Credit transfer policies streamline the process of recognizing previously earned academic credits, enabling you to continue your education without redundancy. These policies vary by institution, often requiring official transcripts and course equivalency evaluations to ensure fair credit acceptance. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to maximize your transfers and save time on your degree journey.
Table of Comparison
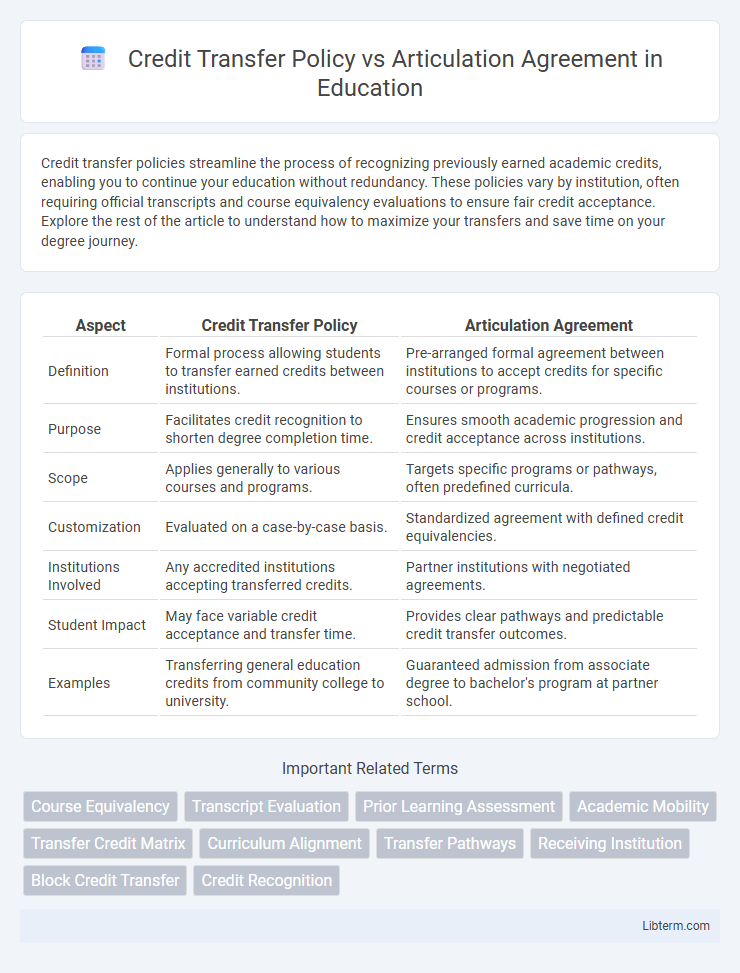
| Aspect | Credit Transfer Policy | Articulation Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal process allowing students to transfer earned credits between institutions. | Pre-arranged formal agreement between institutions to accept credits for specific courses or programs. |
| Purpose | Facilitates credit recognition to shorten degree completion time. | Ensures smooth academic progression and credit acceptance across institutions. |
| Scope | Applies generally to various courses and programs. | Targets specific programs or pathways, often predefined curricula. |
| Customization | Evaluated on a case-by-case basis. | Standardized agreement with defined credit equivalencies. |
| Institutions Involved | Any accredited institutions accepting transferred credits. | Partner institutions with negotiated agreements. |
| Student Impact | May face variable credit acceptance and transfer time. | Provides clear pathways and predictable credit transfer outcomes. |
| Examples | Transferring general education credits from community college to university. | Guaranteed admission from associate degree to bachelor's program at partner school. |
Introduction to Credit Transfer Policy and Articulation Agreement
Credit Transfer Policy defines the criteria and process for recognizing and accepting academic credits earned at one institution toward a program at another institution. Articulation Agreement is a formal partnership between educational institutions that specifies which courses or programs are transferable and guarantees credit acceptance under agreed terms. Both frameworks aim to facilitate student mobility and ensure seamless progression in higher education by standardizing credit recognition and reducing redundancy.
