Transdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge and methods from multiple disciplines to create holistic solutions to complex problems, fostering innovation and comprehensive understanding. This collaborative process transcends traditional boundaries, encouraging synergy between academic fields, industries, and communities. Explore the article to discover how transdisciplinary strategies can transform your projects and drive impactful results.
Table of Comparison
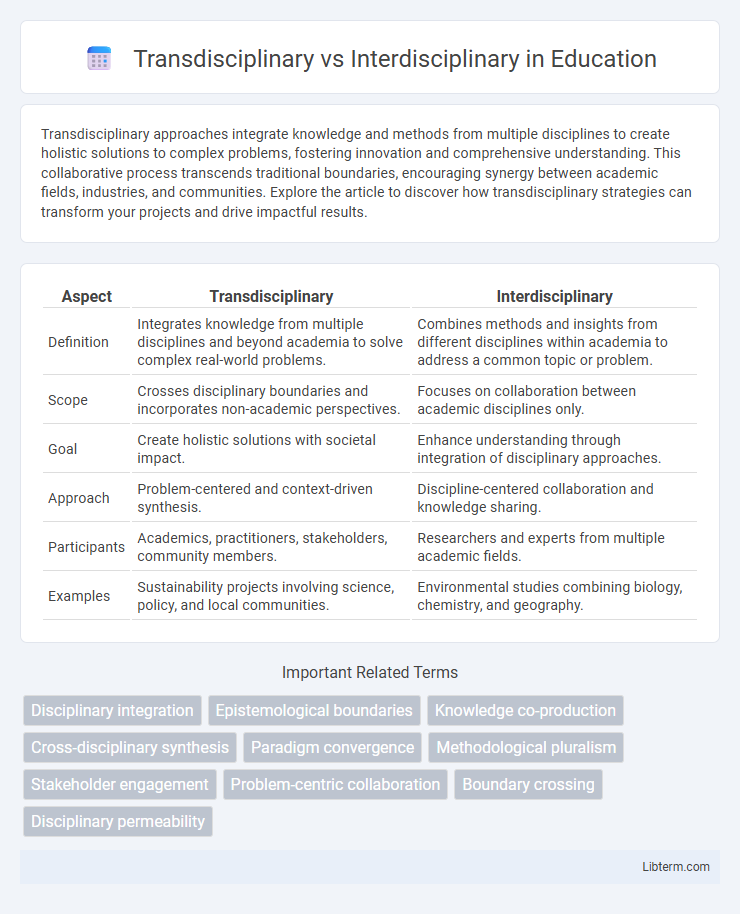
| Aspect | Transdisciplinary | Interdisciplinary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates knowledge from multiple disciplines and beyond academia to solve complex real-world problems. | Combines methods and insights from different disciplines within academia to address a common topic or problem. |
| Scope | Crosses disciplinary boundaries and incorporates non-academic perspectives. | Focuses on collaboration between academic disciplines only. |
| Goal | Create holistic solutions with societal impact. | Enhance understanding through integration of disciplinary approaches. |
| Approach | Problem-centered and context-driven synthesis. | Discipline-centered collaboration and knowledge sharing. |
| Participants | Academics, practitioners, stakeholders, community members. | Researchers and experts from multiple academic fields. |
| Examples | Sustainability projects involving science, policy, and local communities. | Environmental studies combining biology, chemistry, and geography. |
Introduction: Defining Transdisciplinary and Interdisciplinary
Transdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines to create a holistic framework that transcends traditional academic boundaries, emphasizing collaboration among diverse fields and stakeholders. Interdisciplinary methods involve combining concepts and techniques from different disciplines to address complex problems while maintaining distinct disciplinary perspectives. Both approaches aim to foster innovative solutions, but transdisciplinary emphasizes synthesis beyond disciplines, whereas interdisciplinary prioritizes interaction across disciplines.
