Project-based learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging you in hands-on, real-world tasks that mirror professional challenges. This approach fosters collaboration, creativity, and deep understanding through active exploration and application of knowledge. Discover how project-based methods can transform your educational or corporate training experiences by reading the full article.
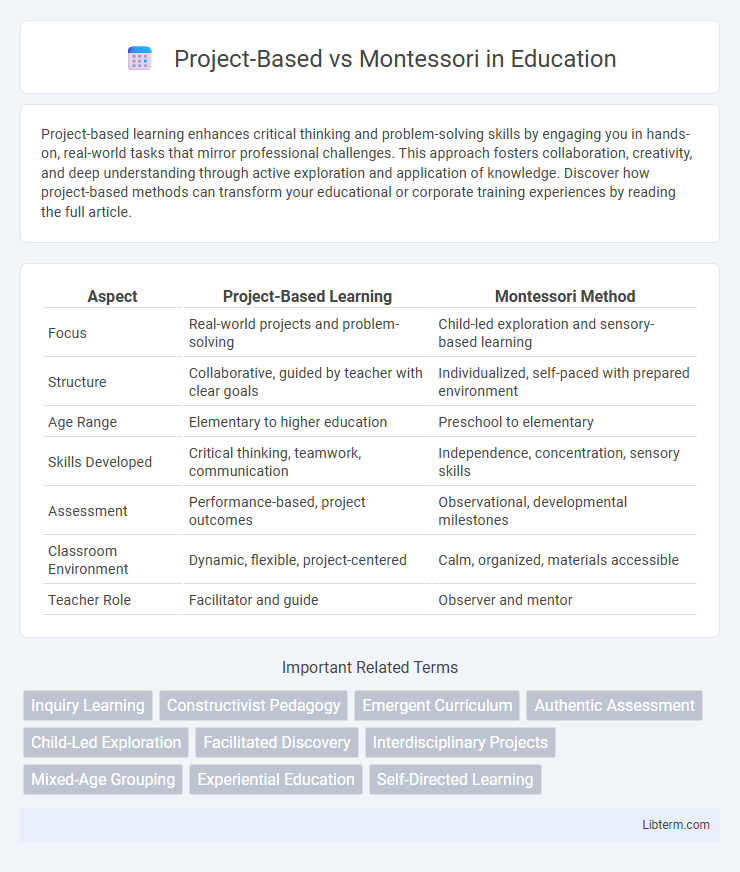
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning | Montessori Method |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Real-world projects and problem-solving | Child-led exploration and sensory-based learning |
| Structure | Collaborative, guided by teacher with clear goals | Individualized, self-paced with prepared environment |
| Age Range | Elementary to higher education | Preschool to elementary |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, teamwork, communication | Independence, concentration, sensory skills |
| Assessment | Performance-based, project outcomes | Observational, developmental milestones |
| Classroom Environment | Dynamic, flexible, project-centered | Calm, organized, materials accessible |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide | Observer and mentor |
Understanding Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes active exploration and real-world problem-solving, encouraging students to develop critical thinking, collaboration, and communication skills through hands-on projects. Unlike the Montessori method, which centers on self-directed activity and individualized learning materials, PBL integrates cross-disciplinary content to foster deeper understanding and practical application of knowledge. This approach prepares learners to navigate complex challenges by engaging in sustained inquiry and reflective assessment.
What Is Montessori Education?
Montessori education emphasizes self-directed learning through hands-on activities and collaborative play in a prepared environment tailored to children's developmental stages. It focuses on fostering independence, sensory exploration, and intrinsic motivation rather than adhering to a fixed curriculum or traditional assessments. The method encourages children to choose tasks that interest them, promoting personalized growth and a deep understanding of concepts over time.
Core Principles of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning centers on experiential education, emphasizing student-driven investigations and real-world problem solving to promote deeper understanding. Core principles include collaboration, inquiry-based tasks, and reflection, encouraging active engagement and critical thinking. Unlike Montessori's structured environment and self-paced learning with predefined materials, Project-Based Learning prioritizes dynamic, interdisciplinary projects that connect academic content to authentic challenges.
Fundamental Tenets of Montessori Method
The Montessori method emphasizes child-led learning, hands-on materials, and mixed-age classrooms to foster independence and intrinsic motivation. Core principles include respect for the child's natural development, freedom within limits, and a prepared environment tailored to individual learning paces. This contrasts with Project-Based learning, which centers on collaborative projects and real-world problem solving but typically follows a more structured curriculum.
Curriculum Structure: Project-Based vs Montessori
Project-Based learning features a curriculum structured around interdisciplinary projects that encourage critical thinking and real-world problem solving. Montessori curriculum emphasizes a child-led approach with individualized, hands-on learning activities designed to foster independence and self-paced progress. This contrast highlights Project-Based learning's collaborative, goal-oriented framework versus Montessori's flexible, developmentally responsive environment.
Classroom Environment and Organization
Project-Based learning environments emphasize collaborative workspaces with flexible seating arrangements that foster creativity and problem-solving among students. Montessori classrooms are meticulously organized with designated areas and hands-on materials, promoting independence and self-directed exploration. Both settings prioritize student engagement but differ in structure; Project-Based spaces adapt dynamically to project needs, while Montessori rooms maintain consistent order to support individualized learning paths.
Teacher’s Role: Facilitators or Guides
In project-based learning, teachers act as facilitators by designing real-world tasks and providing resources that encourage student exploration and collaboration. In Montessori education, teachers serve as guides who observe interests and tailor individualized learning experiences to foster independence and intrinsic motivation. Both roles emphasize creating supportive environments but differ in the degree of structure and student autonomy.
Student Autonomy and Engagement
Project-Based learning enhances student autonomy by encouraging self-directed exploration and problem-solving within real-world contexts, fostering deeper engagement through meaningful, hands-on activities. Montessori education promotes autonomy by allowing students to choose from various prepared materials at their own pace, supporting intrinsic motivation and individualized learning paths. Both approaches emphasize active participation, but Project-Based learning often centers on collaborative tasks, while Montessori nurtures independent discovery, optimizing student engagement through tailored experiences.
Assessment and Evaluation Approaches
Project-Based learning emphasizes continuous, performance-based assessment through authentic tasks that reflect real-world challenges, allowing students to demonstrate understanding and skills over time. Montessori education employs observational assessment, where teachers evaluate student progress through individualized, formative observations within a prepared environment, focusing on developmental stages and intrinsic motivation. Both approaches prioritize formative feedback but differ in structure: Project-Based centers on collaborative, outcome-driven evaluation, whereas Montessori relies on personalized, process-oriented assessment.
Choosing the Right Fit for Your Child
Choosing between Project-Based Learning (PBL) and Montessori education depends on your child's learning style and developmental needs. PBL emphasizes real-world problem solving and collaboration, ideal for children who thrive on hands-on, goal-oriented tasks. Montessori fosters independence and self-paced exploration, best suited for children who benefit from a structured yet flexible environment promoting intrinsic motivation.
Project-Based Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com