Classroom teaching creates an interactive environment where educators can tailor lessons to meet diverse learning styles and foster immediate feedback. Effective classroom strategies enhance student engagement and retention through hands-on activities and collaborative discussions. Discover how optimizing these techniques can transform your teaching experience in the full article.
Table of Comparison
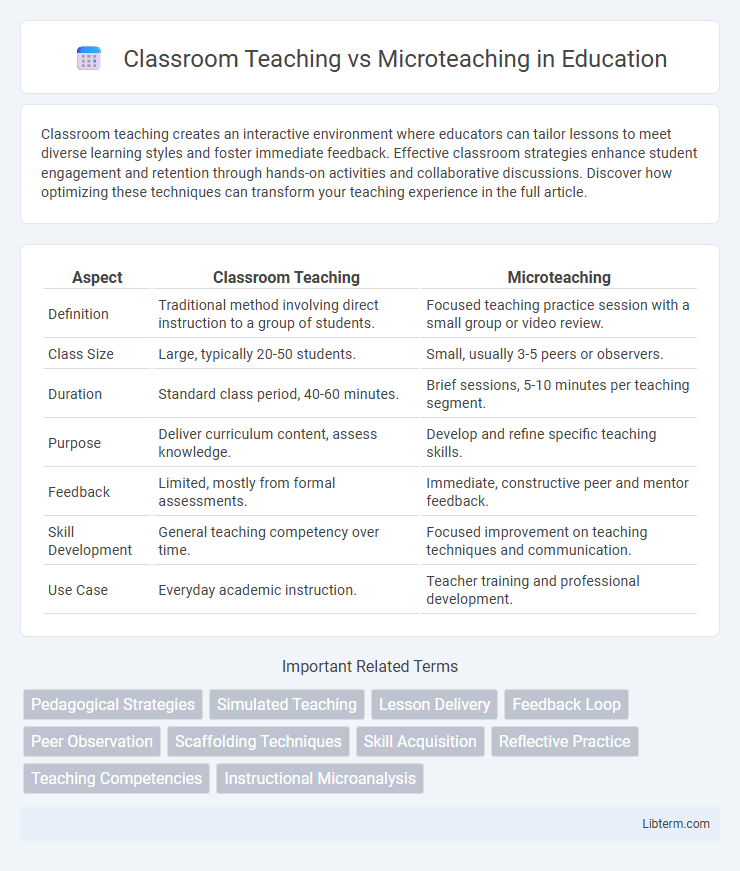
| Aspect | Classroom Teaching | Microteaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional method involving direct instruction to a group of students. | Focused teaching practice session with a small group or video review. |
| Class Size | Large, typically 20-50 students. | Small, usually 3-5 peers or observers. |
| Duration | Standard class period, 40-60 minutes. | Brief sessions, 5-10 minutes per teaching segment. |
| Purpose | Deliver curriculum content, assess knowledge. | Develop and refine specific teaching skills. |
| Feedback | Limited, mostly from formal assessments. | Immediate, constructive peer and mentor feedback. |
| Skill Development | General teaching competency over time. | Focused improvement on teaching techniques and communication. |
| Use Case | Everyday academic instruction. | Teacher training and professional development. |
Introduction to Classroom Teaching and Microteaching
Classroom teaching involves delivering comprehensive lessons to a larger group of students, emphasizing real-time interaction, lesson planning, and classroom management skills. Microteaching is a scaled-down, focused teaching practice designed to improve specific teaching techniques by allowing educators to teach small sessions to peers or mentors. Both methods serve distinct roles in teacher education, with classroom teaching providing practical experience and microteaching offering targeted skill enhancement.
Defining Classroom Teaching
Classroom teaching involves delivering subject content directly to students in a structured environment, emphasizing comprehensive curriculum coverage and interactive learning. It typically includes diverse instructional strategies aimed at addressing varying student needs and promoting critical thinking. Effective classroom teaching prioritizes engagement, assessment, and adapting methods to foster student understanding and academic growth.
What is Microteaching?
Microteaching is a scaled-down, supervised teaching practice designed to improve specific teaching skills through short, focused sessions often lasting 5 to 10 minutes. It allows educators to rehearse lessons in a controlled environment and receive immediate feedback on techniques such as questioning, explaining, and classroom management. Compared to traditional classroom teaching, microteaching emphasizes skill development in a low-pressure setting before applying strategies in full-scale instructional scenarios.
Key Differences Between Classroom Teaching and Microteaching
Classroom teaching involves managing an entire class with diverse learners, focusing on delivering curriculum content in real-time to achieve broad educational goals. Microteaching is a scaled-down, practice-based teaching technique where educators rehearse specific teaching skills to improve effectiveness through feedback and reflection. The key differences lie in scope, complexity, and purpose: classroom teaching addresses full instructional delivery, whereas microteaching targets skill refinement in a controlled, simplified environment.
Advantages of Classroom Teaching
Classroom teaching facilitates real-time interaction between teachers and a diverse group of students, allowing for immediate feedback and dynamic discussions that enhance understanding. It supports the development of social skills and collaborative learning environments, which promote teamwork and communication among students. Additionally, classroom settings provide access to various teaching aids and resources, enriching the learning experience with multimedia tools and hands-on activities.
Benefits of Microteaching for Teachers
Microteaching offers teachers a controlled environment to refine specific instructional skills through focused, short teaching sessions followed by feedback. This method enables educators to identify strengths and areas for improvement, enhancing their overall teaching efficacy and confidence before handling larger classroom settings. Microteaching also fosters reflective practice and peer collaboration, contributing to continuous professional development and improved student engagement.
Limitations of Classroom Teaching
Classroom teaching often faces limitations such as large student-to-teacher ratios, which hinder personalized feedback and active student engagement. The rigid structure and time constraints in classrooms limit opportunities for practice and peer interaction, affecting skill development. Additionally, classroom environments may lack immediate evaluation mechanisms, reducing the effectiveness of instructional adjustments.
Microteaching: Drawbacks and Challenges
Microteaching, while effective for skill development, presents challenges such as limited real-world classroom dynamics and reduced student diversity, which can affect the transferability of teaching skills. The controlled environment often lacks spontaneous interactions and unpredictability found in actual classrooms, leading to an incomplete teaching experience. Furthermore, participants may experience anxiety or performance pressure that hampers natural teaching behavior, limiting authentic skill assessment.
When to Use Classroom Teaching vs Microteaching
Classroom teaching is ideal for delivering comprehensive lessons to larger groups, emphasizing real-time interaction and holistic development of students over extended periods. Microteaching is best used for focused skill development, allowing educators to practice and refine specific teaching techniques with small groups or peers in controlled settings. Use classroom teaching for broader curriculum delivery and microteaching for targeted professional growth and immediate feedback on instructional methods.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Teaching Approach
Selecting the appropriate teaching method depends on educational goals and learner needs, with classroom teaching offering broad interaction and real-time feedback suitable for diverse groups, while microteaching provides focused skill development through controlled practice and detailed evaluation. Classroom teaching enhances communication and adaptability in dynamic settings, whereas microteaching facilitates mastery of specific techniques, benefiting novice educators or targeted training programs. Optimal teaching outcomes arise from integrating both approaches, leveraging the comprehensive engagement of classroom teaching alongside the precision and efficiency of microteaching.
Classroom Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com