Private schools offer a tailored educational experience with smaller class sizes, specialized curricula, and enhanced extracurricular opportunities designed to foster student growth. These institutions often provide a safe and supportive environment that promotes academic excellence and personal development. Discover how enrolling in a private school can benefit Your child by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
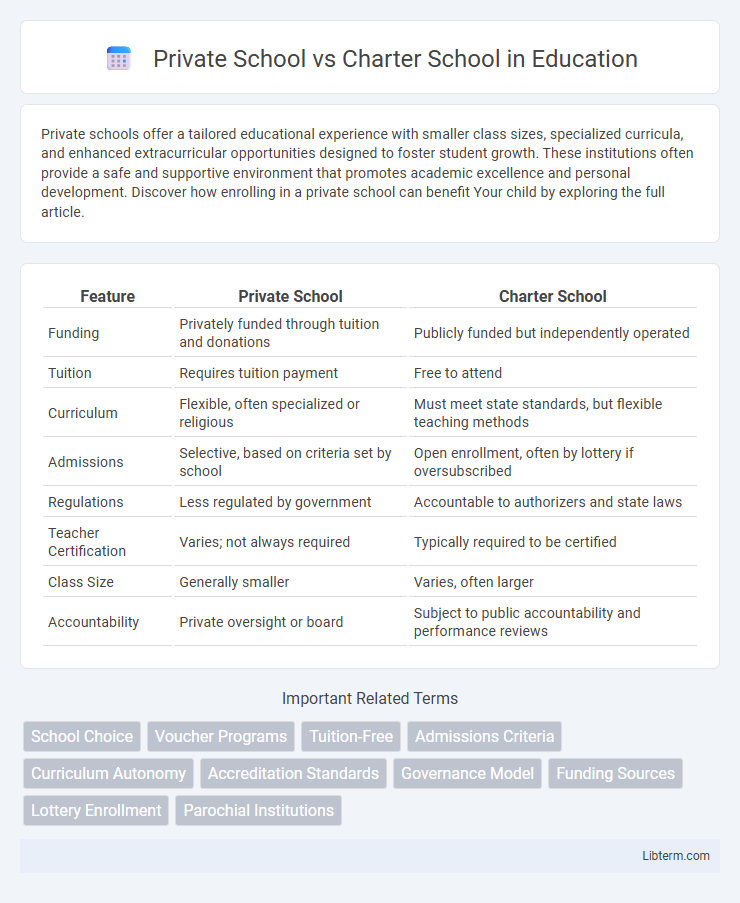
| Feature | Private School | Charter School |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Privately funded through tuition and donations | Publicly funded but independently operated |
| Tuition | Requires tuition payment | Free to attend |
| Curriculum | Flexible, often specialized or religious | Must meet state standards, but flexible teaching methods |
| Admissions | Selective, based on criteria set by school | Open enrollment, often by lottery if oversubscribed |
| Regulations | Less regulated by government | Accountable to authorizers and state laws |
| Teacher Certification | Varies; not always required | Typically required to be certified |
| Class Size | Generally smaller | Varies, often larger |
| Accountability | Private oversight or board | Subject to public accountability and performance reviews |
Introduction to Private and Charter Schools
Private schools operate independently from government funding, relying primarily on tuition fees and private donations, offering specialized curricula and smaller class sizes for tailored education. Charter schools are publicly funded but independently run, providing increased flexibility in teaching methods and curricula while still adhering to state standards. Both types of schools aim to deliver quality education but differ significantly in governance, funding sources, and operational regulations.
Definitions: Private vs Charter Schools
Private schools are independently funded through tuition payments and private donations, operating without direct government control, often allowing for selective admissions and specialized curricula. Charter schools receive public funding but operate independently of the traditional public school system, aiming to provide innovative educational programs while adhering to the terms of their charter agreements. Both types of schools offer alternatives to standard public education, with private schools emphasizing autonomy and charter schools focusing on public accountability and choice.
Admissions Process and Criteria
Private schools often require a rigorous admissions process including application forms, entrance exams, interviews, and submission of prior academic records to assess student fit and capabilities. Charter schools typically use a lottery system for admissions when applications exceed available spots, focusing on residency within the school's designated area and adherence to state-enforced enrollment guidelines. Unlike private institutions, charter schools generally have fewer subjective criteria, aiming to provide equal access rather than selective admissions.
Curriculum and Academic Flexibility
Private schools offer a curriculum often designed with proprietary frameworks emphasizing classical education or religious studies, providing a tailored academic experience. Charter schools implement state-mandated curriculum standards but retain flexibility to innovate with teaching methods, specialized programs, and pacing, fostering adaptive learning environments. The contrast in curriculum control highlights private schools' autonomy in academic content versus charter schools' balance of accountability and innovation.
Teacher Qualifications and Staffing
Private schools often require teachers to hold advanced degrees and specialized certifications, ensuring highly qualified staff with extensive training in their subject areas. Charter schools employ a mix of certified and non-certified teachers, allowing more flexibility in staffing but sometimes resulting in varying levels of teacher qualifications. Research shows that private school teachers generally have higher credentials and more years of experience compared to their charter school counterparts, impacting overall instructional quality.
Tuition Costs and Funding Sources
Private schools rely primarily on tuition fees, which can range from $5,000 to over $50,000 annually depending on the institution's prestige and location, while charter schools are publicly funded and typically free to attend. Funding for charter schools comes from state and local government allocations based on student enrollment, supplemented occasionally by federal grants and private donations. The reliance on tuition in private schools creates significant financial barriers for many families, whereas charter schools aim to provide accessible alternatives by operating without charging tuition.
Class Size and Student-Teacher Ratios
Private schools typically maintain smaller class sizes and lower student-teacher ratios, often averaging around 12 to 15 students per class, which allows for more individualized attention and tailored instruction. Charter schools vary widely but generally have class sizes ranging from 20 to 30 students, with student-teacher ratios often higher than private schools, impacting the level of personalized interaction. Research indicates that smaller class sizes and reduced student-teacher ratios correlate with improved academic performance and student engagement, making these factors critical when comparing private and charter school options.
Extracurricular Activities and Facilities
Private schools often offer extensive extracurricular activities with specialized clubs, advanced sports programs, and arts facilities due to higher funding from tuition and donations. Charter schools provide diverse activities tailored to community needs but may face limitations in facilities and resources compared to private schools. The difference in funding and management directly impacts the quality and variety of extracurricular programs and facilities available to students.
Accountability and Oversight Mechanisms
Private schools operate independently with oversight primarily from their governing boards and accreditation organizations, allowing flexibility but less public accountability compared to charter schools. Charter schools receive public funding and are held accountable through state and district performance standards, regular evaluations, and adherence to charter contracts, ensuring transparency and measurable educational outcomes. This structured oversight demands charter schools meet specific academic and financial benchmarks, contrasting with the broader autonomy found in private schools.
Parent and Community Involvement
Private schools often benefit from strong parent and community involvement through organized volunteer opportunities, fundraising events, and active parent-teacher associations, fostering a close-knit educational environment. Charter schools encourage parent and community participation by emphasizing collaborative governance and community partnerships to enhance educational programs and accountability. Both models engage families and local stakeholders to varying degrees, influencing school culture and student support systems.
Private School Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com