Didactics focuses on effective teaching methods that enhance student learning and engagement through clear communication and structured lesson planning. It incorporates various strategies to tailor education to diverse learning styles and improve knowledge retention. Explore the article to discover practical didactic techniques that can transform Your teaching approach.
Table of Comparison
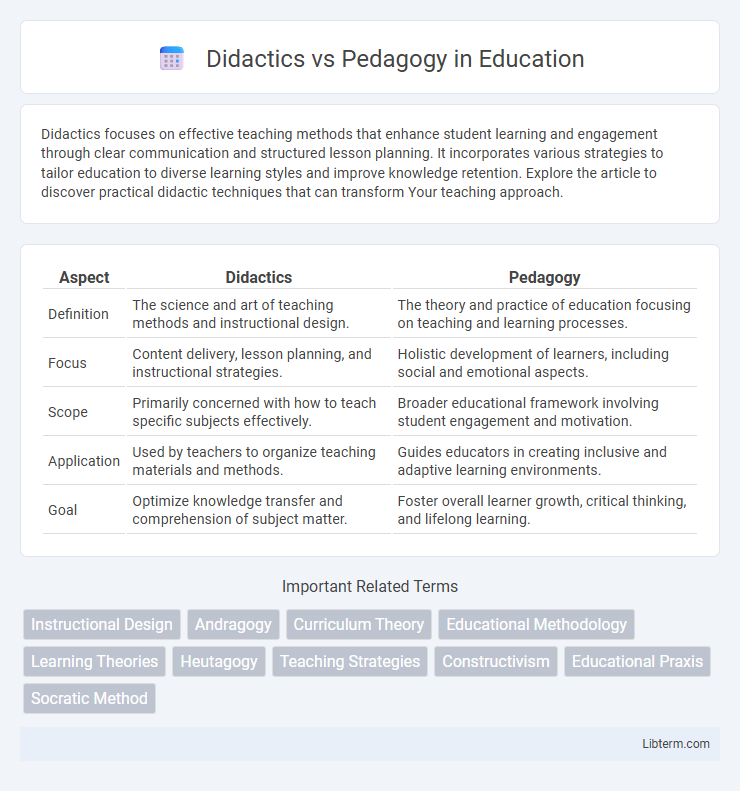
| Aspect | Didactics | Pedagogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The science and art of teaching methods and instructional design. | The theory and practice of education focusing on teaching and learning processes. |
| Focus | Content delivery, lesson planning, and instructional strategies. | Holistic development of learners, including social and emotional aspects. |
| Scope | Primarily concerned with how to teach specific subjects effectively. | Broader educational framework involving student engagement and motivation. |
| Application | Used by teachers to organize teaching materials and methods. | Guides educators in creating inclusive and adaptive learning environments. |
| Goal | Optimize knowledge transfer and comprehension of subject matter. | Foster overall learner growth, critical thinking, and lifelong learning. |
Understanding Didactics: Definition and Scope
Didactics refers to the art and science of teaching, emphasizing the methods, content, and instructional processes used to facilitate effective learning. It encompasses the planning, implementation, and evaluation of teaching strategies aimed at achieving specific educational objectives. The scope of didactics involves analyzing the relationship between teachers, learners, and the subject matter to optimize knowledge transmission and comprehension.
What is Pedagogy? A Comprehensive Overview
Pedagogy refers to the art and science of teaching, encompassing the methods and strategies used to facilitate learning. It involves understanding the psychological, social, and cultural aspects that impact student engagement and knowledge acquisition. Effective pedagogy integrates curriculum design, instructional techniques, and assessment practices tailored to diverse learner needs.
Historical Evolution of Didactics and Pedagogy
Didactics and pedagogy have distinct historical evolutions rooted in ancient educational practices, with didactics emphasizing the art and science of teaching methods, while pedagogy broadly encompasses the theory and practice of education. Didactics evolved significantly during the Enlightenment, focusing on structured instruction and curriculum development, whereas pedagogy has origins in classical philosophy, adapting over centuries to include social, psychological, and cultural dimensions of learning. Key figures like Comenius and Rousseau shaped didactics by promoting systematic teaching techniques, while pedagogy expanded through educational reformers such as Dewey, integrating learner-centered approaches and experiential learning theories.
Key Differences Between Didactics and Pedagogy
Didactics primarily focuses on the methods and content of teaching, emphasizing the structured delivery of knowledge and skill acquisition, while pedagogy encompasses the broader theory and practice of education, including the relationship between teacher, student, and learning environment. Didactics is concerned with the "how" of teaching specific subjects, involving lesson planning and instructional strategies, whereas pedagogy addresses the "why" behind educational approaches, integrating developmental, psychological, and social factors. Key differences lie in didactics' detail-oriented approach to curriculum design and instruction, contrasted with pedagogy's holistic consideration of learner needs and educational contexts.
Theoretical Foundations: Didactics vs Pedagogy
Didactics centers on the systematic study and methodical delivery of instructional content, emphasizing clear objectives, lesson structure, and effective teaching techniques. Pedagogy encompasses a broader theoretical foundation, integrating educational psychology, learner development, and social contexts to tailor teaching approaches for diverse student needs. Theoretical frameworks in didactics often draw from cognitive science and curriculum theory, while pedagogy incorporates sociocultural theories and ethical considerations in education.
Practical Applications in Modern Education
Didactics centers on the methodical planning and delivery of instructional content, emphasizing curriculum design, lesson objectives, and assessment techniques to enhance student comprehension. Pedagogy encompasses broader educational theories and student-teacher interactions that shape learning environments and foster critical thinking skills. In modern education, integrating didactic strategies with pedagogical principles enables educators to create adaptive lessons that address diverse learning needs and promote active engagement.
Teaching Strategies: Didactic vs Pedagogic Methods
Didactic methods emphasize structured, teacher-centered instruction with clear objectives and measurable outcomes, focusing on content delivery and direct knowledge transfer. Pedagogic methods prioritize student-centered approaches that encourage critical thinking, collaboration, and adaptability through interactive and experiential learning strategies. Effective teaching integrates didactic clarity with pedagogic flexibility to optimize student engagement and comprehension.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Approach
Didactics emphasizes structured content delivery and clear learning objectives, enhancing knowledge retention and curriculum alignment but may limit flexibility in addressing diverse learner needs. Pedagogy adopts a learner-centered approach that fosters critical thinking and social interaction, promoting deeper understanding though it can sometimes lack standardized assessment metrics. Balancing didactic clarity with pedagogical adaptability offers comprehensive educational benefits while mitigating their individual limitations.
Integrating Didactics and Pedagogy in the Classroom
Integrating didactics and pedagogy in the classroom enhances instructional effectiveness by combining systematic content delivery with student-centered teaching approaches. Didactics provides structured methods for lesson planning and knowledge transmission, while pedagogy emphasizes understanding learners' needs and fostering engagement. This fusion supports diverse learning styles, improves comprehension, and promotes critical thinking skills in educational settings.
Future Trends in Educational Methodologies
Future trends in educational methodologies emphasize the integration of didactics, which focuses on the systematic delivery of content, with pedagogy that centers on student-centered learning and developmental psychology. Advances in artificial intelligence and adaptive learning platforms will refine didactic approaches to customize instruction, while pedagogical frameworks will increasingly incorporate socio-emotional learning and collaborative skills. Emerging models prioritize experiential and interdisciplinary education, blending didactic precision with pedagogical flexibility to foster critical thinking and lifelong learning competencies.
Didactics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com