Explore the Social Sciences Pathway to gain in-depth understanding of human behavior, societies, and cultural dynamics. This pathway equips you with critical thinking and analytical skills essential for careers in psychology, sociology, anthropology, and political science. Dive into the article to discover how this pathway can shape your academic and professional future.
Table of Comparison
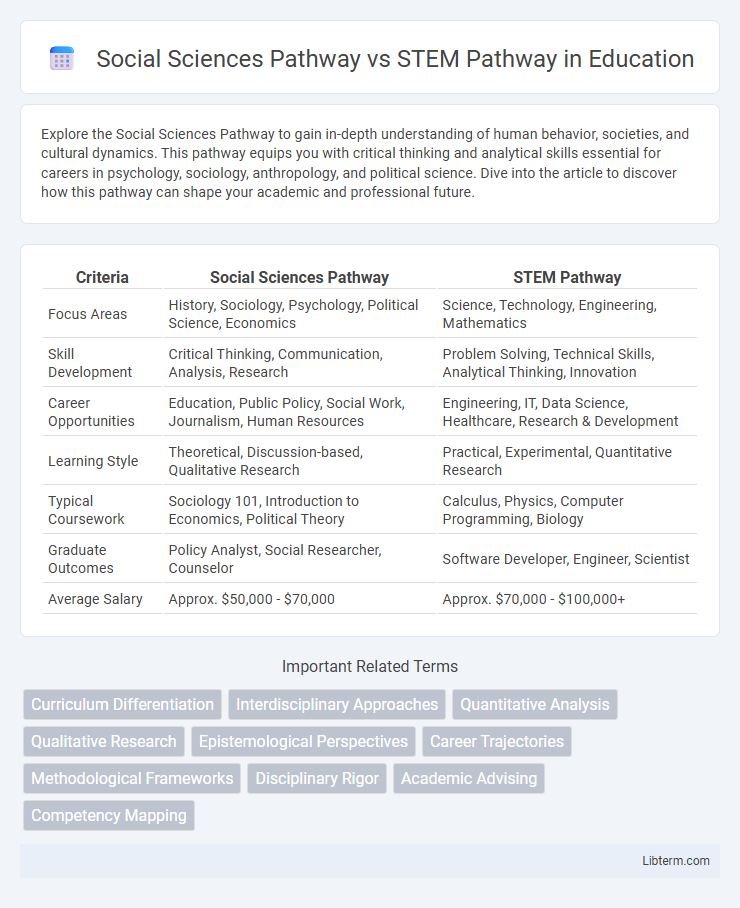
| Criteria | Social Sciences Pathway | STEM Pathway |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Areas | History, Sociology, Psychology, Political Science, Economics | Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics |
| Skill Development | Critical Thinking, Communication, Analysis, Research | Problem Solving, Technical Skills, Analytical Thinking, Innovation |
| Career Opportunities | Education, Public Policy, Social Work, Journalism, Human Resources | Engineering, IT, Data Science, Healthcare, Research & Development |
| Learning Style | Theoretical, Discussion-based, Qualitative Research | Practical, Experimental, Quantitative Research |
| Typical Coursework | Sociology 101, Introduction to Economics, Political Theory | Calculus, Physics, Computer Programming, Biology |
| Graduate Outcomes | Policy Analyst, Social Researcher, Counselor | Software Developer, Engineer, Scientist |
| Average Salary | Approx. $50,000 - $70,000 | Approx. $70,000 - $100,000+ |
Introduction to Academic Pathways: Social Sciences vs STEM
Social Sciences Pathway explores human behavior, society, and cultural dynamics through disciplines like psychology, sociology, and history, emphasizing critical thinking and qualitative analysis. STEM Pathway focuses on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, prioritizing quantitative skills, problem-solving, and empirical research. Both pathways develop unique academic strengths, with Social Sciences nurturing interpretive understanding and STEM fostering technical innovation.
