Apprenticeship offers hands-on experience, blending practical skills with theoretical knowledge to prepare you for a successful career. This approach enhances employability by providing direct industry exposure and mentorship from experienced professionals. Explore the details in the rest of the article to understand how apprenticeship can transform your career path.
Table of Comparison
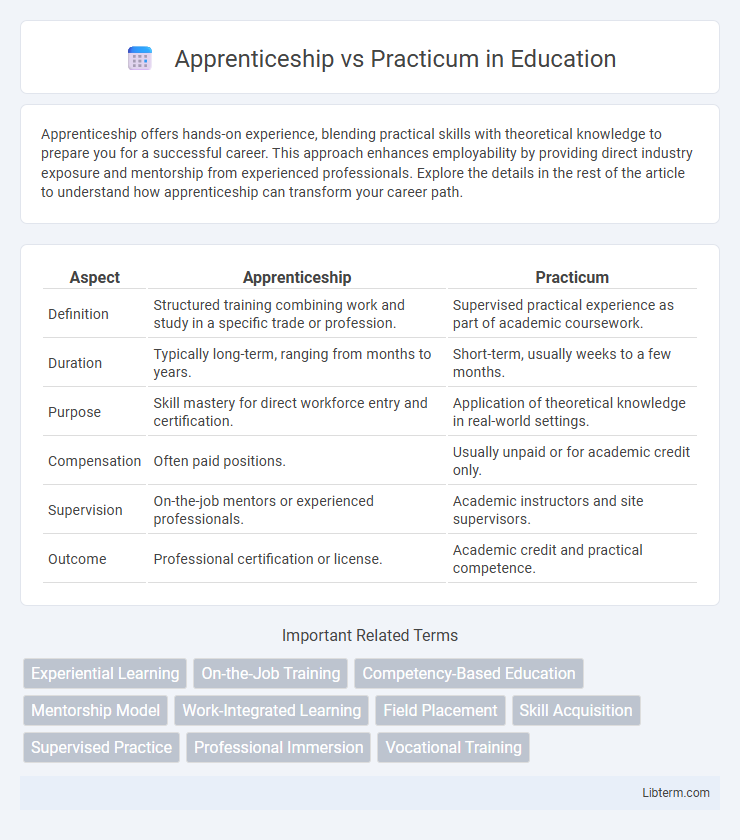
| Aspect | Apprenticeship | Practicum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured training combining work and study in a specific trade or profession. | Supervised practical experience as part of academic coursework. |
| Duration | Typically long-term, ranging from months to years. | Short-term, usually weeks to a few months. |
| Purpose | Skill mastery for direct workforce entry and certification. | Application of theoretical knowledge in real-world settings. |
| Compensation | Often paid positions. | Usually unpaid or for academic credit only. |
| Supervision | On-the-job mentors or experienced professionals. | Academic instructors and site supervisors. |
| Outcome | Professional certification or license. | Academic credit and practical competence. |
Introduction to Apprenticeships and Practicums
Apprenticeships provide hands-on training through long-term work experience combined with classroom instruction, primarily in skilled trades and technical fields. Practicums offer short-term, supervised practical experience in educational or healthcare settings, emphasizing application of academic theories. Both models bridge theoretical learning with real-world practice, enhancing professional skills and employability.
Defining Apprenticeship: Key Features
Apprenticeship is a structured training program combining on-the-job learning with classroom instruction, designed to develop specific industry skills. Key features include a formal agreement between the apprentice and employer, a paid work experience component, and mentoring by experienced professionals. This approach offers hands-on skill acquisition aligned with national occupational standards, ensuring both practical competence and certification.
What is a Practicum? Core Characteristics
A practicum is a supervised, hands-on training experience integrated into an academic program to provide practical application of theoretical knowledge. Core characteristics include structured learning objectives, mentorship from experienced professionals, and placement in real-world settings such as hospitals, schools, or corporate environments. Practicums emphasize skill development, reflection, and direct observation to bridge classroom learning with professional practice.
Learning Outcomes: Apprenticeship vs Practicum
Apprenticeships provide hands-on learning outcomes through extended workplace training, fostering technical skills and real-world problem-solving abilities within a specific trade or profession. Practicums emphasize academic learning outcomes combined with practical experience, enhancing theoretical knowledge application and critical thinking in a controlled setting. Both models improve professional competence but differ in duration, structure, and focus on skill mastery versus academic integration.
Duration and Structure Comparison
Apprenticeships typically span one to four years and combine extensive on-the-job training with classroom instruction, allowing apprentices to earn wages while gaining hands-on experience. Practicums are shorter, often lasting a few weeks to a few months, structured as supervised practical placements within academic programs designed to provide specific skill application. The longer duration and integrated work-study model of apprenticeships contrast with the time-limited, academically embedded nature of practicums.
Supervision and Mentorship Differences
Apprenticeships provide direct supervision by experienced professionals, ensuring hands-on training with immediate feedback in real-world work environments. Practicums offer structured mentorship typically within educational settings, emphasizing guided observation and reflection alongside limited direct supervision. The apprenticeship model centers on skill mastery through active participation, while practicums focus on learning under academic oversight with mentorship to support professional growth.
Industry Application: Where Each Model Fits
Apprenticeships excel in industries requiring long-term skill mastery through hands-on training, such as manufacturing, construction, and healthcare, providing sustained workplace experience under expert supervision. Practicums are better suited for professions like education, social work, and counseling, where short-term, structured fieldwork complements academic learning and emphasizes observation and reflective practice. Both models integrate industry application effectively, but apprenticeships focus on extensive practical proficiency while practicums prioritize experiential learning within a defined timeframe.
Skill Development and Assessment Methods
Apprenticeships offer hands-on skill development through extended, real-world work experiences under the guidance of industry professionals, ensuring practical mastery in a specific trade or profession. Skill assessment in apprenticeships typically involves performance evaluations, on-the-job observations, and competency-based exams designed to measure practical abilities and work readiness. Practicums emphasize applying theoretical knowledge in controlled environments such as classrooms or supervised fieldwork, with assessment methods focusing on reflective journals, instructor feedback, and project-based evaluations to gauge learning and skill acquisition.
Benefits and Challenges of Apprenticeships
Apprenticeships offer hands-on training with real-world experience, enhancing job readiness and earning potential while fostering industry-specific skills under expert mentorship. Challenges include the time commitment required, potential for limited theoretical learning, and dependence on quality training environments that can vary by employer. The structured nature of apprenticeships supports long-term career growth but may limit flexibility in exploring different career paths early on.
Advantages and Limitations of Practicums
Practicums offer hands-on experience in a controlled learning environment, providing students with direct exposure to real-world scenarios and professional settings essential for skill development. They allow learners to apply theoretical knowledge while receiving supervision and feedback, enhancing practical competencies without the long-term commitment of apprenticeships. Limitations of practicums include typically shorter durations and less immersive involvement, which may restrict the depth of skill acquisition compared to extended apprenticeship programs.
Apprenticeship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com