Historical Background of Knowledge Integration
Transdisciplinary research emerged in the 1970s as a response to complex societal challenges, emphasizing the integration of academic and non-academic knowledge to create holistic solutions. Interdisciplinary approaches date back to the early 20th century, rooted in the convergence of distinct academic disciplines to address specific scientific or technical problems. Both frameworks trace their origins to the evolving recognition that traditional disciplinary boundaries limit comprehensive understanding and effective problem-solving in an increasingly interconnected world.
Core Principles of Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge and methods from multiple disciplines, emphasizing collaboration to address complex problems through a synthesis of perspectives. Core principles include the convergence of diverse disciplinary insights, co-creation of knowledge, and the development of shared frameworks that transcend traditional boundaries. These approaches facilitate innovative solutions by fostering continuous communication, mutual respect, and adaptive learning among experts from varied fields.
Fundamentals of Transdisciplinary Methodologies
Transdisciplinary methodologies integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines and non-academic sources to address complex real-world problems holistically, surpassing the boundaries of interdisciplinary approaches which primarily combine academic disciplines. Core fundamentals include collaborative problem formulation, co-creation of knowledge, and integrating diverse epistemologies to produce innovative solutions reflecting societal contexts. This approach emphasizes reflexivity, stakeholder engagement, and systemic thinking to ensure relevance and applicability of research outcomes beyond traditional academic frameworks.
Key Differences between Transdisciplinary and Interdisciplinary
Transdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines to create new frameworks beyond traditional boundaries, fostering holistic problem-solving. Interdisciplinary methods combine insights from different fields while maintaining their distinct perspectives to address complex questions. The key difference lies in transdisciplinary efforts transcending disciplinary limits to develop unified methodologies, whereas interdisciplinary work collaborates across disciplines without fully merging them.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Transdisciplinary research integrates knowledge from multiple disciplines to create holistic solutions, promoting innovation and comprehensive understanding by transcending traditional boundaries; however, it faces challenges in methodological integration and requires strong collaboration and communication skills. Interdisciplinary research combines methodologies and perspectives from different fields to address complex problems, enhancing problem-solving capabilities and fostering creativity, yet it may suffer from coordination difficulties and conflicts in disciplinary norms. Both approaches improve knowledge synthesis and innovation but require careful management of epistemological differences and resource allocation to overcome their inherent limitations.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Transdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines to create holistic solutions, exemplified by urban sustainability projects combining ecology, sociology, and engineering. Interdisciplinary methods foster collaboration across fields, as seen in healthcare innovations where biology, computer science, and clinical practice intersect to enhance patient outcomes. Real-world applications demonstrate that transdisciplinary strategies often address complex societal challenges by transcending traditional academic boundaries, while interdisciplinary efforts optimize expertise for specific problems within existing frameworks.
Impacts on Research, Education, and Innovation
Transdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge from diverse disciplines and non-academic stakeholders to solve complex real-world problems, driving transformative impacts on research by fostering holistic understanding and collaborative innovation. Interdisciplinary methods combine methods and theories from multiple academic fields, enhancing educational programs through enriched curricula and facilitating innovation by encouraging cross-disciplinary problem-solving. Both approaches promote creativity and knowledge integration but transdisciplinary research especially accelerates societal impact by bridging academic and practical domains.
Challenges in Implementing Collaborative Approaches
Challenges in implementing transdisciplinary and interdisciplinary approaches include differing methodologies and terminologies across disciplines that hinder effective communication and collaboration. Power dynamics and institutional barriers can limit equal participation and resource allocation among diverse stakeholders. Measuring outcomes is complex due to varying goals and evaluation criteria, complicating project management and impact assessment.
Future Trends in Interdisciplinary and Transdisciplinary Work
Future trends in interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary work emphasize the integration of diverse knowledge systems to address complex, global challenges such as climate change, healthcare innovations, and sustainable development. Emerging technologies like AI and big data analytics facilitate deeper collaboration across disciplines, enabling dynamic problem-solving that transcends traditional academic boundaries. Increasing institutional support and funding for cross-sector research initiatives highlight a shift toward holistic approaches prioritizing real-world impact and stakeholder engagement.
Transdisciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com