Defining the Social Sciences Pathway
The Social Sciences Pathway focuses on understanding human behavior, societies, and cultural dynamics through disciplines such as psychology, sociology, economics, and political science. It emphasizes critical thinking, qualitative and quantitative research methods, and the analysis of social structures and institutions. This pathway prepares students for careers in public policy, social work, education, and community development, contrasting with the STEM Pathway's focus on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
Overview of the STEM Pathway
The STEM Pathway emphasizes education in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, fostering analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, and innovation. Students in this pathway engage in rigorous coursework including advanced mathematics, computer science, physics, and chemistry to prepare for technical careers and research opportunities. The pathway aligns with industries such as information technology, engineering, healthcare, and environmental science, meeting the growing demand for skilled professionals in rapidly evolving technological fields.
Key Differences in Curriculum and Learning Approaches
The Social Sciences Pathway emphasizes critical thinking, qualitative analysis, and understanding human behavior through subjects like sociology, psychology, and history, fostering interpretive and theoretical skills. The STEM Pathway centers on quantitative problem-solving, scientific methodologies, and technical skills in fields such as mathematics, engineering, and computer science, promoting analytical and experimental learning. Curriculum in social sciences encourages essay writing and debate, whereas STEM focuses on lab work, coding, and data-driven projects.
Career Opportunities in Social Sciences Pathway
The Social Sciences Pathway offers diverse career opportunities in fields such as psychology, sociology, political science, human resources, and social work, emphasizing critical thinking and interpersonal skills. Graduates can pursue roles in research, policy analysis, community development, and public administration, where understanding societal dynamics is crucial. These careers benefit from strong communication abilities and cultural competence, making them essential for addressing social issues and shaping public programs.
Career Prospects in STEM Pathway
The STEM pathway offers robust career prospects in high-demand fields such as engineering, computer science, biotechnology, and data analytics, driven by rapid technological advancements and innovation. Graduates in STEM disciplines often benefit from higher starting salaries, strong job security, and numerous opportunities for specialization and research in sectors like artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and renewable energy. Employers prioritize STEM skills for solving complex problems, leading to sustained growth in employment across industries including healthcare, manufacturing, and information technology.
Skills Developed: Social Sciences vs STEM
The Social Sciences pathway develops critical thinking, analytical skills, and qualitative research methods essential for understanding human behavior and societal trends. Meanwhile, the STEM pathway emphasizes technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and quantitative analysis vital for innovation in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics fields. Both pathways cultivate collaboration and communication skills but apply them within different contexts to prepare students for specialized careers.
Interdisciplinary Connections Between Pathways
The Social Sciences Pathway and STEM Pathway intersect through interdisciplinary connections such as data analysis, research methodologies, and technology integration, enabling a comprehensive understanding of human behavior and societal trends. Both pathways emphasize critical thinking and problem-solving skills, with social sciences applying scientific methods to economics, sociology, and political science, while STEM incorporates social context into engineering and environmental studies. This synergy fosters innovation by bridging qualitative insights with quantitative analysis, enhancing decision-making in policy development, technological advancement, and social impact studies.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Pathway
When choosing between the Social Sciences Pathway and the STEM Pathway, students should evaluate their personal strengths, career goals, and interests in either analytical problem-solving or human behavior and society. Consideration of job market demand, potential salary, and future industry growth is essential for informed decision-making. Access to resources, quality of educational programs, and mentorship opportunities also significantly impact the overall success and satisfaction within either pathway.
Future Trends and Emerging Fields in Social Sciences and STEM
Future trends in the Social Sciences Pathway emphasize data analytics, behavioral economics, and digital humanities, addressing societal challenges through interdisciplinary approaches. Emerging fields include artificial intelligence ethics, environmental sociology, and global health policy, reflecting a shift towards integrating technology with human-centric studies. The STEM Pathway is rapidly evolving with advancements in quantum computing, biotechnology, and renewable energy technologies, driving innovation in AI development, genetic engineering, and sustainable infrastructure.
Social Sciences Pathway Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com