Performance-based assessment measures your ability to apply skills and knowledge in real-world scenarios rather than through traditional testing methods. This approach enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical application, making evaluations more reflective of actual competence. Explore the full article to understand how performance-based assessments can transform your learning and evaluation experience.
Table of Comparison
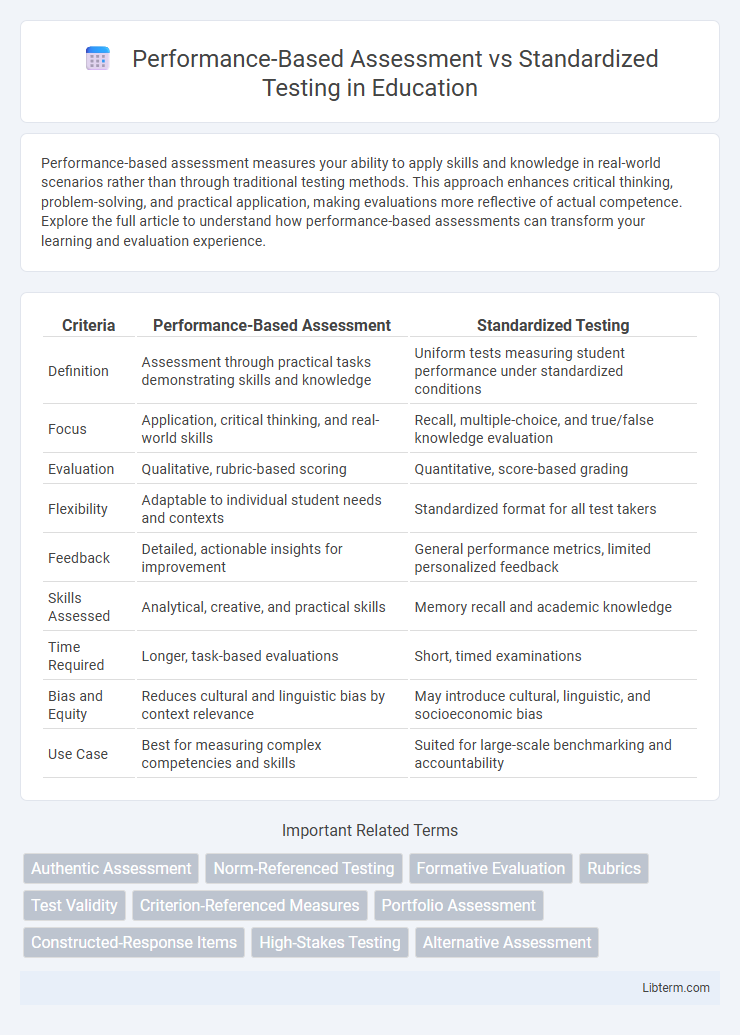
| Criteria | Performance-Based Assessment | Standardized Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment through practical tasks demonstrating skills and knowledge | Uniform tests measuring student performance under standardized conditions |
| Focus | Application, critical thinking, and real-world skills | Recall, multiple-choice, and true/false knowledge evaluation |
| Evaluation | Qualitative, rubric-based scoring | Quantitative, score-based grading |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to individual student needs and contexts | Standardized format for all test takers |
| Feedback | Detailed, actionable insights for improvement | General performance metrics, limited personalized feedback |
| Skills Assessed | Analytical, creative, and practical skills | Memory recall and academic knowledge |
| Time Required | Longer, task-based evaluations | Short, timed examinations |
| Bias and Equity | Reduces cultural and linguistic bias by context relevance | May introduce cultural, linguistic, and socioeconomic bias |
| Use Case | Best for measuring complex competencies and skills | Suited for large-scale benchmarking and accountability |
Understanding Performance-Based Assessment
Performance-based assessment evaluates students by requiring them to demonstrate skills through real-world tasks, such as projects, presentations, or portfolios, emphasizing practical application over rote memorization. Unlike standardized testing, which measures knowledge through multiple-choice or short-answer questions under timed conditions, performance-based assessment provides deeper insights into critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. This assessment method facilitates personalized feedback and supports diverse learning styles, making it an effective tool for comprehensive student evaluation.
