Public schools provide accessible, quality education funded by government resources, ensuring equal opportunities for all students regardless of background. They offer diverse curricula, extracurricular activities, and qualified teachers dedicated to fostering student growth and success. Discover how public schools can support your child's academic journey by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
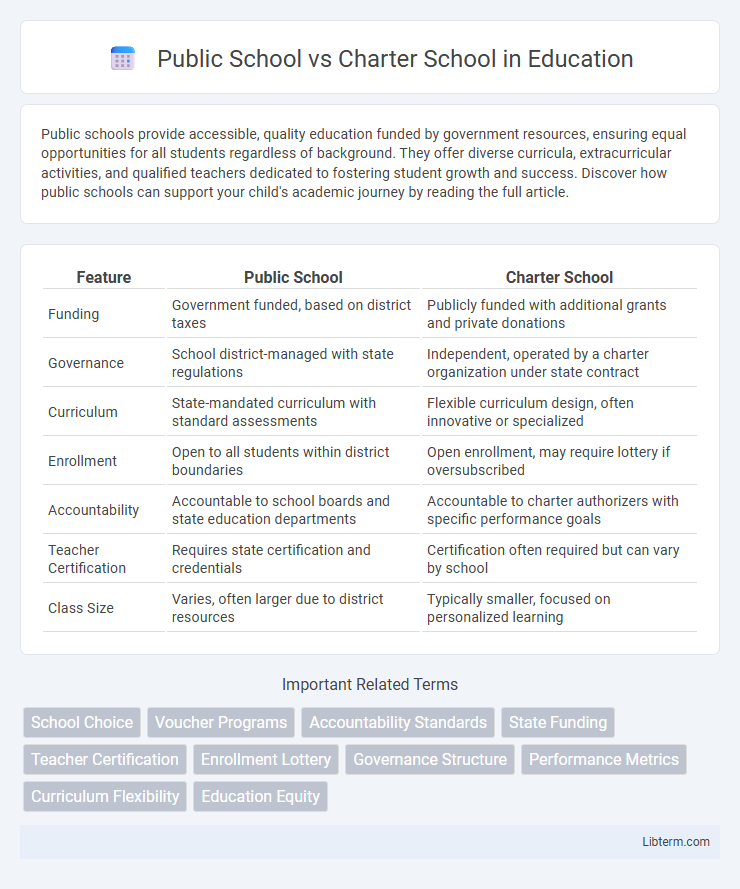
| Feature | Public School | Charter School |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Government funded, based on district taxes | Publicly funded with additional grants and private donations |
| Governance | School district-managed with state regulations | Independent, operated by a charter organization under state contract |
| Curriculum | State-mandated curriculum with standard assessments | Flexible curriculum design, often innovative or specialized |
| Enrollment | Open to all students within district boundaries | Open enrollment, may require lottery if oversubscribed |
| Accountability | Accountable to school boards and state education departments | Accountable to charter authorizers with specific performance goals |
| Teacher Certification | Requires state certification and credentials | Certification often required but can vary by school |
| Class Size | Varies, often larger due to district resources | Typically smaller, focused on personalized learning |
Understanding Public Schools and Charter Schools
Public schools are government-funded institutions that must follow state-mandated curriculums and regulations, providing free education to all students within a district. Charter schools operate independently from traditional public school districts, receiving public funding but having greater flexibility in curriculum design, teaching methods, and school management. Understanding the differences in governance, accountability, and enrollment policies is crucial when comparing public schools and charter schools in terms of educational approach and student outcomes.
Historical Background of Both School Types
Public schools originated in the early 19th century as government-funded institutions aiming to provide free, universal education to all children in a community. Charter schools emerged in the early 1990s as publicly funded but independently operated alternatives designed to foster innovation and choice within the public education system. The distinct historical roots highlight public schools' commitment to standardized education versus charter schools' emphasis on flexibility and accountability through performance-based charters.
Admission and Enrollment Processes
Public school admission typically involves residency requirements within a designated school district, ensuring students attend based on their home address, while enrollment is managed through local education authorities with standardized procedures. Charter schools, operating independently from district guidelines, often implement a lottery system for admission when applications exceed available seats, allowing for a more flexible and competitive enrollment process. This fundamental difference impacts accessibility, with public schools guaranteeing placement for in-district students and charter schools offering choice through selective admission frameworks.
Curriculum Differences and Flexibility
Public schools follow state-mandated curricula designed to meet standardized testing requirements, ensuring uniformity across districts. Charter schools often have greater curricular flexibility, allowing for specialized programs, innovative teaching methods, and tailored learning experiences based on student needs. This flexibility enables charter schools to implement unique educational approaches while still meeting basic academic standards set by authorizing bodies.
Teacher Qualifications and Staffing
Public schools typically require teachers to hold state certification and adhere to district hiring standards, ensuring consistent qualifications across classrooms. Charter schools have more flexibility in hiring, often allowing teachers without traditional certifications, which can lead to varied staffing credentials. This difference impacts teacher experience levels and instructional approaches, with public schools favoring standardized qualifications and charter schools emphasizing innovative or alternative teaching methods.
Funding and Financial Structures
Public schools rely primarily on state and local government funding, supplemented by federal grants, which can limit financial flexibility and result in resource disparities. Charter schools receive a combination of public funding based on enrollment and private donations, allowing for more innovative budget management but often facing funding uncertainties. Differences in financial structures directly impact program offerings, staff salaries, and facility maintenance between public and charter schools.
Academic Performance and Outcomes
Charter schools often demonstrate higher standardized test scores and graduation rates compared to traditional public schools, attributed to specialized curricula and increased autonomy in teaching methods. Public schools typically serve a broader demographic with diverse academic needs, which can impact overall performance metrics but provide comprehensive support services. Studies indicate that charter schools may excel in college enrollment rates, while public schools frequently offer wider extracurricular opportunities and resources.
Accountability and Oversight Measures
Public schools are governed by state and local education agencies with strict accountability through standardized testing, public reporting, and adherence to state curriculum standards. Charter schools operate under a charter contract approved by authorizers such as school districts or independent boards, which enforce performance benchmarks and periodic evaluations to ensure compliance and academic outcomes. Both systems face oversight challenges, but charter schools often have more flexibility in operations paired with targeted accountability measures defined in their charters.
Community Involvement and Parental Choice
Community involvement in public schools often reflects local government and district policies, facilitating broad participation through elected school boards and standardized programs. Charter schools emphasize parental choice by offering specialized curricula or educational approaches, attracting families seeking tailored learning environments and fostering active parental engagement in school governance. This focus on autonomy enables charter schools to create niche communities centered on specific educational values and priorities.
Pros and Cons: Making the Right Choice
Public schools offer tuition-free education with established curricula and diverse extracurricular programs, ensuring accessibility to all students. Charter schools provide innovative teaching methods and specialized programs but may have limited enrollment and less oversight. Choosing between them requires weighing factors like educational goals, community fit, and resource availability to determine the best learning environment for a child.
Public School Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com