A rating scale is a crucial tool for measuring subjective opinions, preferences, and experiences across various fields, including customer feedback, education, and market research. It allows for quantifiable data collection by assigning numerical or descriptive values to responses, facilitating comparison and analysis. Discover how different types of rating scales can enhance your decision-making and improve data interpretation by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
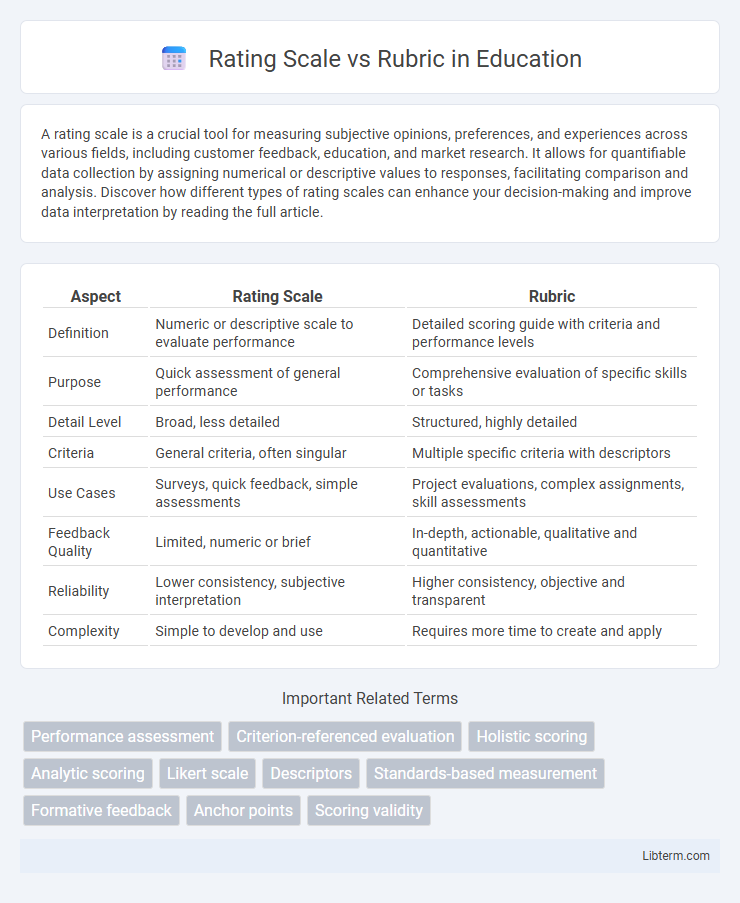
| Aspect | Rating Scale | Rubric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Numeric or descriptive scale to evaluate performance | Detailed scoring guide with criteria and performance levels |
| Purpose | Quick assessment of general performance | Comprehensive evaluation of specific skills or tasks |
| Detail Level | Broad, less detailed | Structured, highly detailed |
| Criteria | General criteria, often singular | Multiple specific criteria with descriptors |
| Use Cases | Surveys, quick feedback, simple assessments | Project evaluations, complex assignments, skill assessments |
| Feedback Quality | Limited, numeric or brief | In-depth, actionable, qualitative and quantitative |
| Reliability | Lower consistency, subjective interpretation | Higher consistency, objective and transparent |
| Complexity | Simple to develop and use | Requires more time to create and apply |
Introduction to Assessment Tools
Rating scales use numeric or descriptive values to measure the extent of a specific attribute or performance, allowing for quick quantification and comparison. Rubrics provide detailed criteria and performance standards across multiple dimensions, offering clear guidance for evaluation and feedback. Both tools are fundamental in assessment, enhancing objectivity and consistency in measuring student learning outcomes.
What is a Rating Scale?
A rating scale is a quantitative tool used to measure the degree or intensity of a specific attribute, behavior, or performance by assigning values along a continuum, such as 1 to 5 or 1 to 10. It provides consistent, straightforward data collection for evaluating subjective criteria like satisfaction, quality, or frequency. Commonly used in surveys, assessments, and feedback forms, rating scales enable easy comparison and statistical analysis of responses.
What is a Rubric?
A rubric is a detailed scoring guide used to assess student work based on specific criteria and performance levels. It breaks down assignments into components with clear descriptions for each level of achievement, ensuring consistent and objective evaluation. Rubrics enhance transparency by communicating expectations and providing targeted feedback.
Key Differences Between Rating Scales and Rubrics
Rating scales assign numerical or descriptive values to assess specific performance levels, while rubrics provide detailed criteria and qualitative descriptions for each score point. Rating scales offer quick, quantifiable evaluations, whereas rubrics facilitate in-depth feedback by clarifying expectations and distinguishing performance quality. The key difference lies in rubrics' ability to guide consistent scoring through explicit standards, contrasting with rating scales' focus on simplistic grading metrics.
Advantages of Using Rating Scales
Rating scales offer clear advantages in assessment by providing quantifiable data that simplifies analysis and comparison across multiple responses or performances. Their straightforward structure allows for consistent evaluation, making them highly efficient for large-scale assessments or surveys. Rating scales enhance objectivity and reduce evaluator bias by standardizing criteria, resulting in more reliable and actionable feedback.
Benefits of Implementing Rubrics
Rubrics provide clear, detailed criteria that enhance consistency and objectivity in grading, enabling both instructors and students to understand performance expectations better. They support targeted feedback, facilitating specific guidance that helps students improve skills and knowledge in measurable ways. The structured framework of rubrics also streamlines the assessment process, saving time while promoting fairness and transparency in evaluation.
When to Use a Rating Scale
Rating scales are ideal when assessing specific attitudes, perceptions, or behaviors that require quantifiable data for easy comparison and statistical analysis. Use rating scales in surveys, customer feedback, and performance evaluations where numerical consistency and quick assessment are essential. They offer simplicity and efficiency for measuring frequency, intensity, or satisfaction levels in a structured format.
When to Choose a Rubric
Choose a rubric when evaluating complex or multi-dimensional tasks that require detailed assessment criteria and qualitative feedback, such as essays, presentations, or projects. Rubrics provide clear performance standards for different levels of achievement, enhancing consistency and transparency in grading. They are especially valuable in educational settings where subjective judgments must be minimized to ensure fair and comprehensive evaluation.
Best Practices for Effective Assessment
Rating scales provide a quantitative measure by assigning numerical values to performance levels, facilitating quick comparison and statistical analysis. Rubrics offer detailed qualitative criteria that describe performance expectations across multiple dimensions, promoting consistent and transparent assessment. Combining clear, specific descriptors with aligned learning objectives ensures accurate evaluation and actionable feedback for students.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Assessment Tool
Choosing between a rating scale and a rubric depends on the assessment goals and the desired precision in evaluation. Rating scales offer quick, quantifiable judgments suitable for large datasets, while rubrics provide detailed, criterion-based feedback essential for nuanced understanding. Organizations benefit from aligning the assessment tool with their specific needs to maximize accuracy and actionable insights.
Rating Scale Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com