Cooperative learning enhances student engagement by promoting teamwork and shared responsibility in the classroom. This instructional strategy improves communication skills and fosters a deeper understanding of the material through peer interaction. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective cooperative learning techniques that can elevate your teaching practice.
Table of Comparison
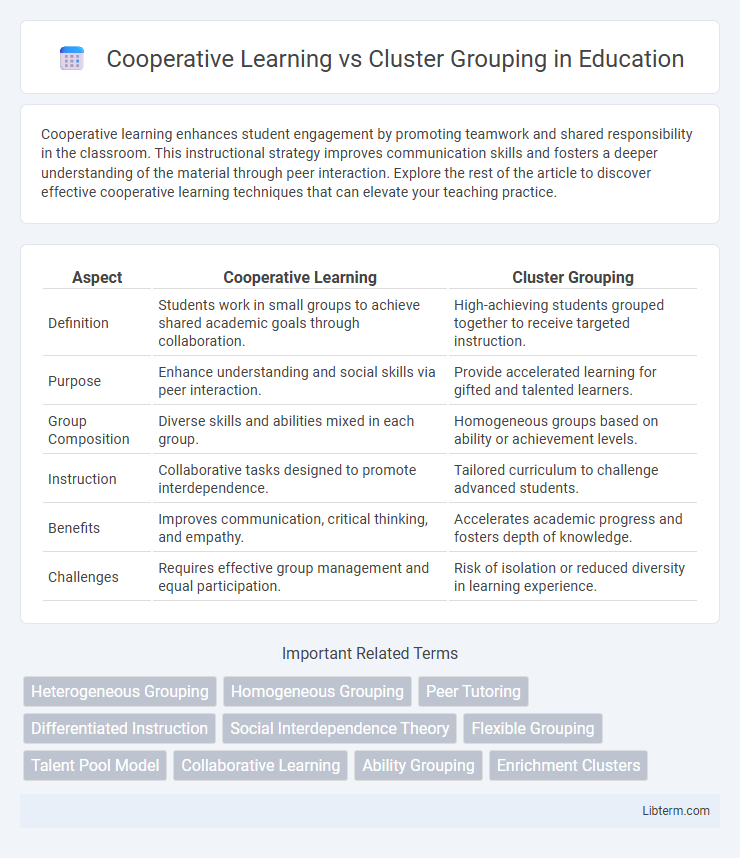
| Aspect | Cooperative Learning | Cluster Grouping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students work in small groups to achieve shared academic goals through collaboration. | High-achieving students grouped together to receive targeted instruction. |
| Purpose | Enhance understanding and social skills via peer interaction. | Provide accelerated learning for gifted and talented learners. |
| Group Composition | Diverse skills and abilities mixed in each group. | Homogeneous groups based on ability or achievement levels. |
| Instruction | Collaborative tasks designed to promote interdependence. | Tailored curriculum to challenge advanced students. |
| Benefits | Improves communication, critical thinking, and empathy. | Accelerates academic progress and fosters depth of knowledge. |
| Challenges | Requires effective group management and equal participation. | Risk of isolation or reduced diversity in learning experience. |
Introduction to Cooperative Learning and Cluster Grouping
Cooperative learning is an educational approach where students work together in small groups to achieve shared academic goals, fostering collaboration, communication, and critical thinking skills. Cluster grouping involves placing students with similar abilities or interests in the same group to tailor instruction more effectively and enhance peer learning. Both strategies aim to improve student engagement and academic outcomes but differ in group formation criteria and instructional focus.
Defining Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning is an instructional strategy where students work together in small, diverse groups to achieve shared academic goals through positive interdependence and individual accountability. This approach emphasizes collaboration, communication, and mutual support, fostering social skills alongside cognitive development. Unlike cluster grouping, which organizes students based on similar abilities, cooperative learning encourages heterogeneous grouping to enhance peer learning and critical thinking.
Understanding Cluster Grouping
Cluster grouping organizes students with similar abilities or interests into specific groups to enhance targeted instruction and maximize academic growth. This method facilitates personalized learning environments by allowing teachers to tailor lessons according to the cluster's shared characteristics and learning needs. Unlike cooperative learning, which emphasizes mixed-ability collaboration, cluster grouping prioritizes homogenized groups for focused skill development and accelerated progress.
Key Differences between Cooperative Learning and Cluster Grouping
Cooperative learning emphasizes small, heterogeneous groups working collaboratively on shared academic tasks to improve social skills and academic achievement. Cluster grouping involves placing high-achieving or gifted students together in a single classroom to tailor instruction to their advanced abilities. The key difference lies in cooperative learning's focus on collaborative interaction across diverse learners, while cluster grouping centers on ability-based grouping to enhance differentiated instruction.
Benefits of Cooperative Learning in the Classroom
Cooperative learning enhances student engagement by promoting active participation and peer-to-peer interaction, leading to improved critical thinking and communication skills. It fosters a supportive classroom environment where diverse learners collaborate, increasing motivation and academic achievement. This method also helps develop social skills and accountability, as students work together to achieve common learning goals.
Advantages of Cluster Grouping for Gifted Students
Cluster grouping enables differentiated instruction tailored to gifted students' advanced learning pace, fostering deeper critical thinking and creativity. This method promotes peer collaboration among intellectual peers, enhancing motivation and social-emotional development. By concentrating gifted learners in specific groups, educators can efficiently allocate specialized resources and challenge students at an appropriate cognitive level.
Challenges and Limitations of Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning often faces challenges such as unequal participation among group members, which can lead to social loafing and decreased accountability. The diversity of student abilities and personalities may cause conflicts or hinder collaboration, affecting overall group productivity. Limited teacher oversight during cooperative tasks can result in off-topic discussions and reduced learning outcomes.
Drawbacks of Cluster Grouping
Cluster grouping can lead to increased social isolation as gifted students are separated from their peers, creating a lack of diversity and reducing opportunities for varied perspectives. It often results in limited collaboration skills since students interact primarily within homogeneous groups, hindering the development of social and emotional competencies. Furthermore, cluster grouping may exacerbate achievement gaps by concentrating high achievers in select classrooms, which can demotivate other students and strain teacher resources.
Effective Strategies for Implementation
Cooperative learning involves structured group activities where students work collaboratively to achieve shared goals, while cluster grouping places students with similar abilities or interests in the same group to tailor instruction more effectively. Effective implementation of cooperative learning requires clear roles, interdependence, and accountability to ensure active participation, whereas cluster grouping benefits from differentiated instruction and targeted support based on group needs. Both strategies enhance student engagement and achievement when combined with ongoing assessment and adaptive teaching methods.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Classrooms
Cooperative learning fosters collaboration by grouping students of varied abilities to achieve shared goals, enhancing communication and peer support in diverse classrooms. Cluster grouping places students with similar strengths or needs together, allowing targeted instruction that addresses specific learning gaps or accelerates advanced learners. Selecting the right approach depends on classroom demographics, instructional goals, and the need for either inclusive interaction or specialized focus to optimize student outcomes.
Cooperative Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com