Defining Standardized Testing
Standardized testing refers to a uniform assessment method where all test-takers answer the same questions under consistent conditions, enabling reliable comparisons across diverse populations. These tests typically measure knowledge or skills in core subjects using multiple-choice or true/false formats to ensure objectivity and scalability. Designed to evaluate educational achievement or aptitude, standardized tests generate quantifiable data for policymakers, educators, and institutions to analyze academic performance trends.
Key Differences Between Assessment Types
Performance-based assessment evaluates students through real-world tasks that demonstrate application of knowledge and skills, emphasizing critical thinking and problem-solving. Standardized testing measures student achievement using uniform questions and scoring, focusing on quantifiable data and broad content coverage. Key differences include authenticity of tasks, assessment format, and flexibility in responses, with performance-based assessments offering personalized evaluation and standardized tests providing comparative metrics.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Performance-based assessments provide a more comprehensive evaluation of student learning outcomes by measuring critical thinking, problem-solving, and application skills, which standardized testing often overlooks. These assessments encourage deeper understanding and retention by engaging students in real-world tasks, leading to improved academic achievement and motivation. Standardized tests primarily assess rote memorization and narrow skill sets, potentially limiting the ability to gauge true learning progress and growth over time.
Measuring Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
Performance-based assessment evaluates critical thinking and problem-solving skills through real-world tasks that require analysis, synthesis, and application of knowledge, offering a nuanced understanding of student abilities. Standardized testing primarily measures recall and basic comprehension via multiple-choice or short-answer questions, often failing to capture complex reasoning processes. Research indicates performance-based methods provide richer data on students' higher-order cognitive skills essential for academic and career success.
Equity and Accessibility Considerations
Performance-based assessment promotes equity by allowing diverse learners to demonstrate skills through real-world tasks tailored to individual strengths, reducing cultural and linguistic biases often present in standardized testing. Standardized tests frequently disadvantage students from marginalized communities due to uniform formats and cultural assumptions, limiting accessibility and reinforcing achievement gaps. Implementing performance-based assessments supports inclusive education by accommodating various learning styles, fostering equitable opportunities for all students to succeed.
Teacher and Student Perspectives
Performance-based assessments offer teachers detailed insights into student critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, allowing for tailored instructional strategies, while standardized tests provide limited data focused on memorization and recall. Students often find performance-based assessments more engaging and reflective of real-world applications, promoting deeper learning and motivation, whereas standardized testing can induce stress and fail to capture individual strengths. From both perspectives, performance-based assessments foster a holistic evaluation of competencies, contrasting with the uniform, quantitative nature of standardized exams.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Performance-based assessment faces implementation challenges such as the need for extensive teacher training, time-consuming grading processes, and variability in scoring consistency. Solutions include adopting clear rubrics, leveraging technology for streamlined evaluation, and providing ongoing professional development to ensure reliable assessment standards. In contrast, standardized testing struggles with issues like limited scope in measuring skills and high-stakes pressure; these can be mitigated by integrating formative assessments and employing adaptive testing technologies to enhance accuracy and student engagement.
Long-Term Effects on Academic Success
Performance-based assessments promote deeper understanding and critical thinking by requiring students to demonstrate knowledge through projects, presentations, and real-world tasks, leading to improved long-term academic success. In contrast, standardized testing often emphasizes rote memorization and test-taking skills, which may not accurately reflect a student's comprehensive abilities or foster sustained academic growth. Research indicates that students evaluated through performance-based methods tend to develop stronger problem-solving skills and retain knowledge more effectively over time, contributing to higher academic achievement and lifelong learning.
Choosing the Right Assessment Approach
Performance-based assessment provides a comprehensive evaluation of students' critical thinking, problem-solving, and application skills, offering deeper insights into learning compared to standardized testing's focus on memorization and uniform metrics. Selecting the right assessment approach depends on educational goals, with performance-based methods suited for real-world skills demonstration and standardized tests useful for benchmarking and large-scale comparisons. Balancing both approaches can create a more holistic assessment strategy that supports diverse learning outcomes and instructional needs.
Performance-Based Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com