Customization allows you to tailor products and services to meet your specific needs and preferences, enhancing satisfaction and usability. This personalized approach can improve efficiency and create a unique experience that stands out from generic options. Discover how customization can transform your choices by exploring the rest of the article.
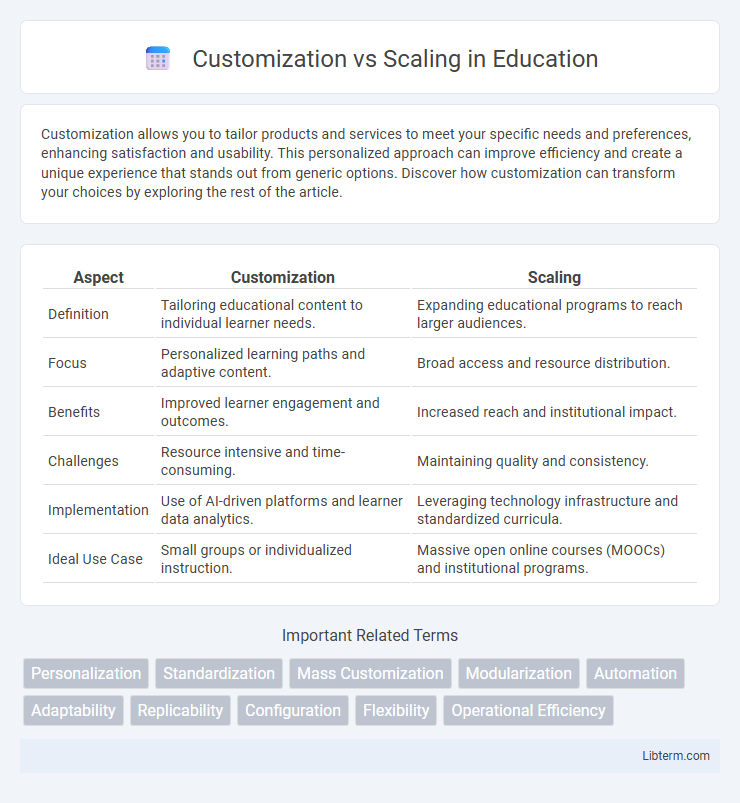
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Customization | Scaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tailoring educational content to individual learner needs. | Expanding educational programs to reach larger audiences. |
| Focus | Personalized learning paths and adaptive content. | Broad access and resource distribution. |
| Benefits | Improved learner engagement and outcomes. | Increased reach and institutional impact. |
| Challenges | Resource intensive and time-consuming. | Maintaining quality and consistency. |
| Implementation | Use of AI-driven platforms and learner data analytics. | Leveraging technology infrastructure and standardized curricula. |
| Ideal Use Case | Small groups or individualized instruction. | Massive open online courses (MOOCs) and institutional programs. |
Understanding Customization
Customization involves tailoring products or services to meet specific client needs, enhancing user experience and satisfaction through unique features. It requires deep insights into customer preferences and flexible design processes to accommodate diverse demands efficiently. Understanding customization is crucial for businesses aiming to build strong brand loyalty and differentiate themselves in competitive markets.
Defining Scaling in Business
Scaling in business refers to the ability of a company to grow its revenue and operations efficiently without a proportional increase in costs. It involves optimizing processes, leveraging technology, and expanding market reach to handle increased demand while maintaining or improving profit margins. Effective scaling enables businesses to maximize resources, enhance customer experience, and achieve sustainable long-term growth.
Key Differences Between Customization and Scaling
Customization involves tailoring products or services to meet specific individual or client needs, enhancing user experience and satisfaction through unique features. Scaling refers to expanding operations, capacity, or output efficiently to accommodate increased demand without sacrificing performance or quality. Key differences include customization prioritizing uniqueness and adaptability, while scaling emphasizes growth, consistency, and resource optimization.
Benefits of Customization
Customization enhances user experience by tailoring products or services to specific needs, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. It enables businesses to differentiate themselves in competitive markets, offering unique solutions that align precisely with client requirements. This targeted approach often leads to higher efficiency and better resource allocation, driving improved overall performance.
Advantages of Scaling
Scaling offers significant advantages such as enhanced operational efficiency and the ability to handle increased workloads without compromising performance. It enables businesses to quickly adapt to market demands, ensuring consistent service quality while reducing incremental costs. By leveraging scalable infrastructure, organizations can optimize resource allocation and drive sustainable growth.
Challenges of Customization
Customization challenges include increased complexity in managing diverse configurations, leading to higher development and maintenance costs. It often results in slower time-to-market due to the need for tailored solutions and frequent adjustments. Ensuring consistent performance and compatibility across customized versions further complicates scaling efforts.
Obstacles in Scaling
Obstacles in scaling often stem from the complexity introduced by extensive customization, which can hinder standardization and increase costs. Customized solutions typically require specialized resources and maintenance, limiting the ability to streamline operations across larger scales. Furthermore, scaling barriers include integration challenges, inconsistent user experiences, and reduced agility in adapting to market demands.
Aligning Business Goals with Customization or Scaling
Customization ensures products and services meet specific client needs, driving customer satisfaction and loyalty, but may limit rapid scaling due to higher resource demands. Scaling focuses on expanding operations efficiently to reach broader markets and increase revenue, potentially sacrificing personalization in favor of standardized solutions. Aligning business goals requires balancing tailored customer experiences with scalable processes to optimize growth while preserving competitive differentiation.
Case Studies: Customization vs Scaling
Case studies on customization versus scaling reveal that businesses prioritizing customization often achieve higher customer satisfaction by tailoring products to niche markets, exemplified by luxury brands like Tesla's personalized vehicle options. In contrast, companies focusing on scaling, such as Amazon, leverage standardized processes and automation to rapidly expand market reach and increase operational efficiency. Data from these case studies indicate a trade-off between personalized customer experiences and the efficiency gains from scaling, highlighting strategic decisions based on target audience and growth objectives.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business
Customization offers tailored solutions that address specific business needs, enhancing user experience and operational efficiency. Scaling focuses on expanding capacity and performance to accommodate growth, ensuring systems remain robust and responsive under increased demand. Businesses should evaluate their current priorities, resources, and long-term goals to determine whether personalized function adjustments or scalable infrastructure investments will deliver the best return on investment.
Customization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com