Survey research is a powerful method for collecting data directly from individuals to understand their opinions, behaviors, and preferences. By carefully designing questionnaires and sampling strategies, surveys can provide reliable and valid insights applicable across diverse populations. Discover how leveraging survey research can enhance your data-driven decisions by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
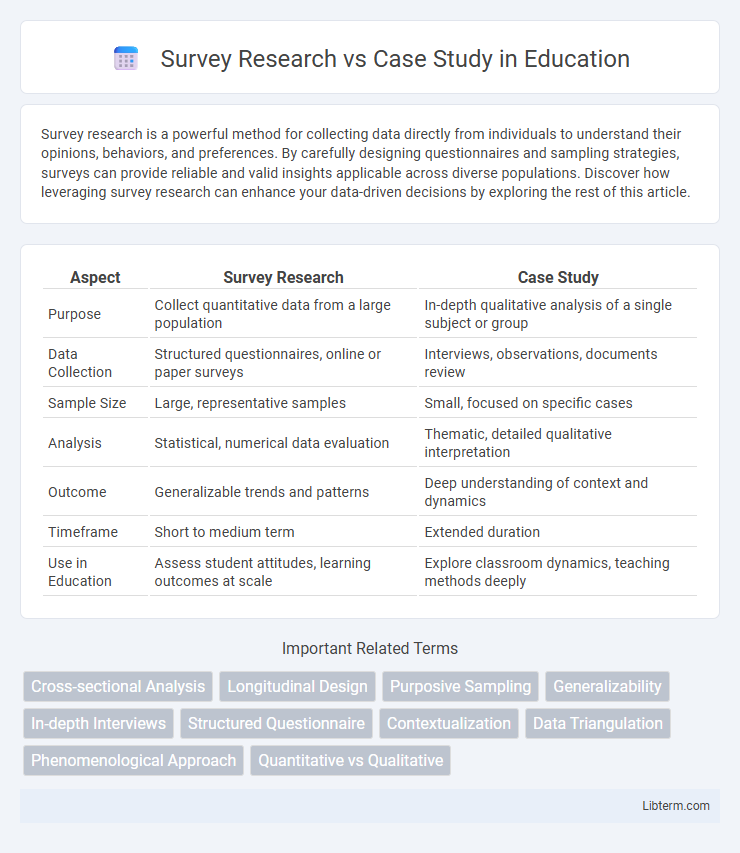
| Aspect | Survey Research | Case Study |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Collect quantitative data from a large population | In-depth qualitative analysis of a single subject or group |
| Data Collection | Structured questionnaires, online or paper surveys | Interviews, observations, documents review |
| Sample Size | Large, representative samples | Small, focused on specific cases |
| Analysis | Statistical, numerical data evaluation | Thematic, detailed qualitative interpretation |
| Outcome | Generalizable trends and patterns | Deep understanding of context and dynamics |
| Timeframe | Short to medium term | Extended duration |
| Use in Education | Assess student attitudes, learning outcomes at scale | Explore classroom dynamics, teaching methods deeply |
Introduction to Survey Research and Case Study
Survey research employs structured questionnaires to collect quantitative data from large populations, enabling statistical analysis and generalization of findings. Case study research involves an in-depth, qualitative examination of a single entity or bounded system, providing detailed contextual insights and understanding of complex phenomena. Both methods offer distinct approaches for data collection and analysis, with surveys emphasizing breadth and case studies focusing on depth.
Key Differences Between Survey Research and Case Study
Survey research collects quantitative data from large, diverse populations using structured questionnaires to identify trends and generalize findings. Case studies provide in-depth, qualitative analysis of a single subject or small group, offering detailed contextual understanding and exploring complex phenomena. The primary difference lies in survey research's breadth and generalizability versus case study's depth and contextual richness.
Definition and Scope of Survey Research
Survey research involves collecting quantitative data from a predefined group of respondents using structured questionnaires to generalize findings across larger populations. Its scope encompasses measuring attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and characteristics within diverse fields such as social sciences, marketing, and health studies. In contrast, case study research emphasizes in-depth qualitative analysis of a single subject or a small group to explore complex phenomena within their real-life contexts.
Definition and Scope of Case Study
A case study is an in-depth, contextual analysis of a single unit such as an individual, group, organization, or event, designed to explore complex phenomena within real-life settings. Unlike survey research that collects quantitative data from large samples to generalize findings, case studies provide detailed qualitative insights and understanding of specific instances or processes. The scope of a case study involves exploring boundaries and interactions within the case, highlighting unique characteristics and underlying mechanisms that surveys may overlook.
Data Collection Methods in Survey Research
Survey research primarily utilizes structured questionnaires and standardized interviews to collect quantitative data from large, diverse populations, ensuring broad generalizability. Data collection methods often include online surveys, telephone interviews, and face-to-face questionnaires, which facilitate systematic sampling and statistical analysis. These techniques contrast with case studies, which rely on in-depth, qualitative data from fewer subjects through observations, unstructured interviews, and document reviews.
Data Collection Techniques in Case Studies
Case study data collection techniques prioritize in-depth, qualitative methods such as interviews, direct observations, and document analysis to gather comprehensive, contextual insights about a single subject or phenomenon. Unlike survey research, which relies on structured questionnaires and large sample sizes for quantitative data, case studies utilize diverse sources to triangulate information and enhance validity. These techniques enable detailed exploration of complex issues within real-life settings, making case studies ideal for understanding processes, behaviors, and motivations.
Advantages of Survey Research
Survey research offers the advantage of collecting data from large, diverse populations, enabling statistically significant results that enhance generalizability. It allows for standardized data collection through structured questionnaires, facilitating easier comparison and analysis across different demographic groups. Additionally, surveys are cost-effective and time-efficient, making them ideal for quickly gathering quantitative data on attitudes, behaviors, and opinions.
Benefits of Using Case Study Approach
The case study approach offers in-depth, contextual analysis of complex phenomena within real-life settings, providing rich qualitative data that captures nuances often missed by survey research. It enables exploration of unique or rare cases, facilitating theory development and practical insights through detailed participant perspectives and environmental factors. This method is particularly beneficial for understanding processes, behaviors, and organizational dynamics that surveys might oversimplify or overlook.
Limitations of Survey Research vs Case Study
Survey research often faces limitations related to self-report bias, superficial data depth, and challenges in capturing complex phenomena, whereas case studies can provide detailed contextual insights but lack generalizability due to their focus on single or limited instances. Survey research may struggle with low response rates and inaccurate answers, restricting the representativeness of findings. Case studies, while rich in qualitative data, require significant time and resources and may not reliably support broad hypotheses testing.
Choosing the Right Method: Survey Research or Case Study
Choosing the right research method depends on the study's objectives and context; survey research excels in collecting quantitative data from large, diverse populations to identify trends and generalize findings, while case studies provide in-depth qualitative insights into complex phenomena within specific real-life contexts. Surveys are ideal for hypothesis testing and statistical analysis across broad samples, whereas case studies suit exploratory research and context-rich understanding of unique or rare cases. Considering factors such as data type, sample size, research questions, and resource availability guides the optimal selection between survey research and case study methodologies.
Survey Research Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com