Content-Based Instruction (CBI) integrates language learning with subject matter teaching, enabling learners to acquire new language skills through meaningful and relevant content. This approach not only improves linguistic competence but also enhances critical thinking and subject knowledge simultaneously. Discover how CBI can transform your language learning experience by exploring the detailed insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
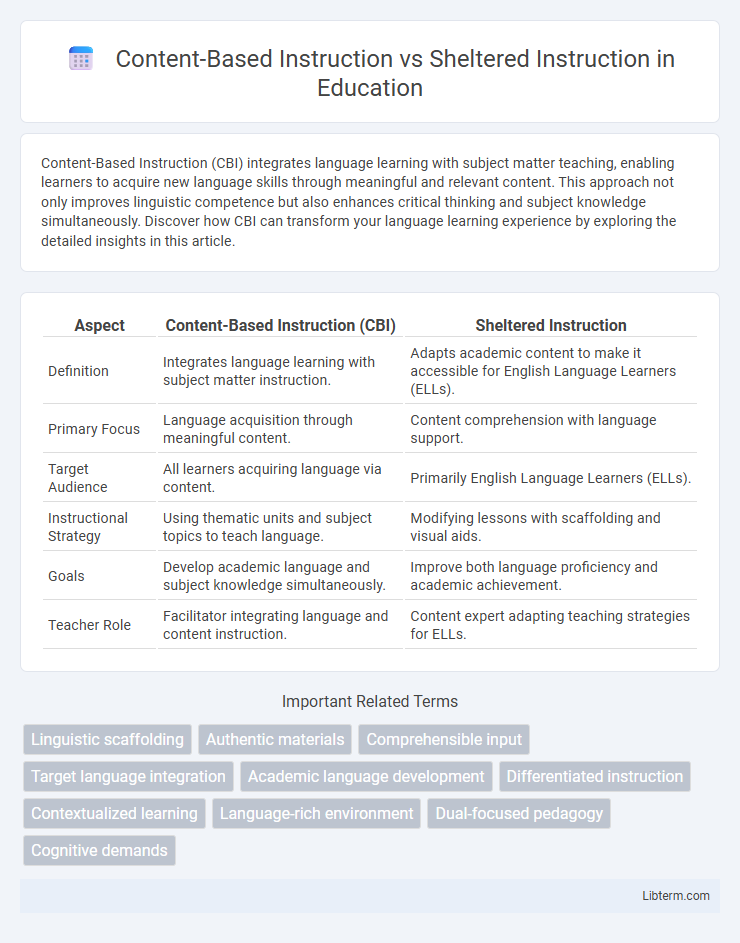
| Aspect | Content-Based Instruction (CBI) | Sheltered Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates language learning with subject matter instruction. | Adapts academic content to make it accessible for English Language Learners (ELLs). |
| Primary Focus | Language acquisition through meaningful content. | Content comprehension with language support. |
| Target Audience | All learners acquiring language via content. | Primarily English Language Learners (ELLs). |
| Instructional Strategy | Using thematic units and subject topics to teach language. | Modifying lessons with scaffolding and visual aids. |
| Goals | Develop academic language and subject knowledge simultaneously. | Improve both language proficiency and academic achievement. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator integrating language and content instruction. | Content expert adapting teaching strategies for ELLs. |
Understanding Content-Based Instruction: An Overview
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) integrates language learning with subject matter instruction, emphasizing meaningful communication and contextual understanding. Unlike Sheltered Instruction, which adapts content to meet the language proficiency of English Language Learners (ELLs), CBI immerses students in academic content while simultaneously developing language skills. This approach enhances cognitive engagement and facilitates deeper comprehension by aligning language acquisition with real-world academic topics.
What is Sheltered Instruction? Key Principles
Sheltered Instruction is a teaching approach designed to make academic content understandable for English Language Learners (ELLs) while promoting English language development. Key principles include using clear, simple language, providing visual aids and hands-on activities, and integrating language objectives with content objectives to ensure comprehension and engagement. This method emphasizes scaffolding instruction, building background knowledge, and encouraging student interaction to support both language acquisition and content mastery.