Defining Credit Transfer Policy
Credit Transfer Policy establishes the formal guidelines and criteria institutions use to evaluate and accept academic credits earned from other colleges or universities. This policy ensures consistency in credit recognition, specifying which courses qualify for transfer based on equivalency and accreditation standards. It plays a critical role in facilitating student mobility by providing clear procedures for credit evaluation, distinct from Articulation Agreements that are prearranged partnerships outlining guaranteed credit acceptance between specific institutions.
Understanding Articulation Agreement
Articulation agreements are formal partnerships between two or more educational institutions that outline the transfer of specific courses or credits to ensure seamless progression for students. These agreements provide a pre-approved pathway, clearly defining which completed courses at a community college or lower-division institution will be accepted by a four-year university toward a degree program. Understanding articulation agreements helps students maximize credit transfer efficiency and avoid loss of credits during academic transitions.
Key Differences Between Credit Transfer Policy and Articulation Agreement
Credit Transfer Policy governs the evaluation and acceptance of individual course credits from one institution to another, ensuring academic consistency and credit recognition. Articulation Agreement is a formal partnership between two institutions outlining specific courses or programs guaranteed to transfer, often simplifying the transfer process for students. The key difference lies in Credit Transfer Policy's broader institutional guidelines versus Articulation Agreement's detailed, pre-established course equivalencies and pathways.
Eligibility Criteria for Credit Transfer and Articulation
Eligibility criteria for credit transfer typically require students to have completed equivalent courses with a minimum grade specified by the receiving institution, along with official transcripts and course descriptions. Articulation agreements focus on predefined pathways between institutions, outlining specific courses and grades that guarantee transfer credit acceptance to ensure seamless progression toward a degree. Both policies emphasize academic performance and course relevance but differ in flexibility, with articulation agreements providing clearer, negotiated criteria for credit acceptance.
Benefits of Credit Transfer Policies
Credit Transfer Policies streamline the recognition of academic credits between institutions, reducing redundancy and accelerating degree completion. They enhance student mobility by providing clear guidelines for transferring coursework, ensuring credits are accurately evaluated and applied. These policies optimize educational pathways, saving time and financial resources while maintaining academic standards.
Advantages of Articulation Agreements
Articulation agreements provide a clear, formalized pathway that guarantees credit transfer between partnering institutions, reducing the risk of lost credits and accelerating degree completion. They offer students detailed course equivalency guides, ensuring smoother transitions and better academic planning. These agreements enhance collaboration between colleges, improving curriculum alignment and supporting consistent educational standards.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Credit Transfer Policy often faces challenges in standardizing course equivalencies across diverse institutions, leading to inconsistencies and potential credit loss for students. Articulation Agreements, while providing clearer pathways, are limited by their typically rigid scope, requiring frequent updates to remain relevant amid curriculum changes. Both approaches struggle with maintaining transparency and equitable recognition of varied academic credentials in an increasingly diverse educational landscape.
Best Practices for Students Navigating Both Options
Students navigating Credit Transfer Policy and Articulation Agreement options should meticulously compare course equivalencies and institutional requirements to maximize transferable credits. Engaging with academic advisors ensures alignment between completed coursework and program prerequisites, reducing credit loss and expediting degree completion. Maintaining organized records of syllabi and official transcripts supports smoother approval processes across institutions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Path for Academic Progression
Selecting between a Credit Transfer Policy and an Articulation Agreement hinges on the clarity and structure of academic progression they offer; Credit Transfer Policies provide flexibility for individual course recognition, while Articulation Agreements ensure a predefined pathway between institutions. Students prioritizing guaranteed acceptance of credits and streamlined transfer should consider institutions with formal Articulation Agreements. Understanding each option's impact on degree completion time and credit applicability is crucial for informed academic planning.
Credit Transfer Policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com