness. Compared to Project-Based Learning, which centers on completing specific tasks or projects, Community-Based Learning emphasizes experiential education and meaningful participation within community contexts.
Core Differences Between Project-Based and Community-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning centers on students completing specific academic projects, emphasizing problem-solving, critical thinking, and knowledge application within a structured timeline. Community-Based Learning integrates real-world community issues, promoting civic engagement, collaboration with local organizations, and social responsibility development. The core difference lies in Project-Based Learning's focus on academic outcomes through structured tasks, while Community-Based Learning prioritizes social impact and active community participation.
Benefits of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration skills by engaging students in real-world projects that require active inquiry and application of knowledge. PBL promotes deeper understanding through hands-on experiences, fostering creativity and motivation as learners take ownership of their educational journey. This approach also improves academic performance and retention by linking curriculum content to practical, meaningful tasks that prepare students for future careers.
Advantages of Community-Based Learning
Community-Based Learning (CBL) enhances real-world engagement by immersing students in local issues, fostering practical problem-solving skills directly connected to their community. CBL promotes social responsibility and civic awareness by encouraging collaboration with diverse community members, which strengthens communication and teamwork abilities. This experiential approach often results in meaningful, lasting learning experiences that contribute to both personal growth and community development.
Challenges in Implementation
Project-Based Learning faces challenges such as ensuring equitable access to resources and maintaining student motivation throughout complex tasks. Community-Based Learning struggles with coordinating partnerships and aligning academic goals with diverse community needs. Both approaches demand significant time investment from educators for planning, assessment, and fostering meaningful engagement.
Assessment Strategies for Both Approaches
Assessment strategies in project-based learning (PBL) emphasize ongoing formative evaluations such as peer reviews, presentations, and reflective journals to gauge student understanding and skill development throughout the project lifecycle. Community-based learning (CBL) assessments prioritize real-world impact and social responsibility by incorporating community feedback, service deliverables, and holistic evaluations of learner engagement with community needs. Both approaches benefit from performance-based assessments but differ in focus: PBL centers on mastery of project goals, while CBL measures contributions to community outcomes and civic competence.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes hands-on projects such as designing sustainable gardens or developing coding applications, fostering problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Community-Based Learning (CBL) integrates real-world engagement, exemplified by students collaborating with local nonprofits to address social issues like food insecurity or urban development. Case studies reveal PBL enhances individual creativity and technical skills, while CBL strengthens civic responsibility and partnership with community stakeholders.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Educational Goals
Project-Based Learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world problem solving that fosters critical thinking and collaboration, ideal for developing technical skills and individual creativity. Community-Based Learning integrates local culture, social issues, and service, promoting civic engagement and empathy well-suited for building social responsibility and community awareness. Selecting the right approach depends on educational goals: choose Project-Based Learning for skill acquisition and innovation, or Community-Based Learning to enhance social consciousness and community impact.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com