Online learning offers flexible access to a vast range of courses and resources, enabling you to tailor your education to fit your schedule and goals. This mode of learning utilizes interactive tools and multimedia to enhance engagement and retention. Explore the full article to discover how online learning can transform your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
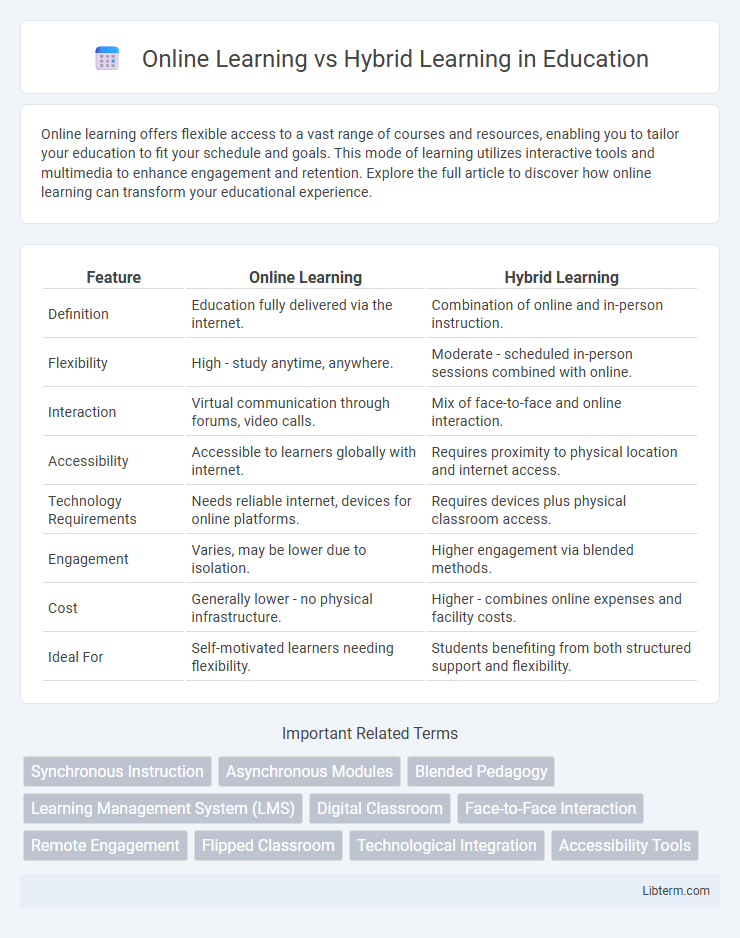
| Feature | Online Learning | Hybrid Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Education fully delivered via the internet. | Combination of online and in-person instruction. |
| Flexibility | High - study anytime, anywhere. | Moderate - scheduled in-person sessions combined with online. |
| Interaction | Virtual communication through forums, video calls. | Mix of face-to-face and online interaction. |
| Accessibility | Accessible to learners globally with internet. | Requires proximity to physical location and internet access. |
| Technology Requirements | Needs reliable internet, devices for online platforms. | Requires devices plus physical classroom access. |
| Engagement | Varies, may be lower due to isolation. | Higher engagement via blended methods. |
| Cost | Generally lower - no physical infrastructure. | Higher - combines online expenses and facility costs. |
| Ideal For | Self-motivated learners needing flexibility. | Students benefiting from both structured support and flexibility. |
Understanding Online Learning
Online learning offers flexible access to educational content through digital platforms, enabling students to study anytime and anywhere while utilizing multimedia resources, interactive modules, and virtual collaboration tools. This mode supports self-paced learning and personalized instruction, often incorporating real-time feedback and assessments via learning management systems. Understanding the technological infrastructure, such as stable internet connectivity and compatible devices, is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of online learning environments.
What Is Hybrid Learning?
Hybrid learning combines traditional in-person classroom instruction with online educational activities, creating a flexible and interactive learning environment. This model allows students to access course materials, engage in discussions, and complete assignments digitally while benefiting from face-to-face interaction with instructors and peers. Hybrid learning maximizes accessibility and adaptability, catering to diverse learning styles and improving student engagement and outcomes.
Key Differences Between Online and Hybrid Learning
Online learning delivers all course content and interaction through digital platforms without physical classroom presence, emphasizing flexibility and remote access. Hybrid learning combines online digital instruction with in-person sessions, offering a blend of virtual convenience and face-to-face engagement. The key differences lie in the balance of physical attendance, with hybrid models requiring scheduled campus visits, versus fully virtual participation in online learning.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Online learning offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing students to access coursework anytime and anywhere with an internet connection, which enhances accessibility for diverse learners including those with geographic or mobility constraints. Hybrid learning combines online and in-person instruction, providing a balanced approach that supports flexible scheduling while maintaining face-to-face interaction for hands-on activities and immediate feedback. Both models improve educational access, but online learning maximizes convenience, whereas hybrid learning optimizes engagement and resource availability.
Student Engagement and Interaction
Online learning offers flexible access to course materials but often limits real-time student engagement and peer interaction compared to hybrid learning. Hybrid learning combines in-person sessions with online components, fostering greater student collaboration, active participation, and immediate feedback. Enhanced interaction in hybrid models positively impacts student motivation, comprehension, and overall academic performance.
Technological Requirements
Online learning demands robust internet connections, compatible devices such as laptops or tablets, and access to digital platforms like Zoom or Canvas to facilitate virtual classrooms and coursework. Hybrid learning requires integrating both in-person attendance and online resources, necessitating technology that supports seamless transitions between physical and virtual environments, including smart classrooms and interactive software. Effective implementation in both modalities depends on reliable bandwidth, user-friendly interfaces, and adequate technical support to minimize disruptions and enhance educational outcomes.
Instructor Roles and Responsibilities
In online learning, instructors primarily facilitate virtual engagement through digital platforms, designing accessible content and providing timely feedback to maintain student motivation. Hybrid learning requires instructors to expertly balance in-person interaction with online instruction, adapting teaching methods to suit both environments and ensuring consistent communication. Both modalities demand strong organizational skills and responsiveness to support diverse learner needs effectively.
Assessing Learning Outcomes
Assessing learning outcomes in online learning relies heavily on digital tools such as quizzes, discussion forums, and automated grading systems to measure student performance and engagement. Hybrid learning combines these digital assessments with in-person evaluations, providing a more comprehensive view of student understanding through direct observation and hands-on activities. Data analytics from both online and hybrid platforms help educators tailor instruction, improve retention, and identify areas where students may struggle.
Challenges and Limitations
Online learning faces challenges such as limited student engagement, lack of hands-on experience, and technology accessibility issues that affect effective participation. Hybrid learning can mitigate some online limitations but struggles with scheduling conflicts, inconsistent access to resources, and the difficulty of seamlessly integrating in-person and virtual instruction. Both models require robust infrastructure and adaptive teaching strategies to overcome obstacles related to student motivation, communication barriers, and equitable access to educational materials.
Choosing the Best Learning Model
Selecting the best learning model depends on individual preferences and educational goals, with online learning offering flexibility, accessibility, and a wide range of digital resources. Hybrid learning combines in-person interaction with online components, enhancing engagement, personalized instruction, and collaboration opportunities. Evaluating factors like learning style, technological access, and course requirements helps determine the optimal balance between virtual and face-to-face education.
Online Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com