Zoned enrollment ensures students attend schools within designated geographic boundaries, promoting balanced access to educational resources and fostering community connections. This system helps manage school capacities and encourages local engagement. Discover how zoned enrollment impacts your child's education and what it means for your family by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
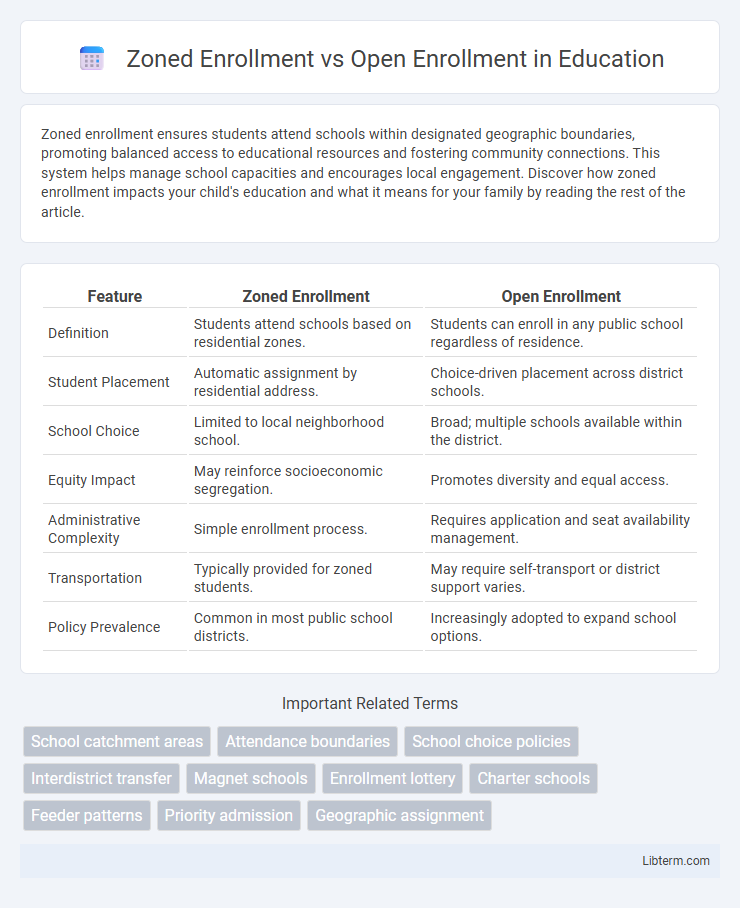
| Feature | Zoned Enrollment | Open Enrollment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students attend schools based on residential zones. | Students can enroll in any public school regardless of residence. |
| Student Placement | Automatic assignment by residential address. | Choice-driven placement across district schools. |
| School Choice | Limited to local neighborhood school. | Broad; multiple schools available within the district. |
| Equity Impact | May reinforce socioeconomic segregation. | Promotes diversity and equal access. |
| Administrative Complexity | Simple enrollment process. | Requires application and seat availability management. |
| Transportation | Typically provided for zoned students. | May require self-transport or district support varies. |
| Policy Prevalence | Common in most public school districts. | Increasingly adopted to expand school options. |
Introduction to School Enrollment Policies
Zoned enrollment assigns students to schools based on geographic boundaries, ensuring community-based education and balanced resource distribution. Open enrollment allows families to choose schools outside their designated zones, promoting school choice and increased competition among institutions. These contrasting policies significantly impact student demographics, school diversity, and access to educational opportunities.
What is Zoned Enrollment?
Zoned enrollment assigns students to public schools based on defined geographic boundaries, ensuring community-based school attendance and balanced resource allocation. This system promotes neighborhood schools by directing students to institutions closest to their residences, which can influence property values and local demographics. Zoned enrollment contrasts with open enrollment, which allows families to choose schools outside their assigned zones without geographic restrictions.
Understanding Open Enrollment
Open Enrollment allows students and families to select schools outside their designated zoned area, offering greater flexibility and choice in education. This system enables access to specialized programs, diverse school environments, and potentially better academic opportunities beyond local boundaries. Understanding Open Enrollment involves recognizing its impact on school demographics, transportation logistics, and resource allocation within public education systems.
Key Differences Between Zoned and Open Enrollment
Zoned enrollment restricts student placement based on geographical boundaries, ensuring students attend schools within their residential zones, which promotes community cohesion and balanced school capacity. Open enrollment allows families to choose schools outside their designated zones, providing greater flexibility but potentially leading to disparities in school demographics and resource allocation. Key differences include the impact on school diversity, student commute times, and the administrative complexity involved in managing enrollment requests.
Pros and Cons of Zoned Enrollment
Zoned enrollment assigns students to schools based on geographic boundaries, ensuring community cohesion and more predictable student populations. This system often reduces transportation costs and promotes neighborhood diversity but can limit parental choice and reinforce socioeconomic disparities due to residential segregation. Despite its drawbacks, zoned enrollment simplifies school capacity management and can foster stronger local engagement.
Pros and Cons of Open Enrollment
Open enrollment allows students the freedom to choose schools outside their assigned zones, expanding access to diverse programs and specialized curricula, which can enhance personalized education and accommodate unique learning needs. However, this flexibility may lead to overcrowding in popular schools, increased transportation challenges, and potential imbalances in student distribution across districts. Families benefit from a wider selection but must navigate competitive admissions and longer commutes, impacting convenience and community cohesion.
Impact on Student Diversity
Zoned enrollment restricts student placement based on geographic boundaries, often resulting in less diverse student populations due to neighborhood segregation patterns. Open enrollment policies allow families to choose schools outside their local zones, promoting increased racial and socioeconomic diversity by broadening access. Research shows open enrollment can reduce achievement gaps by fostering more heterogeneous learning environments and resource distribution.
Effects on Academic Performance
Zoned enrollment often leads to a more homogeneous student population, which can result in consistent instructional pacing but may limit exposure to diverse perspectives that enhance critical thinking skills. Open enrollment increases student diversity by allowing attendance across district boundaries, promoting varied peer interactions that can improve cognitive and social development. Research indicates that open enrollment districts may experience higher academic performance overall due to increased access to specialized programs and resources not available in zoned schools.
Parental Choice and Community Involvement
Zoned enrollment restricts students to schools within specific geographic boundaries, limiting parental choice but fostering stronger community involvement as families often engage with nearby schools. Open enrollment allows parents to select schools outside their residential zones, increasing parental choice and enabling access to diverse educational programs while potentially reducing localized community engagement. Balancing these enrollment policies impacts both educational equity and the level of parental and community participation in school activities.
Future Trends in School Enrollment Policies
Future trends in school enrollment policies indicate an increasing shift toward zoned enrollment to promote community cohesion and equitable resource distribution, while open enrollment remains popular for offering parental choice and access to specialized programs. Innovations in data analytics and geographic information systems (GIS) are enhancing district capacity to design smarter zoning boundaries that balance demographic shifts and capacity constraints. Hybrid models combining zoned and open enrollment options are emerging, leveraging digital platforms to streamline application processes and accommodate diverse family preferences in urban and suburban school districts.
Zoned Enrollment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com