A comprehensive literature review critically evaluates existing research studies, highlighting trends, gaps, and methodologies relevant to your topic. This process helps establish a solid foundation for understanding the academic landscape and supports the formulation of research questions. Dive into the rest of the article to explore effective strategies for conducting a thorough literature review.
Table of Comparison
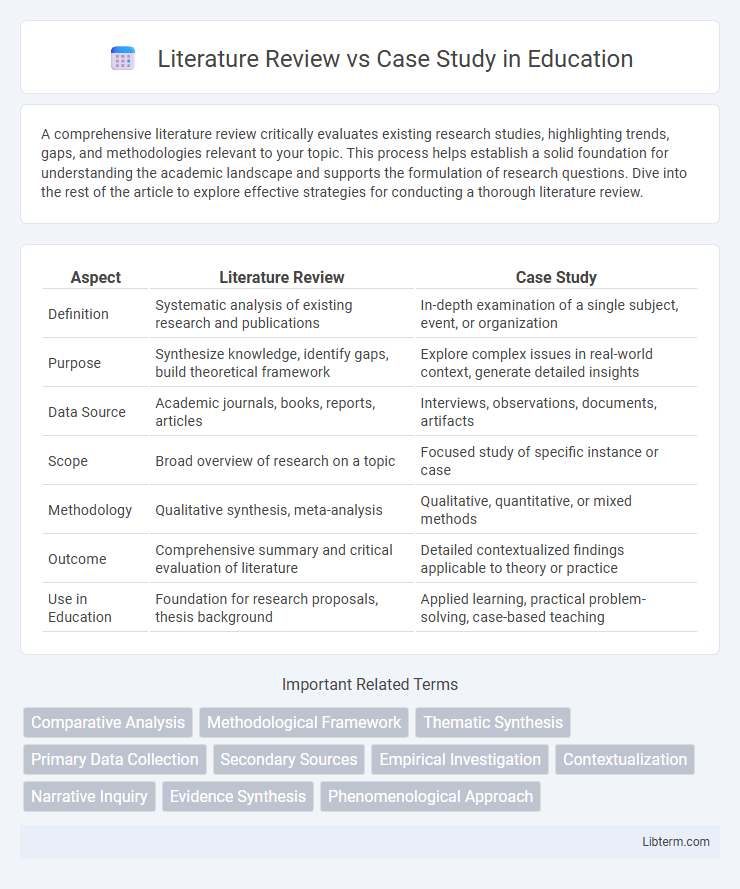
| Aspect | Literature Review | Case Study |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic analysis of existing research and publications | In-depth examination of a single subject, event, or organization |
| Purpose | Synthesize knowledge, identify gaps, build theoretical framework | Explore complex issues in real-world context, generate detailed insights |
| Data Source | Academic journals, books, reports, articles | Interviews, observations, documents, artifacts |
| Scope | Broad overview of research on a topic | Focused study of specific instance or case |
| Methodology | Qualitative synthesis, meta-analysis | Qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods |
| Outcome | Comprehensive summary and critical evaluation of literature | Detailed contextualized findings applicable to theory or practice |
| Use in Education | Foundation for research proposals, thesis background | Applied learning, practical problem-solving, case-based teaching |
Introduction to Literature Review and Case Study
A Literature Review systematically synthesizes existing research and theoretical frameworks related to a specific topic, providing a comprehensive background and identifying gaps in knowledge. A Case Study offers an in-depth, contextual analysis of a particular individual, group, event, or organization, emphasizing real-world application and detailed observation. Both methodologies serve distinct purposes: Literature Reviews establish the foundation for research by summarizing scholarly sources, while Case Studies generate rich, qualitative insights through empirical examination.
Defining Literature Review
A literature review systematically synthesizes existing research and theoretical frameworks relevant to a specific topic, highlighting gaps and establishing a foundation for new inquiries. It involves critical evaluation and integration of diverse sources such as peer-reviewed articles, books, and academic papers. Unlike a case study, which examines a single instance or phenomenon in depth, a literature review offers a comprehensive overview of scholarly knowledge to contextualize research questions.
Defining Case Study
A case study is an in-depth, contextual analysis of a single instance or event, often used to explore complex phenomena within real-life settings. Unlike a literature review, which synthesizes existing research and theories across multiple sources, a case study provides detailed qualitative or quantitative data specific to one subject, group, or situation. This method allows researchers to uncover patterns, causations, and insights that might be overlooked in broader overviews, making it essential for applied research and theory development.
Purpose and Objectives
A literature review aims to synthesize existing research to establish a theoretical framework and identify gaps in knowledge. A case study focuses on an in-depth analysis of a specific instance or phenomenon to explore causation and generate practical insights. The purpose of a literature review is to build context and rationale for research, while a case study seeks to provide detailed, contextual understanding of a real-world example.
Methodological Differences
Literature review involves systematically analyzing existing research to identify trends, gaps, and theoretical frameworks, while case study focuses on in-depth investigation of a single entity or event to generate detailed contextual insights. Literature reviews prioritize synthesis of secondary data across multiple sources, whereas case studies emphasize primary data collection through interviews, observations, and document analysis. Methodologically, literature reviews employ strategies like meta-analysis and thematic synthesis, contrasting with case studies' use of qualitative techniques such as narrative analysis and pattern matching.
Data Collection Techniques
Literature reviews primarily rely on secondary data collection techniques, such as analyzing existing academic papers, books, and credible digital sources, to synthesize current knowledge and identify research gaps. Case studies utilize primary data collection methods including interviews, direct observations, surveys, and document analysis to gather in-depth, contextual insights about specific subjects or phenomena. Both methodologies require systematic data organization, but case studies emphasize qualitative richness and real-world context, whereas literature reviews focus on comprehensive and critical evaluation of established research.
Analysis and Interpretation Approaches
Literature reviews synthesize existing research to identify patterns, gaps, and theoretical frameworks, employing critical analysis to evaluate sources and develop comprehensive interpretations. Case studies conduct in-depth investigations of specific instances or phenomena, using qualitative and quantitative methods to generate contextualized insights and nuanced understandings. Both approaches prioritize systematic analysis and interpretation, but literature reviews emphasize breadth across multiple studies, while case studies focus on depth within a single or limited number of cases.
Advantages and Limitations
A literature review offers comprehensive insight by synthesizing existing research, enabling identification of patterns and gaps, but it may lack context-specific detail and originality. Case studies provide in-depth, contextualized analysis of a single subject or event, facilitating a deep understanding of complex phenomena, though their findings often lack generalizability. Both methods complement each other; literature reviews benefit from broad scope, whereas case studies excel in detailed exploration but face limitations in representativeness.
When to Use Literature Review vs Case Study
Use a literature review when seeking to synthesize existing research, identify gaps, and establish a theoretical framework for a topic by analyzing multiple sources. Opt for a case study when aiming to explore an in-depth, contextual analysis of a single instance, event, or organization to gain detailed insights and practical understanding. Literature reviews suit broad academic inquiries, while case studies are ideal for focused, empirical investigations requiring real-world examples.
Conclusion and Recommendations
A literature review synthesizes existing research to identify trends, gaps, and theoretical frameworks, leading to evidence-based conclusions and broad recommendations for future inquiry. A case study provides an in-depth analysis of a specific instance, yielding detailed conclusions that highlight practical implications and context-specific recommendations. Both methodologies contribute uniquely: literature reviews guide generalized knowledge advancement, while case studies inform actionable strategies tailored to particular scenarios.
Literature Review Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com