Interdisciplinary units integrate multiple subject areas to create a cohesive learning experience that fosters critical thinking and real-world application. These units encourage collaboration and deeper understanding by connecting concepts across disciplines, enhancing your ability to analyze complex problems. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for designing and implementing interdisciplinary units in your educational setting.
Table of Comparison
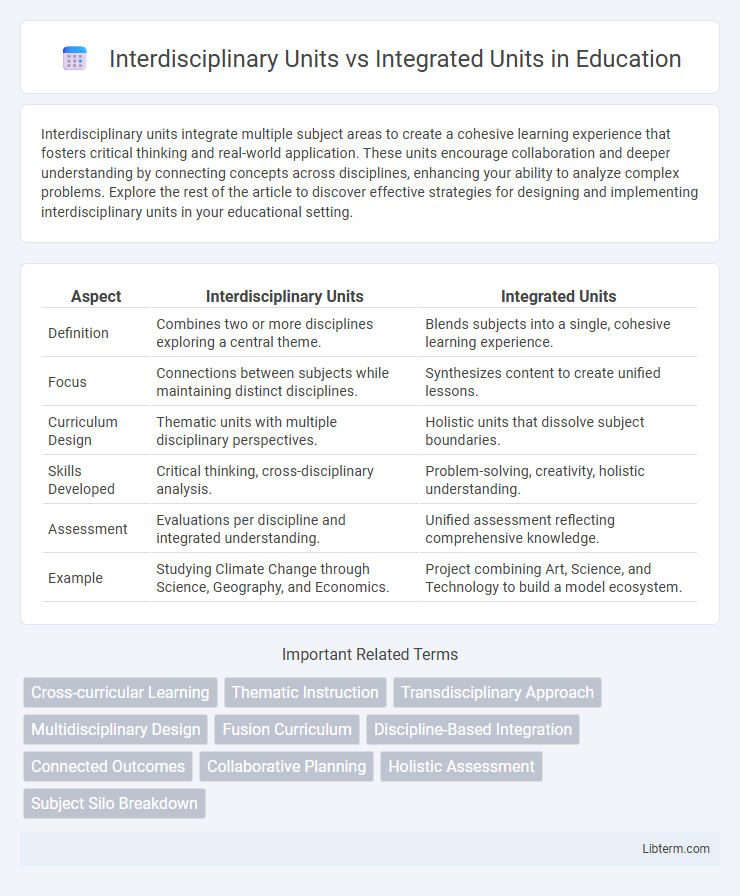
| Aspect | Interdisciplinary Units | Integrated Units |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines two or more disciplines exploring a central theme. | Blends subjects into a single, cohesive learning experience. |
| Focus | Connections between subjects while maintaining distinct disciplines. | Synthesizes content to create unified lessons. |
| Curriculum Design | Thematic units with multiple disciplinary perspectives. | Holistic units that dissolve subject boundaries. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, cross-disciplinary analysis. | Problem-solving, creativity, holistic understanding. |
| Assessment | Evaluations per discipline and integrated understanding. | Unified assessment reflecting comprehensive knowledge. |
| Example | Studying Climate Change through Science, Geography, and Economics. | Project combining Art, Science, and Technology to build a model ecosystem. |
Understanding Interdisciplinary Units
Interdisciplinary units involve combining multiple academic disciplines to create a cohesive learning experience centered around a common theme or problem, enhancing critical thinking and real-world application skills. These units require students to synthesize knowledge from various subjects, fostering deeper understanding and promoting collaboration across fields. Unlike integrated units, which blend subject content for efficiency, interdisciplinary units emphasize the intersection and interplay of disciplines to generate new insights and comprehensive problem-solving approaches.
Defining Integrated Units
Integrated units combine content, skills, and concepts from multiple subject areas into a coherent learning experience, promoting deeper understanding and real-world connections. Unlike interdisciplinary units that link distinct disciplines while maintaining their boundaries, integrated units merge these disciplines to create seamless, cross-curricular instruction. This approach enhances critical thinking and fosters collaboration by blurring traditional subject lines within classroom instruction.
Core Differences Between Interdisciplinary and Integrated Units
Interdisciplinary units combine concepts and methods from multiple disciplines to address complex topics, fostering critical thinking through the synthesis of diverse perspectives. Integrated units blend related subjects within a single discipline, aiming to create coherence and reinforce learning by connecting content areas. The core difference lies in interdisciplinarity's emphasis on crossing disciplinary boundaries versus integration's focus on combining elements within a particular field.
Approaches to Curriculum Design
Interdisciplinary units emphasize connections across multiple subject areas by blending content and skills to foster critical thinking and real-world problem solving. Integrated units combine curriculum components from different disciplines into a cohesive learning experience, often prioritizing thematic or project-based learning to enhance engagement and retention. Both approaches require intentional alignment of objectives, assessment, and instructional strategies to effectively support student learning outcomes.
Key Benefits of Interdisciplinary Units
Interdisciplinary units foster deeper critical thinking by connecting concepts across multiple disciplines, enhancing students' ability to synthesize knowledge. These units promote collaboration among educators from different subject areas, resulting in richer curriculum design and diversified instructional strategies. Students benefit from a more cohesive learning experience that mirrors real-world problem solving and encourages transferable skills.
Advantages of Integrated Units
Integrated units enhance student learning by seamlessly combining multiple subjects, fostering deeper understanding through real-world connections and contextualized knowledge. These units promote critical thinking and creativity by encouraging students to apply skills across disciplines, leading to improved problem-solving abilities. Integration also streamlines curriculum design, reducing redundancy and maximizing instructional time for effective concept reinforcement.
Implementation Strategies for Both Unit Types
Interdisciplinary units require collaboration among teachers from different subject areas to design cohesive lessons that connect concepts, often using co-planning sessions and shared assessments as key implementation strategies. Integrated units blend multiple subjects within a single lesson or theme, typically implemented through project-based learning and thematic instruction that align curriculum standards across disciplines. Effective implementation for both unit types depends on clear communication, aligned learning objectives, and ongoing professional development to ensure instructional coherence.
Challenges in Adopting Each Approach
Adopting interdisciplinary units often faces challenges such as coordinating content across multiple subject areas, balancing depth and breadth of knowledge, and aligning assessment methods to diverse disciplines. Integrated units struggle with maintaining clear learning objectives while blending distinct curriculum standards, which can lead to confusion in both teaching focus and student outcomes. Both approaches require extensive collaboration among educators and ongoing professional development to effectively address curriculum coherence and pedagogical consistency.
Selecting the Right Unit Structure for Your Classroom
Selecting the right unit structure for your classroom involves understanding the distinction between interdisciplinary units, which connect multiple disciplines through a common theme, and integrated units, where subjects are blended seamlessly to create a cohesive learning experience. Interdisciplinary units emphasize the unique contributions of each discipline, facilitating deeper content understanding, while integrated units promote holistic thinking by merging subjects into a unified approach. Effective unit selection depends on your curriculum goals, student needs, and the desired level of collaboration among subject areas to foster engagement and critical thinking.
Future Trends in Unit Integration
Future trends in unit integration emphasize deeper connections across disciplines, promoting interdisciplinary units that foster critical thinking and real-world problem-solving through collaborative methods. Advances in educational technology support dynamic, flexible curricula enabling seamless integration of Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics (STEAM) within interdisciplinary frameworks. Data-driven personalization and competency-based assessments increasingly shape integrated units, aligning learning experiences with evolving workforce demands and 21st-century skills development.
Interdisciplinary Units Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com