Historical Development of Both Approaches
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) originated in the 1980s as a response to the need for integrating language learning with subject matter instruction, influenced by theories of communicative language teaching and curriculum integration. Sheltered Instruction, developed primarily in the 1990s within the U.S. educational system, was designed to support English Language Learners (ELLs) in mainstream classrooms, emphasizing modified content delivery and language support. Both approaches evolved to address the challenges of language acquisition in academic contexts but differ in their historical emphasis--CBI on curriculum-driven integration and Sheltered Instruction on scaffolding content for learners with limited English proficiency.
Theoretical Foundations of CBI and Sheltered Instruction
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) is grounded in theories of second language acquisition that emphasize meaningful interaction with subject matter to develop both language and content knowledge simultaneously, drawing heavily on Krashen's Input Hypothesis and Cummins' distinction between Basic Interpersonal Communicative Skills (BICS) and Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency (CALP). Sheltered Instruction, on the other hand, is rooted in sociocultural theory and Vygotsky's Zone of Proximal Development, focusing on scaffolding language learning through adapted content instruction to make academic subjects more accessible to English Language Learners (ELLs). Both approaches integrate language development with academic content but differ in their instructional strategies and theoretical emphases, with CBI prioritizing content immersion and Sheltered Instruction emphasizing language support within content teaching.
Goals and Objectives: Comparing Both Methods
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) aims to integrate language learning with academic content mastery, focusing on developing both subject knowledge and language proficiency simultaneously. Sheltered Instruction prioritizes making academic content comprehensible for English language learners (ELLs) by adapting teaching strategies and materials to support language development within content areas. Both methods strive to enhance student engagement and achievement, but CBI emphasizes dual-focused learning objectives, whereas Sheltered Instruction centers on scaffolding content to meet diverse linguistic needs.
Instructional Techniques and Classroom Practices
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) emphasizes integrating language learning with subject matter through thematic units, using authentic materials and interactive activities that promote language development alongside content mastery. Sheltered Instruction employs specific strategies such as scaffolding, visual aids, and modified speech to make academic content comprehensible for English Language Learners while supporting language acquisition. Both approaches prioritize meaningful communication, but CBI focuses on content immersion, whereas Sheltered Instruction adapts materials and delivery to meet diverse linguistic needs in the classroom.
Teacher Roles and Training Requirements
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) emphasizes teachers acting as both subject matter experts and language facilitators, requiring deep training in content disciplines alongside language acquisition strategies. Sheltered Instruction prioritizes teachers skilled in scaffolding academic language within grade-level content, necessitating specialized professional development in sheltered teaching methods and learner-centered approaches. Effective implementation of both models demands ongoing training focused on integrating language objectives with content goals to support English Language Learners' academic success.
Advantages and Challenges of Content-Based Instruction
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) enhances language acquisition by integrating subject matter learning with language development, promoting deeper comprehension and meaningful communication. Its advantages include improved academic performance and increased motivation through exposure to authentic materials, but challenges involve the need for teachers skilled in both content and language instruction, as well as the potential difficulty in balancing content complexity with language proficiency levels. Effective implementation of CBI requires ongoing professional development and carefully designed curricula to address diverse learner needs and prevent cognitive overload.
Sheltered Instruction: Benefits and Limitations
Sheltered Instruction enhances English language learners' comprehension by integrating language development with subject matter teaching, promoting meaningful interaction and academic achievement. Its benefits include creating a supportive learning environment, scaffolding complex concepts, and fostering student engagement through visual aids and hands-on activities. However, limitations involve the need for specialized teacher training, potential challenges in adapting curriculum for diverse proficiency levels, and the risk of oversimplifying content, which may hinder deep subject understanding.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) focuses on teaching language through subject matter, enhancing academic vocabulary and critical thinking skills, while Sheltered Instruction integrates language development with content objectives tailored for English Language Learners (ELLs). Choosing the right approach depends on learners' proficiency levels, academic goals, and the need for scaffolding; CBI suits intermediate to advanced learners in content-rich environments, whereas Sheltered Instruction provides structured support for beginners. Effective educators assess student needs, curriculum demands, and language outcomes to implement an approach that maximizes comprehension and engagement across diverse learner populations.
Content-Based Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com