Anecdotal practices rely on personal stories and individual experiences rather than systematic research, often leading to biased or unverified conclusions. These methods can influence your decision-making, but they lack the scientific rigor required for reliable outcomes. Explore the rest of this article to understand the impact and limitations of anecdotal evidence in various fields.
Table of Comparison
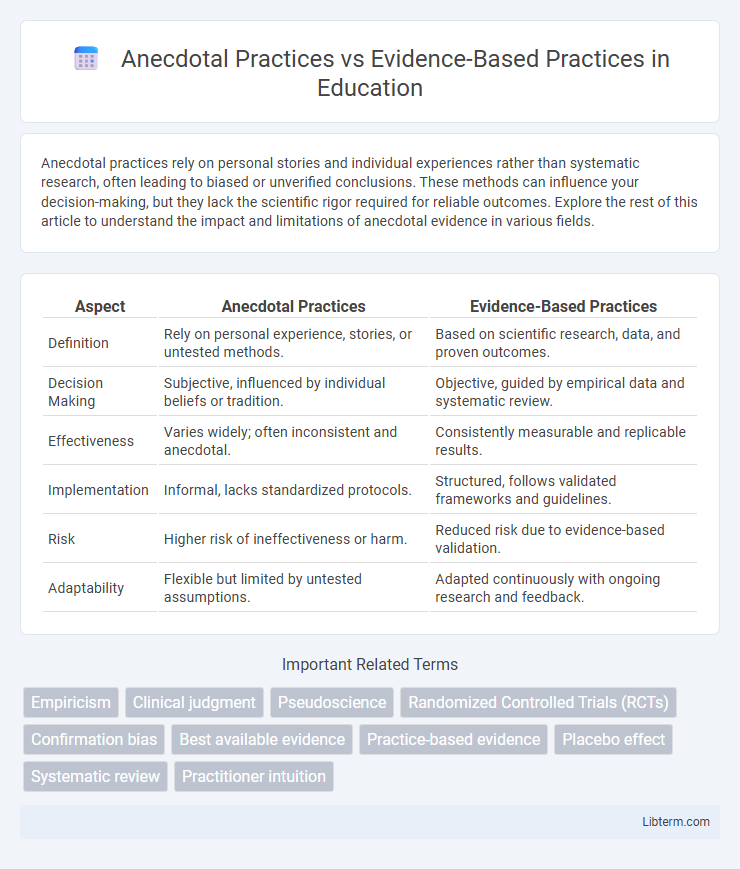
| Aspect | Anecdotal Practices | Evidence-Based Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rely on personal experience, stories, or untested methods. | Based on scientific research, data, and proven outcomes. |
| Decision Making | Subjective, influenced by individual beliefs or tradition. | Objective, guided by empirical data and systematic review. |
| Effectiveness | Varies widely; often inconsistent and anecdotal. | Consistently measurable and replicable results. |
| Implementation | Informal, lacks standardized protocols. | Structured, follows validated frameworks and guidelines. |
| Risk | Higher risk of ineffectiveness or harm. | Reduced risk due to evidence-based validation. |
| Adaptability | Flexible but limited by untested assumptions. | Adapted continuously with ongoing research and feedback. |
Understanding Anecdotal Practices
Anecdotal practices rely on personal experiences, individual stories, and unverified observations rather than systematic research or clinical trials. These practices often persist due to cultural traditions, anecdotal success stories, or intuitive reasoning, despite lacking empirical support. Understanding anecdotal practices involves recognizing their role in shaping beliefs and behaviors while emphasizing the need for rigorous evidence to validate effectiveness.
Defining Evidence-Based Practices
Evidence-based practices (EBPs) refer to interventions and strategies that are grounded in rigorous research, systematic data analysis, and clinical expertise to ensure effective outcomes. These practices rely on empirical evidence obtained through controlled studies, including randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses, to validate their efficacy and reliability. Implementing EBPs enhances decision-making by integrating scientific findings with professional judgment and client values.
Historical Context of Both Approaches
Anecdotal practices have historically relied on personal experiences, traditions, and subjective observations passed down through generations, often lacking rigorous validation. In contrast, evidence-based practices emerged prominently in the 20th century with the rise of scientific methods, emphasizing empirical research, controlled trials, and reproducibility to inform decision-making. The shift from anecdotal to evidence-based approaches reflects a broader movement toward scientific rigor and objectivity in fields such as medicine, psychology, and education.
Key Differences Between Anecdotal and Evidence-Based Methods
Anecdotal practices rely on personal stories, individual experiences, and informal observations that lack systematic validation, often leading to biased or inconsistent outcomes. Evidence-based practices depend on rigorous research, statistical analysis, and peer-reviewed studies ensuring reliability, reproducibility, and effectiveness. The key difference lies in anecdotal methods being subjective and unverified, whereas evidence-based approaches prioritize empirical data and scientific rigor for decision-making.
Common Examples of Anecdotal Practices
Common examples of anecdotal practices include using folk remedies like drinking ginger tea for nausea or relying on personal testimonies to choose alternative therapies such as homeopathy or aromatherapy. These practices often lack rigorous scientific validation and are based primarily on individual or cultural experience rather than controlled clinical studies. Despite their popularity, anecdotal practices may lead to inconsistent outcomes and delay effective treatment options supported by evidence-based medicine.
The Scientific Basis Behind Evidence-Based Practices
Evidence-based practices rely on rigorous scientific research, including randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews, to validate their effectiveness and ensure reliable outcomes. These practices prioritize data-driven decision-making by integrating clinical expertise with high-quality empirical evidence and patient values. Anecdotal practices, by contrast, lack this scientific foundation and are often based on personal experience or isolated observations, which can lead to inconsistent and unverified results.
Benefits and Risks of Anecdotal Approaches
Anecdotal practices offer personalized insights and quicker adaptation by relying on individual experiences, which can enhance creativity and responsiveness in decision-making. However, these approaches carry risks such as bias, lack of generalizability, and potential for misinformation, leading to inconsistent or ineffective outcomes. Relying solely on anecdotal evidence may undermine the rigor and reliability that evidence-based practices provide through systematic research and validated data.
Advantages of Adopting Evidence-Based Practices
Adopting evidence-based practices enhances decision-making by relying on scientifically validated data, leading to improved outcomes and reduced risks. These practices promote consistency and accountability across professional fields, ensuring interventions are replicable and effective. Utilizing evidence-based methods supports continual improvement through ongoing research and updated protocols, fostering innovation and best results.
Integrating Anecdotal and Evidence-Based Strategies
Integrating anecdotal practices with evidence-based strategies enhances decision-making by combining real-world experiences with scientifically validated data. This hybrid approach allows healthcare professionals to personalize treatments while maintaining reliability and effectiveness supported by clinical research. Balancing subjective insights and objective evidence fosters more comprehensive patient care and continuous improvement in outcomes.
The Future of Decision-Making in Practice
The future of decision-making in practice increasingly relies on evidence-based practices, leveraging robust data, systematic reviews, and clinical guidelines to enhance accuracy and outcomes. Anecdotal practices, while offering valuable experiential insights, lack the consistency and reproducibility necessary for widespread application in modern healthcare and professional settings. Integrating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning will further empower practitioners to prioritize evidence-based decisions, improving quality and reducing variability in care.
Anecdotal Practices Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com