Auditory learning focuses on absorbing information through listening, which enhances memory retention and comprehension for many individuals. Techniques such as listening to lectures, audio books, and engaging in discussions can significantly boost your learning efficiency. Discover effective strategies to harness auditory learning in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
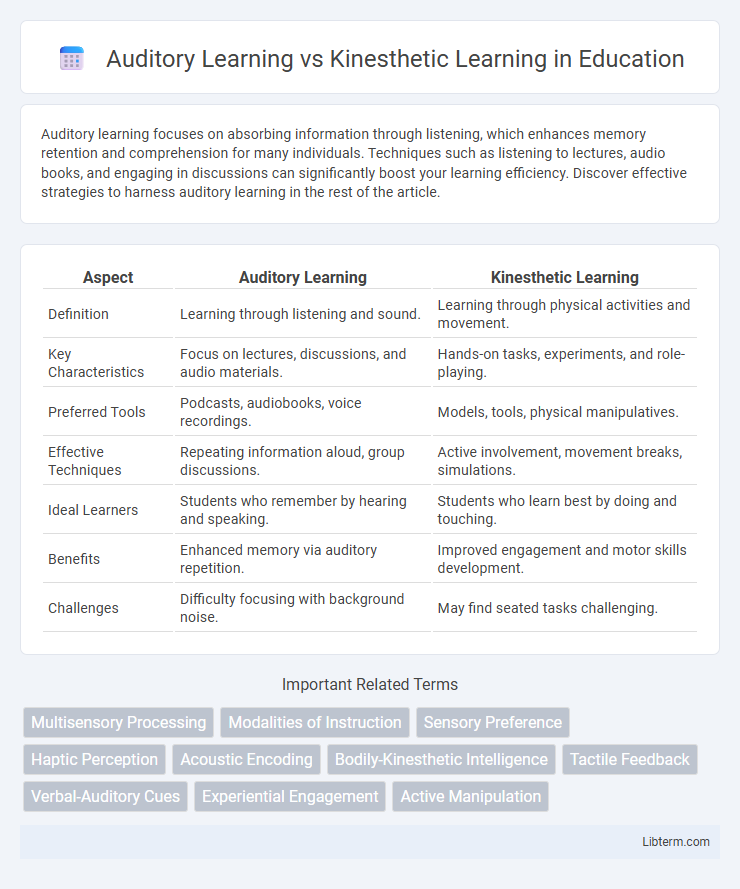
| Aspect | Auditory Learning | Kinesthetic Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through listening and sound. | Learning through physical activities and movement. |
| Key Characteristics | Focus on lectures, discussions, and audio materials. | Hands-on tasks, experiments, and role-playing. |
| Preferred Tools | Podcasts, audiobooks, voice recordings. | Models, tools, physical manipulatives. |
| Effective Techniques | Repeating information aloud, group discussions. | Active involvement, movement breaks, simulations. |
| Ideal Learners | Students who remember by hearing and speaking. | Students who learn best by doing and touching. |
| Benefits | Enhanced memory via auditory repetition. | Improved engagement and motor skills development. |
| Challenges | Difficulty focusing with background noise. | May find seated tasks challenging. |
Introduction to Learning Styles
Auditory learning emphasizes understanding and retaining information through listening, leveraging sounds, rhythms, and verbal instructions to enhance memory and comprehension. Kinesthetic learning relies on physical movement and hands-on activities, engaging muscle memory and tactile experiences to facilitate knowledge acquisition. Recognizing these distinct learning styles helps tailor educational approaches for improved student engagement and effectiveness.
What is Auditory Learning?
Auditory learning is a style in which individuals absorb and retain information more effectively through listening and hearing. This learning preference involves processing spoken words, sounds, and rhythms, making lectures, discussions, and audio materials highly beneficial. Auditory learners excel in environments with clear verbal instructions and often use repetition and vocalization to reinforce memory.
Key Characteristics of Auditory Learners
Auditory learners excel at processing information through listening and often remember details by hearing lectures, discussions, or audio materials. They prefer oral instructions and tend to benefit from repeating information aloud or engaging in group discussions to reinforce learning. Key characteristics include strong verbal skills, sensitivity to tone and sound nuances, and the ability to retain information through auditory patterns and rhythms.
What is Kinesthetic Learning?
Kinesthetic learning involves acquiring knowledge through physical activities and hands-on experiences, engaging the body's movement and tactile senses. This learning style helps individuals understand and retain information by actively doing rather than passively listening or observing. Kinesthetic learners excel in environments where they can manipulate objects, perform tasks, or engage in role-playing to reinforce concepts.
Distinctive Traits of Kinesthetic Learners
Kinesthetic learners exhibit a distinctive preference for hands-on activities and physical engagement, thriving through movement and tactile experiences that enhance memory retention and understanding. They often struggle with passive learning methods such as listening or reading but excel when they can manipulate objects or participate in interactive tasks. Their cognitive processing is closely linked to muscle memory and spatial awareness, making activities like role-playing, building models, or using gestures highly effective for reinforcing concepts.
Auditory vs Kinesthetic Learning: Core Differences
Auditory learning emphasizes the processing and retention of information through listening, making it effective for learners who grasp concepts best via sound, speech, and verbal instructions. Kinesthetic learning relies on physical movement and hands-on activities, enabling learners to understand and remember material through tactile experiences and motor skills. The core difference lies in sensory engagement: auditory learners depend on hearing, while kinesthetic learners prioritize bodily interaction to enhance comprehension and memory.
Benefits of Auditory Learning
Auditory learning enhances memory retention by engaging the brain through listening, making it easier to absorb information in lectures or audio materials. This learning style strengthens skills such as critical thinking and comprehension through verbal instructions and discussions. Auditory learners benefit from improved focus and the ability to process complex concepts by hearing explanations, which supports better academic and professional performance.
Advantages of Kinesthetic Learning
Kinesthetic learning offers significant advantages by engaging learners through physical activities, enhancing memory retention and understanding via hands-on experience. This approach supports improved motor skills development and caters to learners who struggle with traditional auditory or visual methods, making abstract concepts tangible. Kinesthetic learning also promotes active involvement, increasing motivation and boosting cognitive connections through movement and touch.
Strategies for Supporting Each Learning Style
Auditory learning strategies include using verbal instructions, engaging in discussions, and incorporating audio resources such as podcasts and recordings to enhance retention. Kinesthetic learners benefit from hands-on activities, physical movement during lessons, and interactive experiments that reinforce concepts through bodily engagement. Tailoring teaching methods to these learning styles improves comprehension and skill acquisition by aligning educational techniques with the learner's natural preferences.
Choosing the Right Approach: Auditory or Kinesthetic?
Choosing the right approach between auditory learning and kinesthetic learning depends on individual preferences and the nature of the material studied. Auditory learners benefit from listening to lectures, discussions, and audio materials, which enhance their retention and comprehension. Kinesthetic learners excel through hands-on activities, movement, and experiential tasks that engage their sense of touch and physical involvement for deeper understanding.
Auditory Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com